leetcode二叉树题目总结
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/detail/data-structure-binary-tree/
前序遍历(NLR)
- 代码总结
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
preOrder(root, res);
return res;
}
public void preOrder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null)
return;
res.add(root.val);
preOrder(root.left, res);
preOrder(root.right, res);
}
中序遍历(LNR)
- 代码总结
public void inOrder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null)
return;
inOrder(root.left, res);
res.add(root.val);
inOrder(root.right, res);
}
后序遍历( LRN )
- 代码总结
public void postOrder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null)
return;
postOrder(root.left, res);
postOrder(root.right, res);
res.add(root.val);
}
层次遍历
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
结果
[
[3],
[9,20],
[15,7]
]
关键代码
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
// 空树判断
if(root == null) return result;
// 返回的结果
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
// 队列
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 根节点入队
queue.add(root);
// 队列不为空则循环
while(queue.size()>0){
// 内层节点序列
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
// 遍历队列,把当前层的元素从队列取出来,将下一层放入队列
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
// 当前节点放入结果数组
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
temp.add(cur);
// 左节点入队
if(cur.left){
queue.add(cur.left);
}
// 右节点入队
if(cur.right){
queue.add(cur.right)
}
}
result.add(temp);
}
return result;
}
二叉树最大深度
递归解决:
- 递归出口 当前节点 == null 返回0
- 递归逻辑 Math.max(maxDept(root.left) +1, maxDepth(root.right) +1)
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left)+1, maxDepth(root.right)+1);
}
对称二叉树
递归法:
递归出口: 两个节点同时为空 return true 有一个为空 return false
递归逻辑: 返回当前节点值是否相等 && 递归节点1的左节点和节点2的右节点 && 递归节点2的右节点和节点1的左节点
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return isMirror(root, root);
}
public boolean isMirror(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
if (t1 == null && t2 == null) return true;
if (t1 == null || t2 == null) return false;
return (t1.val == t2.val)
&& isMirror(t1.left, t2.right)
&& isMirror(t1.right, t2.left);
}
}
路径总和
递归法: 递归出口: 当前节点==null判断 当前的 target是否为0,是则返回true,否返回false
递归逻辑: DFS所有节点,每次遍历到当前节点将target-cur.val
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum){
// 处理root为空的情况
if(root == null){
return false;
}
// 叶子节点判定当前路径是否可行
if(root.left==null && root.right==null){
return root.val == targetSum;
}
return hasPathSum(root.left,targetSum-root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right,targetSum-root.val);
}
}
中序后序构造二叉树
思路:
- 通过后序遍历确定每一个根节点
- 通过DFS递归,限定范围得到左右子树
- 递归出口 后序遍历的head > tail
- 通过找到当前节点在中序遍历中的位置限定范围
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
int len=inorder.length;
if(len==0)return null;
return dfs(inorder,postorder,0,len-1,0,len-1);
}
TreeNode dfs(int[] inorder, int[] postorder,int head1,int tail1, int head2,int tail2){
// 由于postOrder每次都会在tail-1 所以当只有一个元素则会返回
