实验六
实验六
任务一:
代码部分:
utils.hpp:
#pragma once #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #include <stdexcept> #include <string> #include <vector> #include "contestant.hpp" // ACM 排序规则:先按解题数降序,再按罚时升序 inline bool cmp_by_solve(const Contestant& a, const Contestant& b) { if(a.solved != b.solved) return a.solved > b.solved; return a.penalty < b.penalty; } // 将结果写至任意输出流 inline void write(std::ostream& os, const std::vector<Contestant>& v) { for (const auto& x : v) os << x << '\n'; } // 将结果打印到屏幕 inline void print(const std::vector<Contestant>& v) { write(std::cout, v); } // 将结果保存到文件 inline void save(const std::string& filename, const std::vector<Contestant>& v) { std::ofstream os(filename); if (!os) throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + filename); write(os, v); } // 从文件读取信息(跳过标题行) inline std::vector<Contestant> load(const std::string& filename) { std::ifstream is(filename); if (!is) throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + filename); std::string line; std::getline(is, line); // 跳过标题 std::vector<Contestant> v; Contestant t; int seq; while (is >> seq >> t) v.push_back(t); return v; }
contestant.hpp:
#pragma once #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #include <stdexcept> #include <string> #include <vector> #include "contestant.hpp" // ACM 排序规则:先按解题数降序,再按罚时升序 inline bool cmp_by_solve(const Contestant& a, const Contestant& b) { if(a.solved != b.solved) return a.solved > b.solved; return a.penalty < b.penalty; } // 将结果写至任意输出流 inline void write(std::ostream& os, const std::vector<Contestant>& v) { for (const auto& x : v) os << x << '\n'; } // 将结果打印到屏幕 inline void print(const std::vector<Contestant>& v) { write(std::cout, v); } // 将结果保存到文件 inline void save(const std::string& filename, const std::vector<Contestant>& v) { std::ofstream os(filename); if (!os) throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + filename); write(os, v); } // 从文件读取信息(跳过标题行) inline std::vector<Contestant> load(const std::string& filename) { std::ifstream is(filename); if (!is) throw std::runtime_error("fail to open " + filename); std::string line; std::getline(is, line); // 跳过标题 std::vector<Contestant> v; Contestant t; int seq; while (is >> seq >> t) v.push_back(t); return v; }
