浅入深出Java输入输出流主线知识梳理
按流的方向,分为输入流与输出流,注意这里的输出输出是相对于程序而言的,如:如对于一个Java程序创建了一个输入流(Input),此时应该是进行读取操作将数据读到程序中。
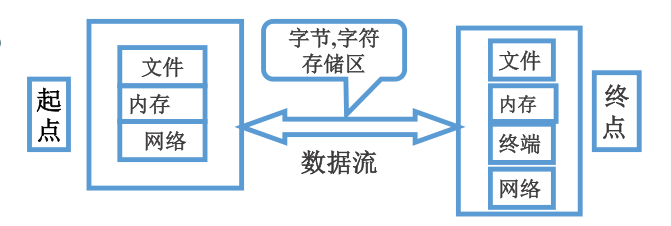

流既然是用来进行输入输出的,那么在所有的流中可以按每次输入输出的量分成两类流:字节流、字符流。顾名思义字节流每次操作为一个一个字节、字符流则每次读取一个一个字符。
额外的,在字符流中对于一个字符,不同编码方式他也有不同的表现形式,比如汉字,到底是这些字符采用UTF-8(多个字节),还是国标码(2个字节),不同编码对应不同的字节数。所以使用字符流时需要额外指定编码方式。
分成四个超类(很重要):
| 字节流 | 字符流 | |
| 输入流 | InputStream | Reader |
| 输出流 | OutputStream | Writer |
InputStream类
read(),逐字节地以二进制的原始方式读取数据
- public int read(); 读入一个字节,-1表示无
- public int read(byte b[]); 返回读入的字节数
- public int read(byte[] b, int off, int len);
OutputStream类
- write()方法,它的功能是将字节写入流中
- public void write (int b);// 将参数b的低位字节写入到输出流
- public void write (byte b[]);// 将字节数组b[]中的全部字节顺序写入到输出流
- public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len);// 将字节数组b[]中从off开始的len个字节写入到流中
Output的另外两个方法是flush()及close()。
- public void flush (); 刷新缓存,实际写入到文件、网络
- public void close(); 关闭流
Reader类
与InputStream类相似,都是输入流,但差别在于Reader类读取的是字符(char),而不是字节。
Reader的重要方法是read()
- public int read(); //返回:作为整数读取的字符(需要将int转char),如果已到达流的末尾,则返回 -1
- public int read(char b[]); //返回:读取的字符数
- public int read(char[] b, int off, int len);
Writer类
与OutputStream类相似,都是输出流,但差别在于Writer类写入的是字符(char),而不是字节。
Writer的方法有:
- public void write (int b);// 将参数b的低两字节写入到输出流
- public void write (char b[]);// 将字符数组b[]中的全部字节顺序写入到输出流
- public void write(char[] b, int off, int len);// 将字节数组b[]中从off开始的len个字节写入到流中
- public void write( String s);// 将字符串写入流中
- public void write( String s, int off, int len);// 将字符串写入流中, off为位置,len为长度
- public void flush ();// 刷新流
- public void close();// 关闭流
既然上面Reader、Writer、InputStream、OutputStream四类是根据每次操作的量以及输入输出划分出来的,那么就有其他的划分方式,划分为:节点流、处理流
节点流:可以向特定的地方(如文件)读写数据,如文件流FileInputStream、内存流ByteArrayInputStream.
处理流:可以对以及存在的流进行操作,也被称为过滤流(Filter),如缓冲处理流BufferedReader
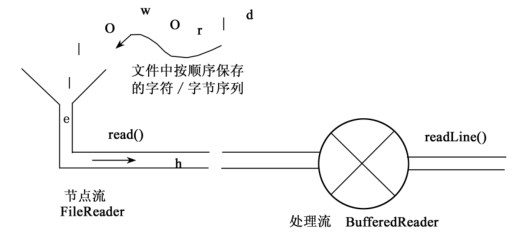

上图是就是使用节点流和处理流的例子,先通过FileReader读入文件中的字符串,然后使用处理流对这个流进行处理,有了这个处理流后就不必通过节点流提供的read()一个一个进行读取,BufferedReader这个处理流提供了readLine()方法可以一次读出节点流中的一行。这样的两者结合起来的操作实现了对流的包装(链接)。
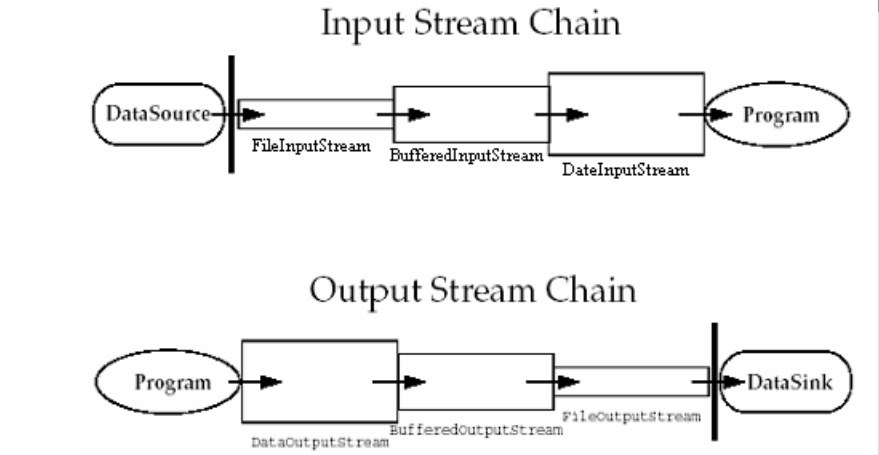
同时使用节点流和处理流的实际使用例子:
BufferedReader in =
new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
BufferedReader in2 =
new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader( //该处理流是字节流通向字符流的桥梁
new FileInputStream(file), “utf-8”));
s = in2.readLine();
从上图和例子看出,处理流构造时总是需要带一个其他流对象作为参数,一个流对象经过其他流的多次包装,称为流的链接。
通过节点流、处理流这样的划分方式,当我们进行I/O操作时,只需使用对应的数据类型对应的流,然后通过处理流进行链接,对流进行层层操作,便可以实现所需要的功能。
常用的节点流:
| 节点类型 | 字节流 | 字符流 |
| File 文件 |
FileInputStream FileOutputStream |
FileReader FileWriter |
| Memory Array 内存数组 |
ByteArrayInputStream ByteArrayOutputStream |
CharArrayReader CharArrayWriter |
| Memory String 字符串 |
StringReader StringWriter |
|
| Pipe 管道 |
PipedInputStream PipedOutputStream |
PipedReader PipedWriter |
常用的处理流:
| 处理类型 | 字节流 | 字符流 |
| Buffering 缓冲 |
BufferInputStream BufferOutputStream |
BufferedReader BufferedWriter |
| Filtering 过滤 |
FilterInputStream FilterOutputSteam |
FilterReader FilterWriter |
| Converting between bytes and character 字节流转换为字符流 |
InputStreamReader OutputStreamWriter 与字符编码有关 |
|
| Object Serialization 对象序列化 |
ObjectInputStream ObjectOutputStream |
|
| Data conversion 基本数据类型转化 |
DataInputStream DataOutputStream |
