Linux iptables与Docker bridge网络
关于Iptables和Netfilter
Iptables是什么
Iptables是主机防火墙,常见于CentOS,Redhat,Kylin及Openeuler等Linux操作系统上,其作用与硬件防火墙类似,可对网络层或传输层的流量进行包的过滤及转发;
Iptables工作于网络七层模型中的网络层与传输层(如图):
网络层:基于IP地址的过滤与转发
传输层:基于端口的过滤与转发
Netfilter是什么
Netfilter是Linux内核中自带的包过滤器,因为用户是通过用户空间的iptables来操作内核中的Netfilter,所以iptables用户态下的管理工具。同样的工具还有Firewalld、NFtables,尽管不同管理工具的语法不尽相同,但操作的终究是内核中的Netfilter。
Iptables与Netfilter的关系图

Iptables工作原理
与防火墙黑白名单类似,iptables也是通过策略来管理进站及出站流量,他的策略由四表五链组成(第五个表security按下不表):
四表:
raw
mangle
nat
filter
五链:Prerouting Forward Input Output Postrouting
当服务器网卡接收到请求时,在四表五链中的匹配流程如下图所示:
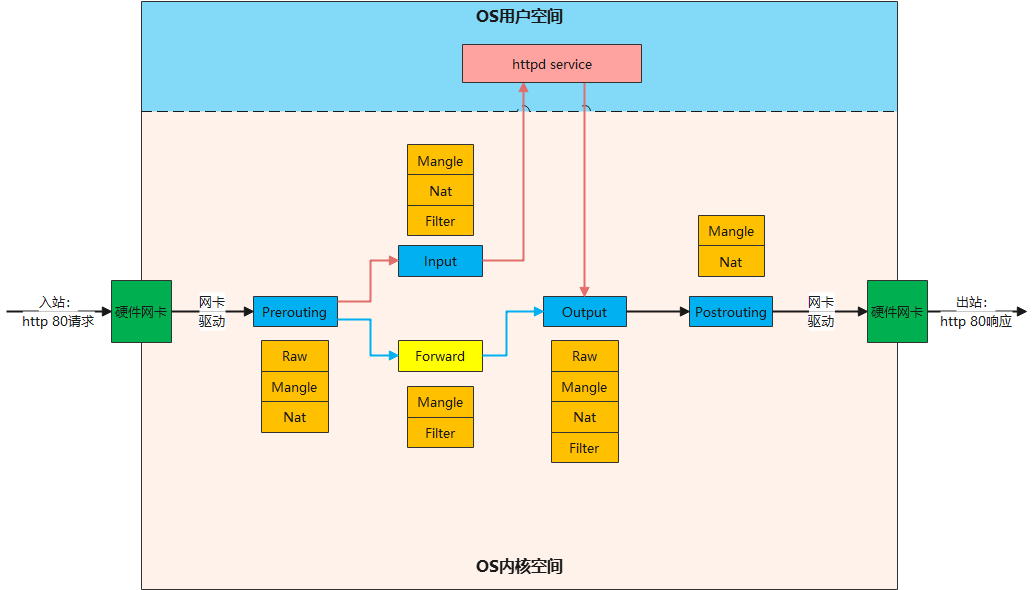
由图可知,流量进站后,Netfilter通过判断是否需要转发来决定路由:
1.当不需要转发时,流量进入Input链及后续处理后,通过网卡出站,流量不经过Forward链;
2.当需要转发时,流量进入Forward链及后续处理后,通过网卡出站,流量不经过Input链。
查看raw表策略
[root@bogon ~]# iptables -t raw -L
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
查看mangle表策略
[root@bogon ~]# iptables -t mangle -L
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
查看nat表规则
[root@bogon ~]# iptables -t nat -L
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
[root@bogon ~]# iptables -t filter -L
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
启动docker守护进程后Nat表的变化
[root@bogon ~]# iptables -t nat -L
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
DOCKER all -- anywhere anywhere ADDRTYPE match dst-type LOCAL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
DOCKER all -- anywhere !loopback/8 ADDRTYPE match dst-type LOCAL
Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
MASQUERADE all -- bogon/16 anywhere
Chain DOCKER (2 references)
target prot opt source destination
RETURN all -- anywhere anywhere
启动docker守护进程后Filter表变化
[root@bogon ~]# iptables -t filter -L
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
DOCKER-USER all -- anywhere anywhere
DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 all -- anywhere anywhere
ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED
DOCKER all -- anywhere anywhere
ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere
ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain DOCKER (1 references)
target prot opt source destination
Chain DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 (1 references)
target prot opt source destination
DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 all -- anywhere anywhere
RETURN all -- anywhere anywhere
Chain DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 (1 references)
target prot opt source destination
DROP all -- anywhere anywhere
RETURN all -- anywhere anywhere
Chain DOCKER-USER (1 references)
target prot opt source destination
RETURN all -- anywhere anywhere
可以看到,启动docker引擎后,iptables的NAT和FILTER表中增加了一些规则链
此时在服务器查看网卡信息:
[root@localhost ~]# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens32: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:3a:e4:f7 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.5.128/24 brd 192.168.5.255 scope global noprefixroute dynamic ens32
valid_lft 1311sec preferred_lft 1311sec