task1.cpp:
#include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <stdexcept> #include <vector> #include "contestant.hpp" #include "utils.hpp" const std::string in_file = "./data.txt"; const std::string out_file = "./ans.txt"; void app() { std::vector<Contestant> contestants; try { contestants = load(in_file); std::sort(contestants.begin(), contestants.end(), cmp_by_solve); print(contestants); save(out_file, contestants); } catch (const std::exception& e) { std::cerr << e.what() << '\n'; return; } } int main() { app(); }
结果截图:
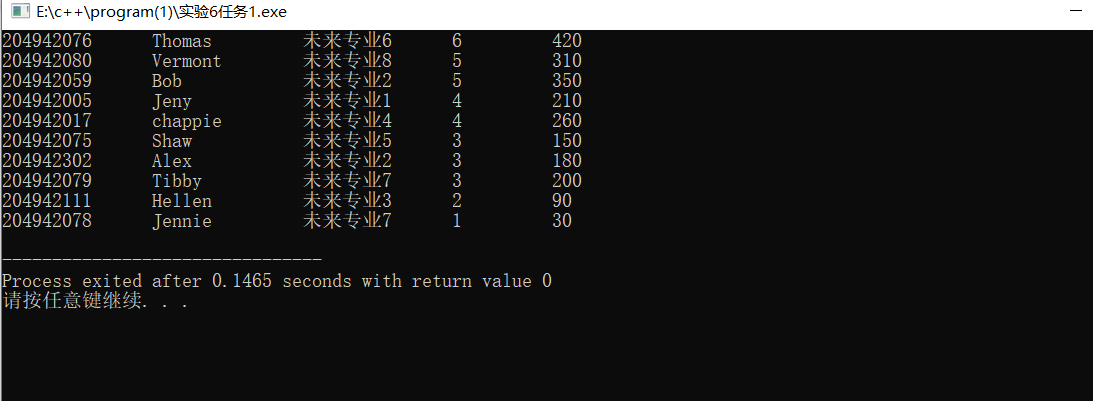
问题回答:
问题1:(1):
std::cout 是 std::ostream 类型的全局对象
std::ofstream 继承自 std::ostream
根据 C++ 的 Liskov 替换原则,派生类对象可以赋值给基类引用
(2)
不需要改动 write() 函数。
原因:基于抽象接口的设计
std::ostream 是抽象接口:任何继承自 std::ostream 的类都可以使用,write() 只依赖于 std::ostream 的公共接口
问题2:(1):
第一处:
// 无法打开文件时抛出异常 if (!in) { throw std::runtime_error("无法打开文件: " + filename); }
触发条件:文件不存在,文件路径错误,没有文件读取权限,磁盘错误,文件被其他程序占用
第二处:
// 如果 data.txt 不存在,将抛出: // std::runtime_error("无法打开文件: data.txt") contestants = load("data.txt");
触发条件:文件格式错误(如非数字出现在数字字段),数据类型不匹配,文件损坏,读取过程中发生I/O错误
第三处:
// 无法创建或写入文件时抛出异常 if (!out) { throw std::runtime_error("无法写入文件: " + filename); }
触发条件:磁盘空间不足,没有写入权限,路径无效,文件被锁定
(2):
异常捕获位置在 app() 函数中:
try { contestants = load(in_file); std::sort(contestants.begin(), contestants.end(), cmp_by_solve); print(contestants); save(out_file, contestants); } catch (const std::exception& e) { std::cerr << "错误: " << e.what() << '\n'; return; }
处理操作:
std::cerr << "错误: " << e.what() << '\n'; return;
1.将错误信息输出到标准错误流(std::cerr)
2.提前返回,终止 app() 函数执行
3.错误信息包含具体的错误描述(通过 e.what())
问题3:
可以替换,而且功能、性能、结果完全一致。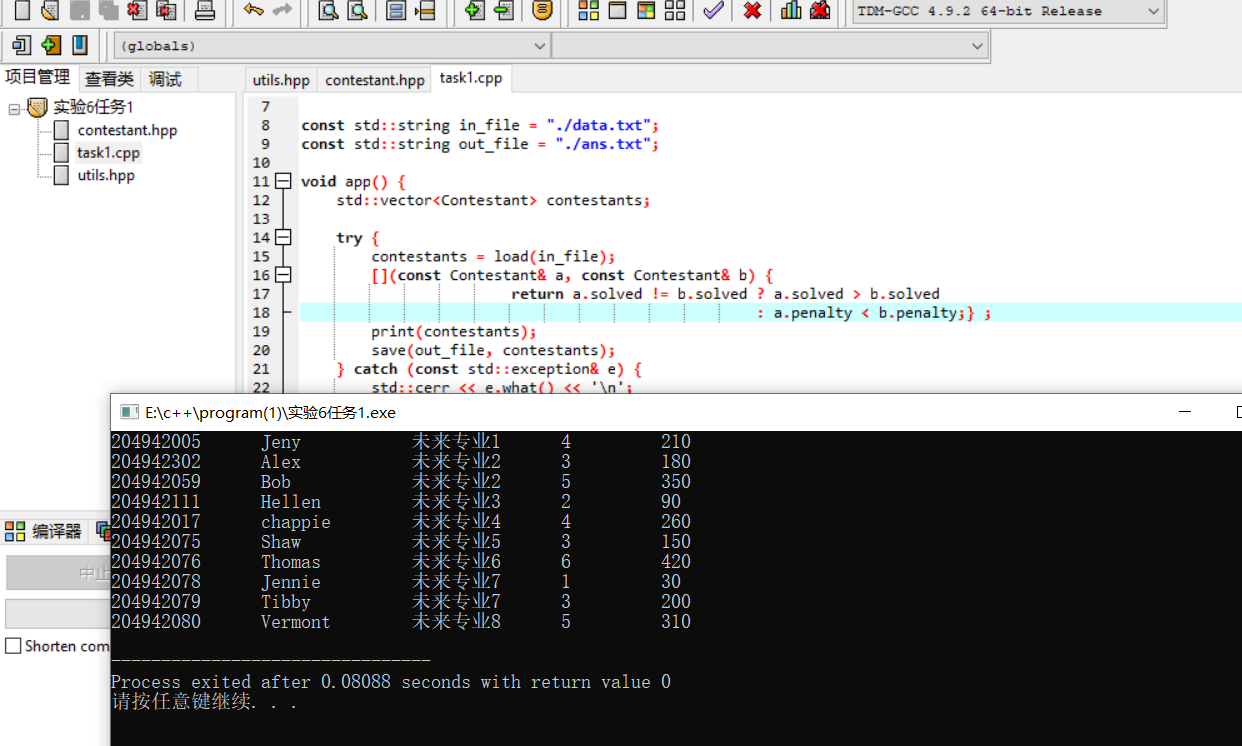
问题4:(1)
结果截图:
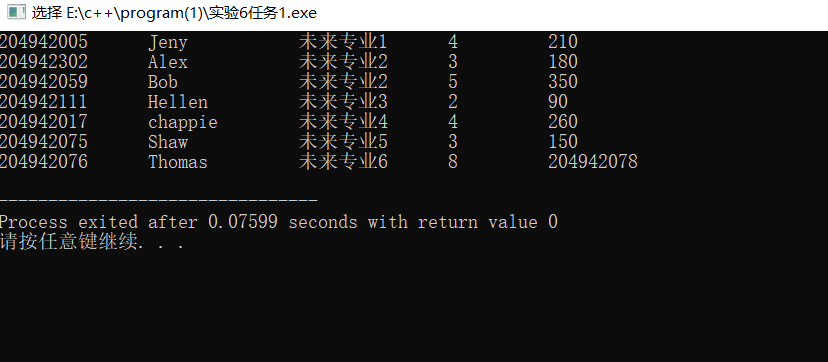
出现问题:
数据错位: 第7条记录 Thomas 的数据完全混乱
解题数变成了 8(应该是空值)
总罚时变成了 204942078(这是下一条记录的学号!)
