图论拆点(二维最短路)
例一:
一个国家有 n 个城市,城市编号为 0 到 n - 1 ,题目保证 所有城市 都由双向道路 连接在一起 。道路由二维整数数组 edges 表示,其中 edges[i] = [xi, yi, timei] 表示城市 xi 和 yi 之间有一条双向道路,耗费时间为 timei 分钟。两个城市之间可能会有多条耗费时间不同的道路,但是不会有道路两头连接着同一座城市。
每次经过一个城市时,你需要付通行费。通行费用一个长度为 n 且下标从 0 开始的整数数组 passingFees 表示,其中 passingFees[j] 是你经过城市 j 需要支付的费用。
一开始,你在城市 0 ,你想要在 maxTime 分钟以内 (包含 maxTime 分钟)到达城市 n - 1 。旅行的 费用 为你经过的所有城市 通行费之和 (包括 起点和终点城市的通行费)。
给你 maxTime,edges 和 passingFees ,请你返回完成旅行的 最小费用 ,如果无法在 maxTime 分钟以内完成旅行,请你返回 -1 。
示例 1:
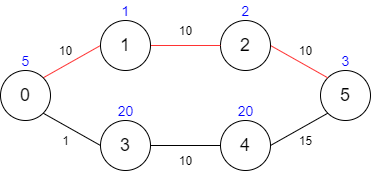
输入:maxTime = 30, edges = [[0,1,10],[1,2,10],[2,5,10],[0,3,1],[3,4,10],[4,5,15]], passingFees = [5,1,2,20,20,3]
输出:11
解释:最优路径为 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 5 ,总共需要耗费 30 分钟,需要支付 11 的通行费。
示例 2:
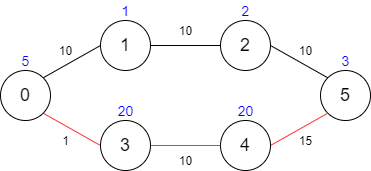
输入:maxTime = 29, edges = [[0,1,10],[1,2,10],[2,5,10],[0,3,1],[3,4,10],[4,5,15]], passingFees = [5,1,2,20,20,3]
输出:48
解释:最优路径为 0 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 ,总共需要耗费 26 分钟,需要支付 48 的通行费。
你不能选择路径 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 5 ,因为这条路径耗费的时间太长。
示例 3:
输入:maxTime = 25, edges = [[0,1,10],[1,2,10],[2,5,10],[0,3,1],[3,4,10],[4,5,15]], passingFees = [5,1,2,20,20,3]
输出:-1
解释:无法在 25 分钟以内从城市 0 到达城市 5 。
提示:
1 <= maxTime <= 1000
n == passingFees.length
2 <= n <= 1000
n - 1 <= edges.length <= 1000
0 <= xi, yi <= n - 1
1 <= timei <= 1000
1 <= passingFees[j] <= 1000
图中两个节点之间可能有多条路径。
图中不含有自环。
上面的是官方的题解,其实这个要用到拆点的技巧,f[t][i]指的是使用恰好t分钟到达i需要的最少通行费总和。
其实就是加上了一维,时间的维度
#define x first #define y second typedef pair<int,int> PII; const int N=1010,M=2010,INF=0x3f3f3f3f; int h[N],e[M],w[M],ne[M],cnt; int dis[N][N]; bool vis[N][N]; class Solution { public: void add(int a,int b,int c){ e[cnt]=b; w[cnt]=c; ne[cnt]=h[a]; h[a]=cnt++; } int minCost(int m, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& pf) { int n=pf.size(); memset(h,-1,sizeof(h)),cnt=0; for(auto e: edges){ int a=e[0],b=e[1],c=e[2]; add(a,b,c); add(b,a,c); } memset(dis,0x3f,sizeof(dis)); dis[0][0]=pf[0]; queue<PII> q; q.push({0,0}); while(!q.empty()){ auto t=q.front(); q.pop(); vis[t.x][t.y]=false; for(int i=h[t.x];~i;i=ne[i]){ int x=e[i],y=t.y+w[i]; if(y>m){ continue; } if(dis[x][y]>dis[t.x][t.y]+pf[x]){ dis[x][y]=dis[t.x][t.y]+pf[x]; if(!vis[x][y]){ vis[x][y]=true; q.push({x,y}); } } } } int res=INF; for(int i=0;i<=m;i++){ res=min(res,dis[n-1][i]); } if(res==INF){ res=-1; } return res; } };
例二:
小明和小芳出去乡村玩,小明负责开车,小芳来导航。
小芳将可能的道路分为大道和小道。
