Nearest Common Ancestors(LCA+倍增+dfs)
2019-08-08 19:52 木木王韦 阅读(103) 评论(0) 收藏 举报Nearest Common Ancestors
A rooted tree is a well-known data structure in computer science and engineering. An example is shown below:
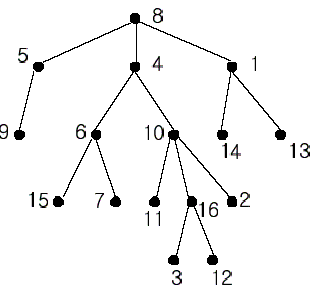
In the figure, each node is labeled with an integer from {1, 2,…,16}. Node 8 is the root of the tree. Node x is an ancestor of node y if node x is in the path between the root and node y. For example, node 4 is an ancestor of node 16. Node 10 is also an ancestor of node 16. As a matter of fact, nodes 8, 4, 10, and 16 are the ancestors of node 16. Remember that a node is an ancestor of itself. Nodes 8, 4, 6, and 7 are the ancestors of node 7. A node x is called a common ancestor of two different nodes y and z if node x is an ancestor of node y and an ancestor of node z. Thus, nodes 8 and 4 are the common ancestors of nodes 16 and 7. A node x is called the nearest common ancestor of nodes y and z if x is a common ancestor of y and z and nearest to y and z among their common ancestors. Hence, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 16 and 7 is node 4. Node 4 is nearer to nodes 16 and 7 than node 8 is.
For other examples, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 2 and 3 is node 10, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 6 and 13 is node 8, and the nearest common ancestor of nodes 4 and 12 is node 4. In the last example, if y is an ancestor of z, then the nearest common ancestor of y and z is y.
Write a program that finds the nearest common ancestor of two distinct nodes in a tree.
Input
The input consists of T test cases. The number of test cases (T) is given in the first line of the input file. Each test case starts with a line containing an integer N , the number of nodes in a tree, 2<=N<=10,000. The nodes are labeled with integers 1, 2,…, N. Each of the next N -1 lines contains a pair of integers that represent an edge --the first integer is the parent node of the second integer. Note that a tree with N nodes has exactly N - 1 edges. The last line of each test case contains two distinct integers whose nearest common ancestor is to be computed.
Output
Print exactly one line for each test case. The line should contain the integer that is the nearest common ancestor.
Sample Input
2
16
1 14
8 5
10 16
5 9
4 6
8 4
4 10
1 13
6 15
10 11
6 7
10 2
16 3
8 1
16 12
16 7
5
2 3
3 4
3 1
1 5
3 5
Sample Output
4
3
LCA:最近公共祖先,这道题存入就说明了父子的关系,所以这是一个有向图,稍微简便了一点,不要忘了加init啊。。。(好多人入坑)
ac代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=10005;
vector<int> G[N];
long long bit[30];
int depth[N];
int f[N][30];
int dis[N];
void init(){
bit[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=29;i++){
bit[i]=(bit[i-1]<<1);
//printf("%lld ",bit[i]);
}
}
void dfs(int u,int par){//u:子结点,par:父结点
depth[u]=depth[par]+1;//子结点的深度为父结点的深度+1
f[u][0]=par; //子结点的往上找2的0次方是他的父结点
for(int i=1;i<=29;i++){
f[u][i]=f[f[u][i-1]][i-1];//结点u的距离2的i次方的结点是距离2的i-1次方结点有2的i-1次方距离的结点
}
for(int i=0;i<(int)G[u].size();i++){
int v=G[u][i];//存图中与u相连的点
dfs(v,u);//此时遍历子结点v和父结点u
}
}
int LCA(int a,int b){
if(depth[a]<depth[b]){
swap(a,b);//保证a结点的深度大于b结点的深度
}
int dif=depth[a]-depth[b];//深度差
//printf("dif:%d a:%d b:%d\n",dif,a,b);
for(int i=29;i>=0;i--){
if(dif>=bit[i]){
//printf("&&&&&%d\n",a);
a=f[a][i];//f[f[a][i-1]][i-1]=f[a][i] ,a结点往上查找,并更新结点a
dif-=bit[i];//深度差更新为往上查找到的节点深度与b结点深度的深度差
}
}
if(a==b) return a;//如果a和b相等,那么证明b是a的祖先结点,即最近公共祖先为其本身
for(int i=29;i>=0;i--){//此时a和b的深度一样,共同往上查找其祖先,直至相等,即为最近公共祖先
//printf("%%%%%%%%%((()))%d %d\n",a,b);
if(depth[a]>=bit[i]&&f[a][i]!=f[b][i]){//当a的深度为目前可查找的深度,并且向上查找2的i次方的深度后两结点仍不相等,是为了避免查找到最近公共祖先之上的公共祖先
//printf("%d %d\n",a,b);
a=f[a][i];//更新两个结点
b=f[b][i];
}
}
return f[a][0];//此时a结点为最近公共祖先的子结点,即a的父结点即为最近公共祖先
}
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
init();
memset(dis,0,sizeof(dis));
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
G[i].clear();
}
int a,b;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
G[a].push_back(b);
dis[b]++;
}
int s;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(dis[i]==0){
s=i;
break;
}
}
//printf("%d ",s);
dfs(s,0);
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
printf("%d\n",LCA(a,b));
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号