两个链表的第一个公共结点
题目描述
输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。
节点类:
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
分析
首先要理解什么是公共节点,并不是两个节点的值相同就是公共节点。
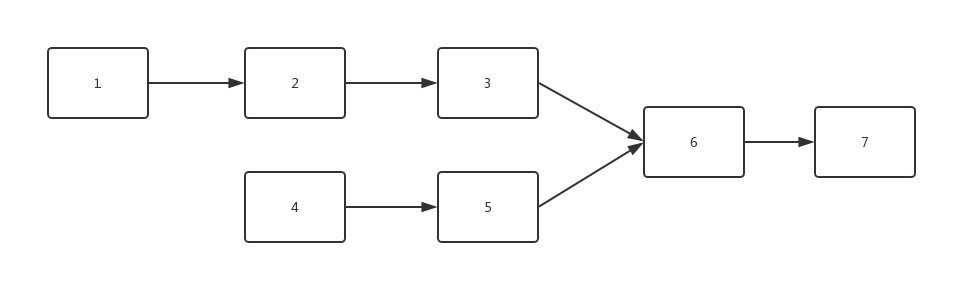
而是在第一链表和第二链表中都存在一个节点,该节点往后的子链表在两个链表中是相同的。
如下图中链表6 - 7就是两个链表的公共链表,而节点6就是第一个公共节点。
方法一
最直观就是暴力法,在第一链表上顺序遍历每个节点,每遍历到一个节点,就在第二个链表上顺序遍历每个节点。如果在第二个链表上有一个节点和第一个链表上的节点一样,则说明两个链表在这个节点上重合,但是这种方法的复杂度为O()(第一个链表长度为m,第二个链表的长度为n)
方法二
如果两个链表存在公共节点,那么公共节点出现在两个链表的尾部。如果我们从两个链表的尾部开始往前比较,那么最后一个相同的节点就是我们要找的节点。但是这两个链表是单向的,要实现尾节点最先比较,我们可以借助两个辅助栈。分别将两个链表的节点放入两个栈中,这样栈顶就是两个链表的尾节点,比较两个栈顶节点是否相同,如果相同,将栈顶弹出比较下一个栈顶,直到找到最后一个相同的栈顶。时间复杂度O(m + n)。
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
if(pHead1 == null || pHead2 == null) {
return null;
}
Stack<ListNode> pStack1 = new Stack<ListNode>();
Stack<ListNode> pStack2 = new Stack<ListNode>();
while(pHead1 != null) {
pStack1.add(pHead1);
pHead1 = pHead1.next;
}
while(pHead2 != null) {
pStack2.add(pHead2);
pHead2 = pHead2.next;
}
ListNode temp = null;
while(!pStack1.isEmpty() && !pStack2.isEmpty()) {
ListNode pH1 = pStack1.pop();
ListNode pH2 = pStack2.pop();
if(pH1.val == pH2.val) {
temp = pH1;
}
else {
break;
}
}
return temp;
}
方法三
先获得两个链表的长度,然后在较长的链表上先走若干步(两链表长度之差),接着同时在两个链表上遍历,找到的第一个相同的节点就是他们的第一个公共节点。时间复杂度O(m + n)。
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode_2(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
if(pHead1 == null || pHead2 == null) {
return null;
}
int pHead1Length = getListLength(pHead1);
int pHead2Length = getListLength(pHead2);
int gap = pHead1Length - pHead2Length;
ListNode tempList1 = pHead1;
ListNode tempList2 = pHead2;
if(pHead2Length > pHead1Length) {
tempList1 = pHead2;
tempList2 = pHead1;
gap = pHead2Length - pHead1Length;
}
for (int i = 0; i < gap; i++) {
tempList1 = tempList1.next;
}
while((tempList1 != null) && (tempList2 != null) && (tempList1.val != tempList2.val)) {
tempList1 = tempList1.next;
tempList2 = tempList2.next;
}
return tempList1;
}
public int getListLength(ListNode list) {
int number = 0;
while(list != null) {
++number;
list = list.next;
}
return number;
}
方法四
很玄学的代码。。。
用两个指针扫描”两个链表“,最终两个指针到达 null 或者到达公共结点。
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode_3(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
if(pHead1 == null || pHead2 == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode temp1 = pHead1;
ListNode temp2 = pHead2;
while(temp1 != temp2) {
temp1 = (temp1 == null ? pHead2 : temp1.next);
temp2 = (temp2 == null ? pHead1 : temp2.next);
System.out.println(pHead1.val);
}
return temp1;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号