1、动态输出
打开E:\study\openresty\openresty-1.19.9.1-win64 目录下的 conf/nginx.conf 文件
在server中增加一下代码
location /hello {
default_type text/html;
content_by_lua 'ngx.say("<p>hello, world</p>")';
}
运行后,效果如下图 localhost/hello

2、优化动态输出
上面的代码直接把lua代码写在nginx配置里面了,维护起来不方便。 我们把它拿出来一个单独的文件,放到E:\study\openresty\openresty-1.19.9.1-win64/lua目录下。
新建lua/hello2.lua
ngx.say("<p>hi,world</p>")
配置如下
location / {
default_type text/html;
content_by_lua_file lua/hello2.lua;
}
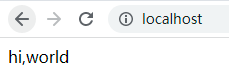
重启nginx nginx -s reload
验证: localhost
上面lua文件是固定的,如何动态指定lua文件名.
1) 增加配置
location ~ /lua/(.+) {
default_type text/html;
content_by_lua_file lua/$1.lua;
}
2、增加lua/one.lua
ngx.print("<p>hi,one</p>")
增加lua/tow.lua
ngx.print("<p>hi,two</p>")
3、验证
localhost/lua/one

localhost/lua/two

3、接收参数
1 ) lua/req.lua 文件
支持GET、POST两种参数
local _M = {}
-- 获取http get/post 请求参数
function _M.getArgs()
-- 获取http请求方式 GET or POST
local request_method = ngx.var.request_method
-- 这里是一个table,包含所有get请求参数
local args = ngx.req.get_uri_args()
-- 如果是post参数获取
if "POST" == request_method then
-- 先读取请求体
ngx.req.read_body()
-- 这里也是一个table,包含所有post请求参数
local postArgs = ngx.req.get_post_args()
if postArgs then
for k, v in pairs(postArgs) do
args[k] = v
end
end
end
return args
end
return _M
2)conf/nginx.conf 添加
http {
# 这里一定要指定package_path,否则会找不到引入的模块,然后会500
lua_package_path E:\study\openresty\openresty-1.19.9.1-win64\lua\?.lua;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location ~ /lua/(.+) {
default_type text/html;
content_by_lua_file lua/$1.lua;
}
}
3) 创建lua/test.lua 文件
-- 引入req模块
local req = require "req"
-- 获取请求参数列表
local args = req.getArgs();
-- 获取key为name的值
local name = args['name']
-- 如果不存在指定默认值
if name == nil or name == "" then
name = "default name zhang san"
end
-- 输出结果
ngx.say("<p>hello " .. name .. "!</p>")
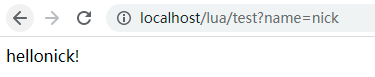
4)验证
http://localhost/lua/test?name=nick
作者:Work Hard Work Smart
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/linlf03/
欢迎任何形式的转载,未经作者同意,请保留此段声明!




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号