if(head2>tail2)return null;
int val=postorder[tail2];
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(val);
if(head2==tail2)return root;
int mid=0; //拆分点mid的位置是相对的,因为h1!=h2
while(inorder[head1+mid]!=val)mid++;
root.left=dfs(inorder, postorder, head1, head1+mid-1, head2, head2+mid-1);
root.right=dfs(inorder, postorder, head1+mid+1, tail1, head2+mid, tail2-1);
return root;
}
}
笔记:
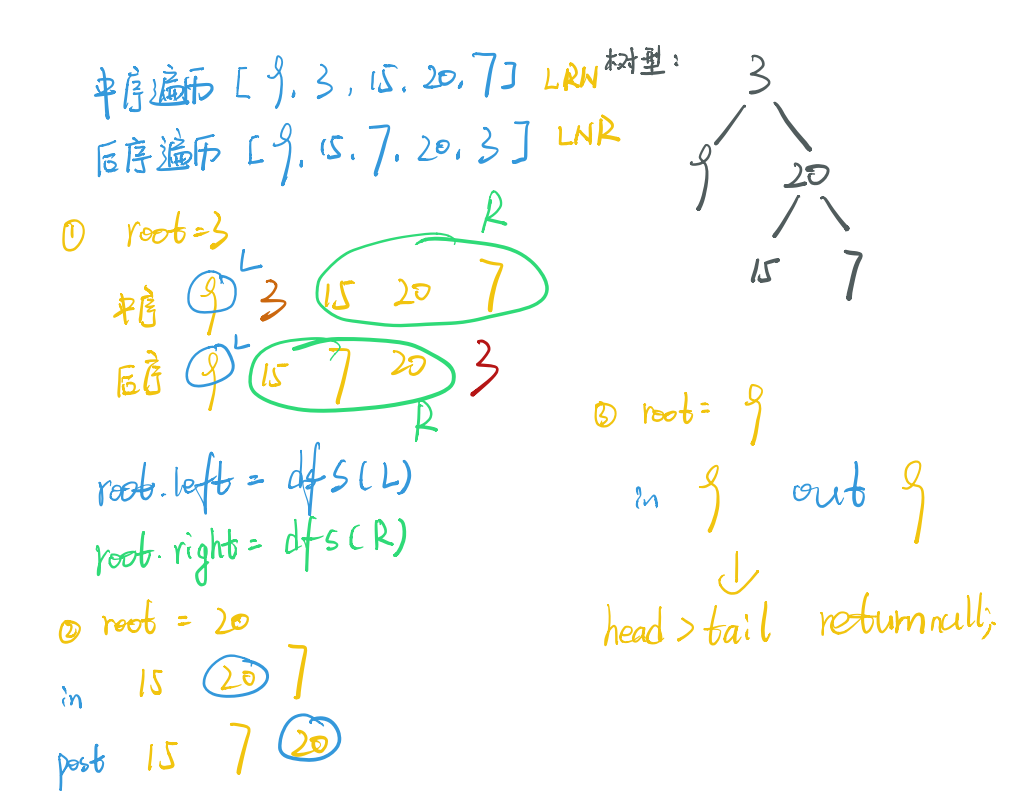
前序中序构造二叉树类似
和中序前序类似, 只是每次的限定范围不同
二叉树填充右侧指针
递归法: 限定完美二叉树
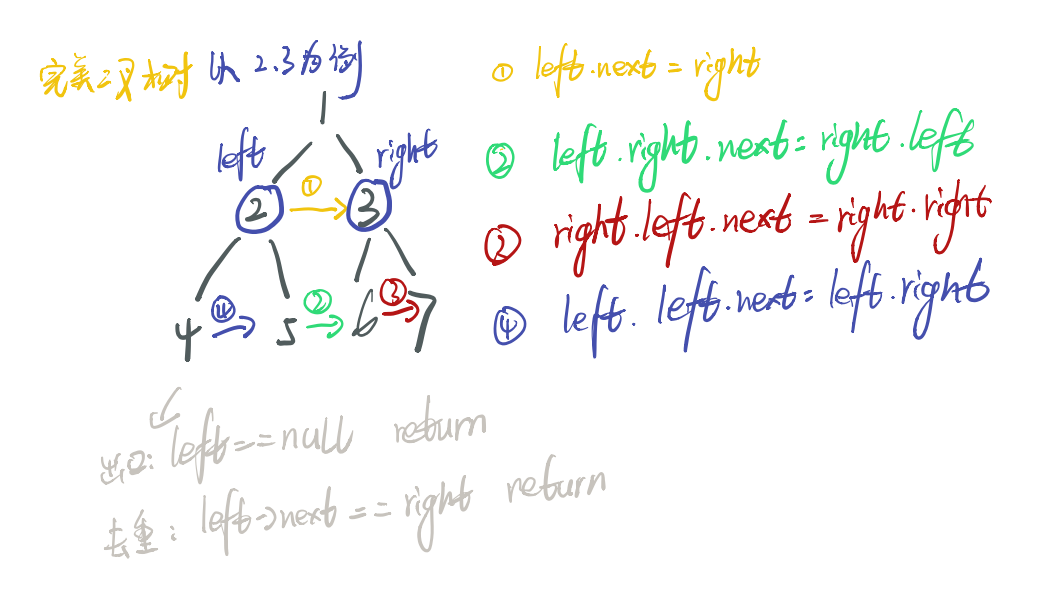
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root){
if(root!=null) dfs(root.left, root.right);
return root;
}
void dfs(Node left, Node right){
if(left ==null || left.next == right) return;
left-> next = right;
dfs(left.left, left.right);
dfs(left.right, right.left);
dfs(right.left, right.right);
}
}
一般情况
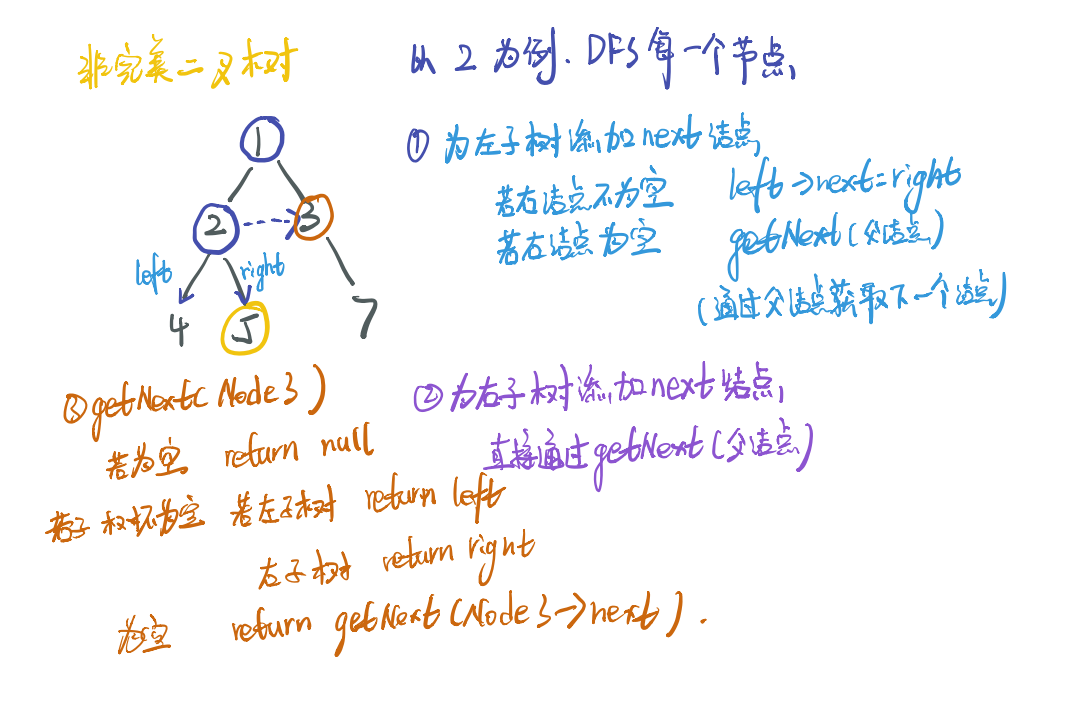
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node* next;
Node() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}
Node(int _val) : val(_val), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {}
Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right, Node* _next)
: val(_val), left(_left), right(_right), next(_next) {}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
// 空树判断
if( root == nullptr ) return nullptr;
// 左树为空
if( root -> left != nullptr ) {
if( root -> right != nullptr){
// 最普遍的情况
root -> left -> next = root -> right;
}
else