|
| Counting 行号处理 |
LineNumberInputStream | LineNumberReader |
| Peeking ahead 可回退流 | PushbackInputStream | PushbackReader |
| Pinting 可显示流 | PrintStream | PrintWriter |
标准输入和输出
平时我们常用的System.in实际上是InputStream类型,而System.out、System.err为PrintStream类型,是一个字符输出流。平时用到的就是流,所以在使用的时候我们经常将System.in用各种处理流封装起来使用。如:
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in));
br.readLine();
在jdk1.5后增加了Scanner类,使用起来方便了些。
实例!常见内容(二进制、文本、对象)的读写:
二进制流的读写:
tip:IO中“二进制”指的是除了文本、对象之外的其他内容,在这里是一个比较笼统的概念
import java.io.*;
public class Dump {
public static void main(String[]args) {
try
{
dump( new FileInputStream("aaa.bmp"), //FileInputStream节点流
new FileOutputStream("bbb.bmp"));
}
catch(FileNotFoundException fex)
{
fex.printStackTrace();
}
catch (IOException ioe)
{
ioe.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void dump(InputStream src, OutputStream dest) //这里使用InputStream、OutputStream类型作为参数
throws IOException
{
InputStream input = new BufferedInputStream(src); //使用处理流进行包装
OutputStream output = new BufferedOutputStream(dest); //向上转型
byte[] data = new byte[1024];
int length = -1;
while ((length = input.read(data)) != -1) { //read()将流中数据读取到data中
output.write(data, 0, length);
}
input.close();
output.close();
}
}
字符的读写:
import java.io.*;
public class CopyFileAddLineNumber {
public static void main (String[] args) {
//将文件的每一行注释去掉,然后加上行号
String infname = "CopyFileAddLineNumber.java";
String outfname = "CopyFileAddLineNumber.txt";
if( args.length >= 1 ) infname = args[0];
if( args.length >= 2 ) outfname = args[1];
try {
File fin = new File(infname);
File fout = new File(outfname);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fin));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter(fout));
int cnt = 0; // 行号
String s = in.readLine();
while ( s != null ) {
cnt ++;
s = deleteComments(s); //去掉以//开始的注释
out.println(cnt + ": \t" + s ); //写出
s = in.readLine(); //读入
}
in.close(); // 关闭缓冲读入流及文件读入流的连接.
out.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e1) {
System.err.println("File not found!" );
} catch (IOException e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
static String deleteComments( String s ) //去掉以//开始的注释
{
if( s==null ) return s;
int pos = s.indexOf( "//" );
if( pos<0 ) return s;
return s.substring( 0, pos );
}
}
序列化与反序列化(要求对象实现Serializable接口)
import java.io.*;
class Person implements Serializable
{
String name;
int age;
Person(String name, int age) {
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
public String toString() {
return name + "(" + age + ")";
}
}
public class SerializeDemo {
public static void main (String[] args)
throws IOException
{
Person [] ps = {
new Person("Li",18),
new Person("Wang",19)
};
String fileName = "s.temp";
//Serialize
ObjectOutputStream output = new ObjectOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(fileName) );
for(Person p : ps) output.writeObject(p);
output.close();
//deserialize
ObjectInputStream input = new ObjectInputStream(
new FileInputStream(fileName) );
Person p = null;
try {
while( (p=(Person)input.readObject()) != null ) {
System.out.println(p);
}
} catch(ClassNotFoundException ex) {}
catch(EOFException eofex) {}
input.close();
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号