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fe3a:e4f7/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: docker0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 02:42:56:f2:d9:37 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.17.0.1/16 brd 172.17.255.255 scope global docker0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::42:56ff:fef2:d937/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
9: vethe30124f@if8: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue master docker0 state UP group default
link/ether 26:4f:72:e5:e4:84 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet6 fe80::244f:72ff:fee5:e484/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
不难发现输出中多了"docker0"和"vethe30124f@if8"网卡信息,其中网卡"docker0"的地址是"172.17.0.1"。
此时启动一个nginx容器,使用桥接模式,将容器内80端口的请求映射出来。
[root@localhost ~]# docker run -itd --rm --name nginx -p 80:80 nginx:latest
fb9dfd1adb7d9160ce15baefe15be0720ac6f9645c23568540de7b28f832dce0
再次查看iptables的NAT和FILTER表
# NAT表
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -t nat -nL
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
DOCKER all -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ADDRTYPE match dst-type LOCAL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
DOCKER all -- 0.0.0.0/0 !127.0.0.0/8 ADDRTYPE match dst-type LOCAL
Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
MASQUERADE all -- 172.17.0.0/16 0.0.0.0/0
MASQUERADE tcp -- 172.17.0.3 172.17.0.3 tcp dpt:80
Chain DOCKER (2 references)
target prot opt source destination
RETURN all -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
DNAT tcp -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:80 to:172.17.0.3:80
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
# FILTER表
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -t filter -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 955 packets, 64317 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
26 3509 DOCKER-USER all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
26 3509 DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
12 1298 ACCEPT all -- * docker0 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED
2 120 DOCKER all -- * docker0 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
12 2091 ACCEPT all -- docker0 !docker0 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT all -- docker0 docker0 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 695 packets, 64648 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain DOCKER (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
2 120 ACCEPT tcp -- !docker0 docker0 0.0.0.0/0 172.17.0.3 tcp dpt:80
Chain DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
12 2091 DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 all -- docker0 !docker0 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
26 3509 RETURN all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 DROP all -- * docker0 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
12 2091 RETURN all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain DOCKER-USER (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