大道比较好走,每走 1 公里小明会增加 1 的疲劳度。
小道不好走,如果连续走小道,小明的疲劳值会快速增加,连续走 s 公里小明会增加 s2的疲劳度。
例如:有 5 个路口,1 号路口到 2 号路口为小道,2 号路口到 3 号路口为小道,3 号路口到 4 号路口为大道,4 号路口到 5 号路口为小道,相邻路口之间的距离都是 2 公里。
如果小明从 1 号路口到 5 号路口,则总疲劳值为 (2+2)^2+2+2^2=16+2+4=22。
现在小芳拿到了地图,请帮助她规划一个开车的路线,使得按这个路线开车小明的疲劳度最小。
输入格式
输入的第一行包含两个整数 n,m,分别表示路口的数量和道路的数量。路口由 1 至 n 编号,小明需要开车从 1 号路口到 n 号路口。
接下来 m 行描述道路,每行包含四个整数 t,a,b,c,表示一条类型为 t,连接 a 与 b 两个路口,长度为 c公里的双向道路。其中 t 为 0 表示大道,t 为 1 表示小道。
保证 1 号路口和 n 号路口是连通的。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示最优路线下小明的疲劳度。
数据范围
对于 30% 的评测用例,1≤n≤8,1≤m≤10;
对于另外 20% 的评测用例,不存在小道;
对于另外 20% 的评测用例,所有的小道不相交;
对于所有评测用例,1≤n≤500,1≤m≤10^5,1≤a,b≤n,t 是 0 或 1,c≤10^5。
保证答案不超过 10^6。
输入样例:
6 7
1 1 2 3
1 2 3 2
0 1 3 30
0 3 4 20
0 4 5 30
1 3 5 6
1 5 6 1
输出样例:
76
样例解释
从 1 走小道到 2,再走小道到 3,疲劳度为 5^2=25;然后从 3 走大道经过 4 到达 5,疲劳度为 20+30=50;最后从 5 走小道到 6,疲劳度为 1。
总共为 76。
Dis[i][j]表示从1到点i的最短距离,第二维j表示1到i点这条路径上最后那段(连接i)的小路的长度。如果1到i的路径最后那段是大路,那么j 置为0.
那最后的答案是什么呢? 是dis[n][i],枚举每个i从0到1000,取出最小值即可。
这个题会卡掉spfa的,然后要用堆优化的dijkstra()
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<queue> #include<cstring> #define x first #define y second using namespace std; const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f; const int N=3e3+100; const int M=3e3+100; const int maxn=2e5+100; int dis[N][M]; bool st[N][M]; struct node{ int e,ne,w,f;//最短 }edge[maxn]; int head[maxn]; int cnt=0; struct Node{ int x,y,v; bool operator<(const Node& t)const{ return v>t.v; } }; void add(int a,int b,int c,int w){ edge[cnt].e=b; edge[cnt].ne=head[a]; edge[cnt].f=c; edge[cnt].w=w;//最短 head[a]=cnt++; } void dijkstra(){ priority_queue<Node>q; memset(dis,0x3f,sizeof(dis)); q.push({1,0,0}); dis[1][0]=0; while(!q.empty()){ Node t=q.top(); q.pop(); if(st[t.x][t.y]) continue; st[t.x][t.y]=1; for(int i=head[t.x];~i;i=edge[i].ne){ int x=edge[i].e,y=t.y; if(edge[i].f){ y+=edge[i].w; if(y<=1000){ if(dis[x][y]>t.v- t.y * t.y + y * y){ dis[x][y]=t.v- t.y * t.y + y * y; if(dis[x][y]<=INF){ q.push({x,y,dis[x][y]}); } } } } else{ if(dis[x][0]>t.v+edge[i].w){ dis[x][0]=t.v+edge[i].w; if(dis[x][0] <= INF) q.push({x,0, dis[x][0]}); } } } } } int main(){ int n,m; memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); cin>>n>>m; for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ int a,b,c,w; cin>>c>>a>>b>>w; add(a,b,c,w); add(b,a,c,w); } dijkstra(); int ans=INF; for(int i=0;i<=1000;i++){ ans=min(ans,dis[n][i]); } cout<<ans<<endl; }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号