处理流程异常:程序没有抛出异常,而是继续运行
数据丢失:最后3条记录(Jennie、Tibby、Vermont)没有被处理
原因分析:直接使用 >> 进行格式化输入,>> 遇到空白(缺失字段)时不会自动跳过,而是设置失败位,但是当读取失败时,不会立即抛出异常,而是将变量保持原值(或0),然后继续读取后续字段,造成数据错位
任务2:
代码部分:
#pragma once #include <iostream> #include <string> class Student { public: Student() = default; ~Student() = default; const std::string get_major() const; int get_grade() const; friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Student& s); friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& is, Student& s); private: int id; std::string name; std::string major; int grade; // 0-100 };
#include "student.hpp" #include <iomanip> // 获取专业 const std::string Student::get_major() const { return major; } // 获取成绩 int Student::get_grade() const { return grade; } // 重载输出运算符 std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const Student& s) { os << std::left; os << std::setw(6) << s.id << std::setw(10) << s.name << std::setw(10) << s.major << std::setw(6) << s.grade; return os; } // 重载输入运算符 std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& is, Student& s) { is >> s.id >> s.name >> s.major >> s.grade; // 验证成绩范围 if (s.grade < 0 || s.grade > 100) { is.setstate(std::ios::failbit); } return is; }
#pragma once #include <string> #include <vector> #include "student.hpp" class StuMgr { public: void load(const std::string& file); // 加载数据文件(空格分隔) void sort(); // 排序: 按专业字典序升序、同专业分数降序 void print() const; // 打印到屏幕 void save(const std::string& file) const; // 保存到文件 private: void write(std::ostream &os) const; // 把数据写到任意输出流 private: std::vector<Student> students; };
#include "stumgr.hpp" #include <fstream> #include <algorithm> #include <stdexcept> #include <iostream> #include <iomanip> #include <string> // 加载数据文件 void StuMgr::load(const std::string& file) { std::ifstream in(file); if (!in) { throw std::runtime_error("cannot open file: " + file); } // 跳过表头行(假设第一行是表头) std::string header; std::getline(in, header); students.clear(); // 清空原有数据 Student s; while (in >> s) { students.push_back(s); } // 检查读取是否完全成功 if (!in.eof() && in.fail()) { throw std::runtime_error("file format error in: " + file); } std::cout << "加载成功\n" << std::endl; } // 排序:按专业字典序升序、同专业分数降序 void StuMgr::sort() { if (students.empty()) { std::cout << "(empty)\n"; return; } std::sort(students.begin(), students.end(), [](const Student& a, const Student& b) { if (a.get_major() != b.get_major()) { return a.get_major() < b.get_major(); // 专业升序 } return a.get_grade() > b.get_grade(); // 同专业成绩降序 }); std::cout << "排序已完成\n" << std::endl; } // 写入数据到输出流(私有辅助函数) void StuMgr::write(std::ostream &os) const { os << std::left; os << std::setw(6) << "学号" << std::setw(10) << "姓名" << std::setw(10) << "专业" << std::setw(6) << "成绩" << '\n'; os << "----------------------------------------\n"; for (const auto& s : students) { os << s << '\n'; } } // 打印到屏幕 void StuMgr::print() const { if (students.empty()) { std::cout << "没有数据可显示\n"; return; } write(std::cout); std::cout << "打印已完成\n" << std::endl; } // 保存到文件 void StuMgr::save(const std::string& file) const { std::ofstream out(file); if (!out) { throw std::runtime_error("cannot save file: " + file); } write(out); std::cout << "导出成功\n" << std::endl; }
#include <iostream> #include <limits> #include <string> #include "stumgr.hpp" const std::string in_file = "./data.txt"; const std::string out_file = "./ans.txt"; void menu() { std::cout << "\n**********简易应用**********\n" "1. 加载文件\n" "2. 排序\n" "3. 打印到屏幕\n" "4. 保存到文件\n" "5. 退出\n" "请选择:"; } void app() { StuMgr mgr; while(true) { menu(); int choice; std::cin >> choice; try { switch (choice) { case 1: mgr.load(in_file); std::cout << "加载成功\n"; break; case 2: mgr.sort(); std::cout << "排序已完成\n"; break; case 3: mgr.print(); std::cout << "打印已完成\n"; break; case 4: mgr.save(out_file); std::cout << "导出成功\n"; break; case 5: return; default: std::cout << "不合法输入\n"; } } catch (const std::exception& e) { std::cout << "Error: " << e.what() << '\n'; } } } int main() { app(); }
结果截图:
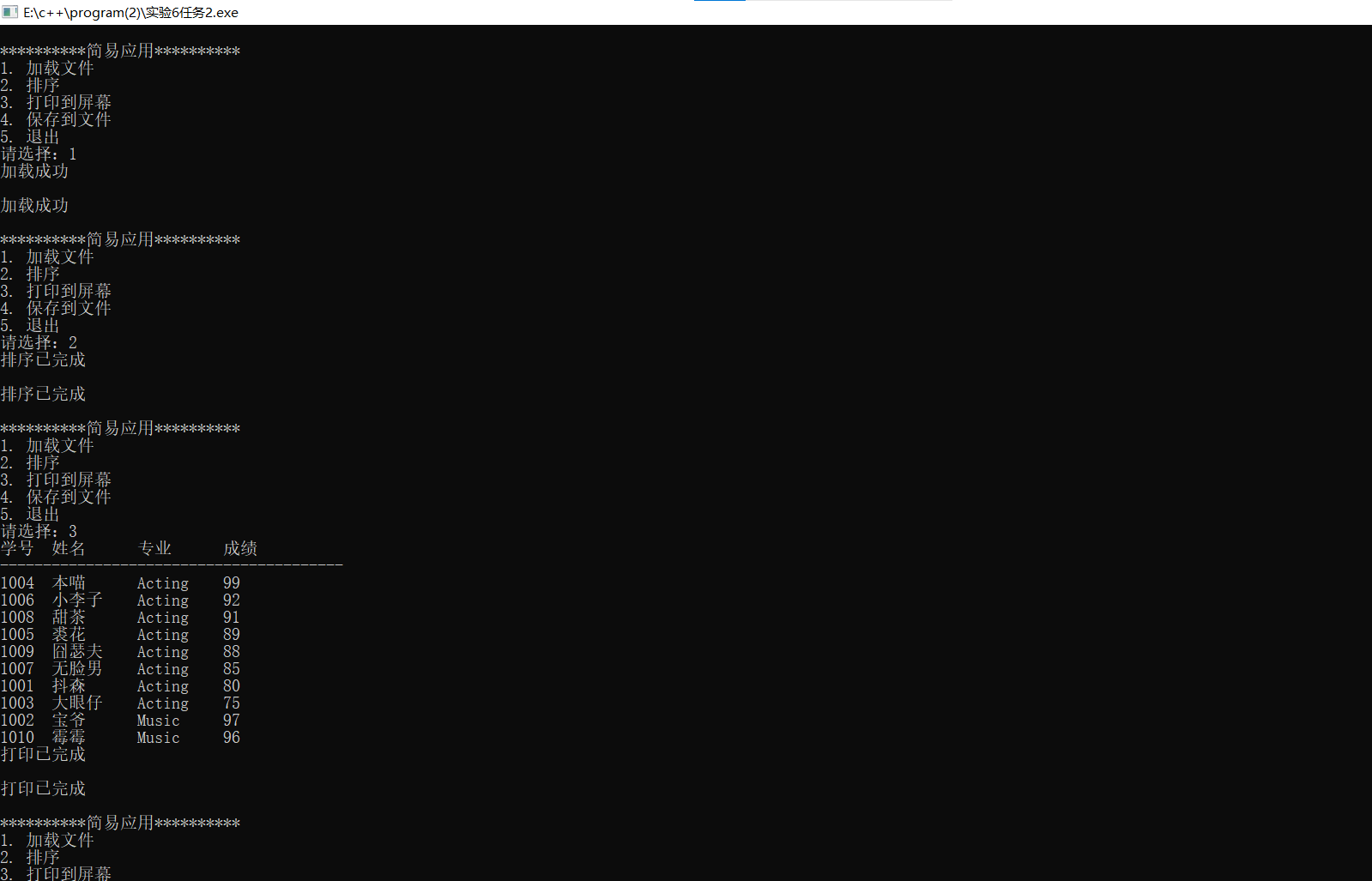




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号