全局标志位,while语法及for循环补充
目录
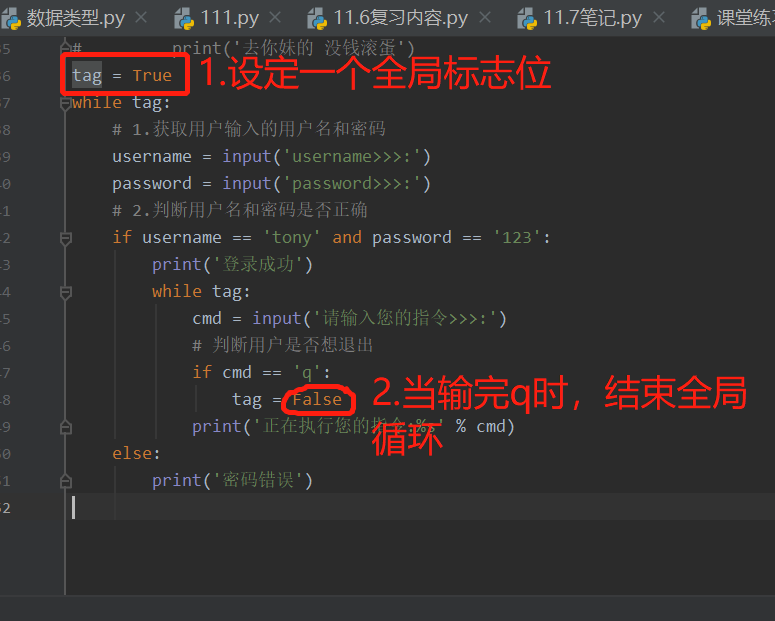
全局标志位使用:
1.使用while循环打印出0-10
count = 0
while count < 11:
print(count)
count += 1
2.使用while循环打印出0-10但是不打印4
①.定义一个起始变量
count = 0
②.循环
while count < 11:
⑤.判断 如果count为4则不打印
if count == 4:
count += 1
continue 跳过本次循环 开始下一次循环
③.打印变量的值
print(count)
④.变量值自增1
count += 1
continue会让循环体代码直接回到条件判断处重新判断
while+else
count = 0
while count < 5:
print(count)
count += 1
else:
print('嘿嘿嘿') 会执行else子代码
count = 0
while count < 5:
if count == 3:
break
print(count)
count += 1
else:
print('嘿嘿嘿') 不会执行else子代码
当while循环没有被人为中断(break)的情况下才会走else
死循环
while True:
print(1)
死循环会让CPU极度繁忙 甚至奔溃 尽量不要犯这种错误!!!
for循环
for循环能做到的事情 while循环都可以做到
但是for循环语法更加简洁 并且在循环取值问题上更加方便
name_list = ['jason', 'tony', 'kevin', 'jack', 'xxx']
循环取出列表的每一个元素并打印
while实现:
count = 0
while count < 5:
print(name_list[count])
count += 1
for循环
for name in name_list:
print(name)
for 变量名 in 可迭代对象: # 字符串、列表、字典、元组、集合
for循环体代码
ps:变量名如果没有合适的名称 那么可以使用i,j,k,v,item等
name_list = ['jason', 'tony', 'kevin', 'jack', 'xxx']
循环取出列表的每一个元素并打印
while实现:
count = 0
while count < 5:
print(name_list[count])
count += 1
for循环:
for name in name_list:
print(name)
for循环字符串:
for i in 'hello world':
print(i)
结果是
h
e
l
l
o
w
o
r
l
d

for循环字典:默认只能拿到k
d = {'username': 'jason', 'pwd': 123, 'hobby': 'read'}
想取K值要这么操作:
for k in d:
print(k, d[k])
range关键字(牢记)
第一种:一个参数 从0开始 顾头不顾尾
for i in range(10):
print(i)
打印0-9
第二种:两个参数 自定义起始位置 顾头不顾尾
for i in range(4, 10):
print(i)
打印4-9
第三种:三个参数 第三个数字用来控制等差值
for i in range(2, 100, 10):
print(i)
打印2,12,22,32...92
第三个数字控制等差值
range在不同版本的解释器中 本质不同
在python2.X中range会直接生成一个列表
在python2.X中有一个xrange也是迭代器(老母猪)
在python3.X中range是一个迭代器(老母猪) 节省内存空间
'''python2.X中xrange就是python3.x里面的range'''
for+break
break功能也是用于结束本层循环
for i in range(10):
if i == 4:
break
print(i)
for+continue
continue功能也是用于结束本次循环
for i in range(10):
if i == 4:
continue
print(i)
for+else
else也是在for循环正常结束的
情况下才会执行
for i in range(10):
if i == 4:
break
print(i)
else:
print('你追我!!!')
for循环的嵌套使用
for i in range(3):
for j in range(5):
print("*", end='')
print()
for i in range(1, 10):
for j in range(1, i + 1):
print('%s*%s=%s' % (i, j, i * j), end=' ')
print()

end...
全局标志位,while语法及for循环补充到这里就结束啦~拜了个拜



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号