java中字节流与字符流以及字节流多余字节问题
1.字节流
字节流byte为单位对文件的数据进行写入与读取操作。字节的方式在复制音频图片文件时比较适用,但在对于普通文件的读写上有两大缺陷:
第一,字节流在读取中文字符时,若设定的字节数组长度刚好末尾的中文字不能获取完整,那么容易将这个字符拆开而造成乱码
第二,字节流在读取数据时,对于取不满字节数组的数据会自动进行填充,而该填充编译器无法识别,就会造成末尾会输出许多方框,关键是转码方面的问题
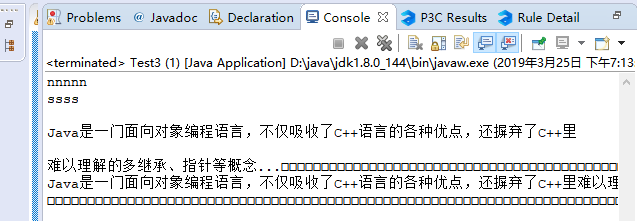
1 String name = "D:/test.txt"; 2 File file = new File(name); 3 if(!file.exists()) { 4 file.createNewFile(); 5 } 6 OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(file); 7 byte[] b = new byte[1024]; 8 b = "Java是一门面向对象编程语言,不仅吸收了C++语言的各种优点,还摒弃了C++里难以理解的多继承、指针等概念...".getBytes(); 9 os.write(b, 0, b.length); 10 System.out.println("nnnnn"); 11 os.flush(); 12 os.close(); 13 14 OutputStream os2 = new FileOutputStream("test1.txt"); 15 InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file); 16 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(is); 17 b = new byte[100]; 18 19 //ByteBuffer bytebuf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); 20 //int sum = 0; 21 22 byte[] b2 = new byte[100]; 23 int flag = 0 ; 24 while((flag = bis.read(b)) != -1) { 25 //bytebuf.put(b); 26 //sum += flag; 27 os2.write(b,0,flag); 28 29 } 30 31 //byte[] bytes = new byte[sum]; 32 // for(int i = 0; i < sum; i++) { 33 // bytes[i] = bytebuf.get(i); 34 //} 35 36 //String test = new String(bytes,"utf-8"); 37 //System.out.println(test);; 38 os2.close(); 39 bis.close();
这里推荐一种简单的方法,read方法会返回该字节数组的长度,可以采用这个将数据写入
另外一种解决方案可以参考https://blog.csdn.net/woshimalingyi/article/details/49226463
https://www.cnblogs.com/jiduoduo/p/6397454.html,ByteBuffer的应用
2.字符流
字符流相对简单,能够通过readLine读取一行的数据
1 // /** 2 // * 文字采用字符流,图片等采用字节流 3 // */ 4 // InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file)); 5 // BufferedReader rd = new BufferedReader(isr); 6 // 7 // OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("test1.txt")); 8 // BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(osw); 9 // 10 // String str = ""; 11 // while((str = rd.readLine()) != null){ 12 // System.out.println(str); 13 // bw.write(str); 14 // } 15 // bw.close(); 16 // rd.close();



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号