26 3509 RETURN all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
此时访问主机地址的80端口:
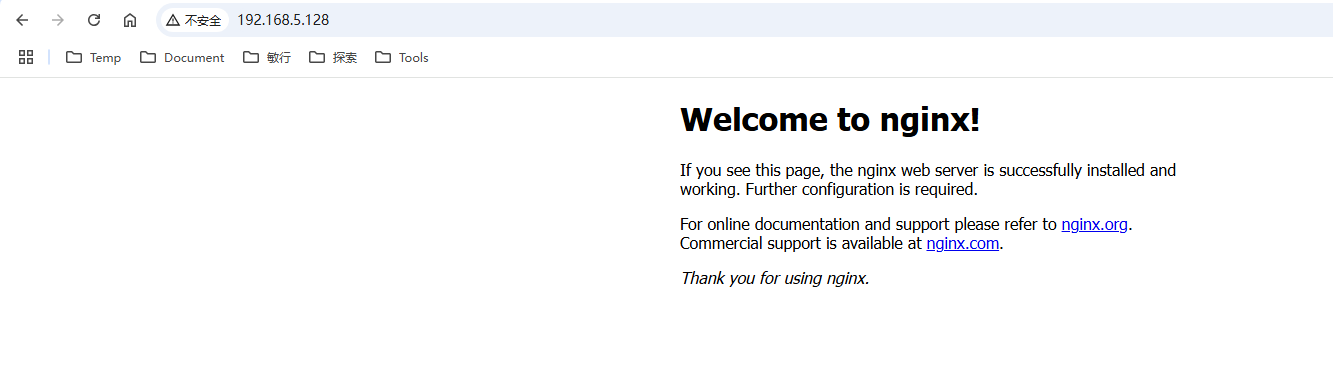
访问主机的80端口时,看到能访问到容器的80端口,通过分析上面iptables规则链来了解下:
在上面已经介绍了四表五链的匹配顺序。
1.当流量进站后,先通过IPTABLES的PREROUTING链进行匹配,此时NAT表中PREROUTING链只有一条规则
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
DOCKER all -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ADDRTYPE match dst-type LOCAL
该规则的意思是将所有目的地址为本地地址的数据包发送到 DOCKER 链进行处理
2.根据PREROUTING规则,此时流量要去NAT表中DOCKER链匹配
Chain DOCKER (2 references)
target prot opt source destination
RETURN all -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
DNAT tcp -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:80 to:172.17.0.3:80
流量匹配到NAT表中的第一条规则,但该规则的目标是"RETURN",所以它会继续向下匹配;
流量匹配到NAT表中的第二条规则,该规则是DNAT转发,此时数据包的TCP头变化如下:
DNAT前:
source destination dest_port
* 192.168.5.128 80
# "*"代表客户端地址
# "192.168.5.128"是我本地server地址
DNAT后
source destination dest_port
* 172.17.0.3 80
3.因该是转发,所以流量在iptables中应进入FORWARD链进行处理,而不是INPUT链了。
4.流量去匹配FILTER表的FORWARD链
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
26 3509 DOCKER-USER all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
26 3509 DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
12 1298 ACCEPT all -- * docker0 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED
2 120 DOCKER all -- * docker0 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
12 2091 ACCEPT all -- docker0 !docker0 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT all -- docker0 docker0 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
在FILTER的FORWARD链中,首先匹配到第一条规则,将流量转去DOCKER-USER链进行匹配。
Chain DOCKER-USER (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
26 3509 RETURN all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
DOCKER-USER链匹配并将流量返回到FORWARD链继续匹配,此时匹配到FORWARD链中第二条规则,将流量转去DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1链进行匹配
Chain DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1 (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
12 2091 DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-2 all -- docker0 !docker0 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
26 3509 RETURN all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
由于DOCKER-ISOLATION-STAGE-1中第一条规则因入站网卡和出站网卡不匹配,所以匹配到的是第二条规则,返回FORWARD继续处理。
FORWARD中第三条规则
ACCEPT all -- * docker0 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED
# ctstate 表示要匹配数据包的状态
# ESTABLISHED:表示数据包属于一个已经建立的连接。
# RELATED:表示数据包与一个已经建立的连接相关联,但不是该连接的一部分。
表示是对已建立连接以及建立连接后续相关联的数据包进行检测,不匹配,则继续匹配FORWARD链的下一条规则,将数据包转到DOCKER链进行匹配
Chain DOCKER (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
2 120 ACCEPT tcp -- !docker0 docker0 0.0.0.0/0 172.17.0.3 tcp dpt:80
根据这条规则,最终进站网卡非docker0,出站方向是docker0,源和目标地址、端口都匹配成功,最终被"ACCEPT"接受。
以上就是从外部访问桥接模式容器端口时,数据包在IPTABLES的转发过程,我们就知道为啥DOCKER说如果用户向针对容器指定策略为何要在DOCKER-USER链中加规则了,也知道了为啥你在INPUT链中加规则为何不对容器生效了。
本文来自博客园,作者:Linux小飞象,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/linux-xiaofeixiang/p/18597146



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号