// 父节点的next的第一个子节点作为next
root -> left -> next = getNext(root -> next);
}
// 右节点不为空
if( root->right != nullptr){
// next
root -> right -> next = getNext( root-> next );
}
// 先判断右节点
connect(root->right);
connect(root->left);
return root;
}
// 通过父节点获取子节点的next结点
Node* getNext(Node* uncle){
if( uncle == nullptr ) return nullptr;
if( uncle -> left != nullptr) return uncle->left;
if( uncle -> right != nullptr ) return uncle->right;
return getNext(uncle->next);
}
};
最近公共祖先
整体思路:
-
通过BFS得到每个节点和其父节点的Map
-
通过Set,保存p到根节点的路径
-
在通过获得q到根节点的路径,判断第一个包含在原来的set的节点为最先公共祖先
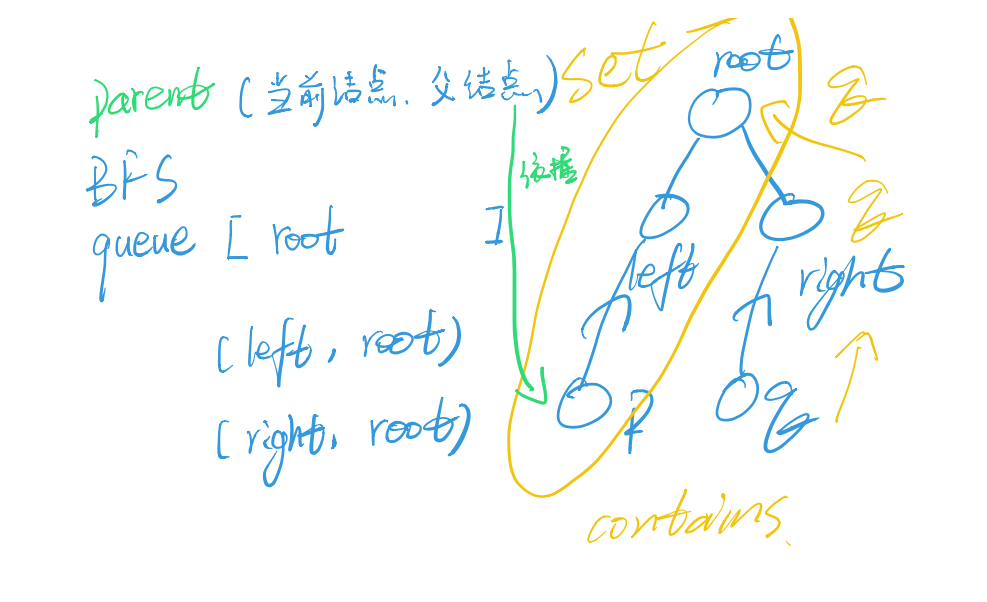
代码总结:
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
//记录遍历到的每个节点的父节点。
Map<TreeNode, TreeNode> parent = new HashMap<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//根节点没有父节点,所以为空
parent.put(root, null);
//队列入队
queue.add(root);
//直到两个节点都找到为止。
while (!parent.containsKey(p) || !parent.containsKey(q)) {
//队列是一边进一边出,这里poll方法是出队,
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
//左子节点不为空,记录下他的父节点
parent.put(node.left, node);
//左子节点不为空,把它加入到队列中
queue.add(node.left);
}
//右节点同上
if (node.right != null) {
parent.put(node.right, node);
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
Set<TreeNode> ancestors = new HashSet<>();
//记录下p和他的祖先节点,从p节点开始一直到根节点。
while (p != null) {
ancestors.add(p);
p = parent.get(p);
}
//查看p和他的祖先节点是否包含q节点,如果不包含再看是否包含q的父节点……
while (!ancestors.contains(q))
q = parent.get(q);
return q;
}
二叉树的序列化和反序列化
分析思路:
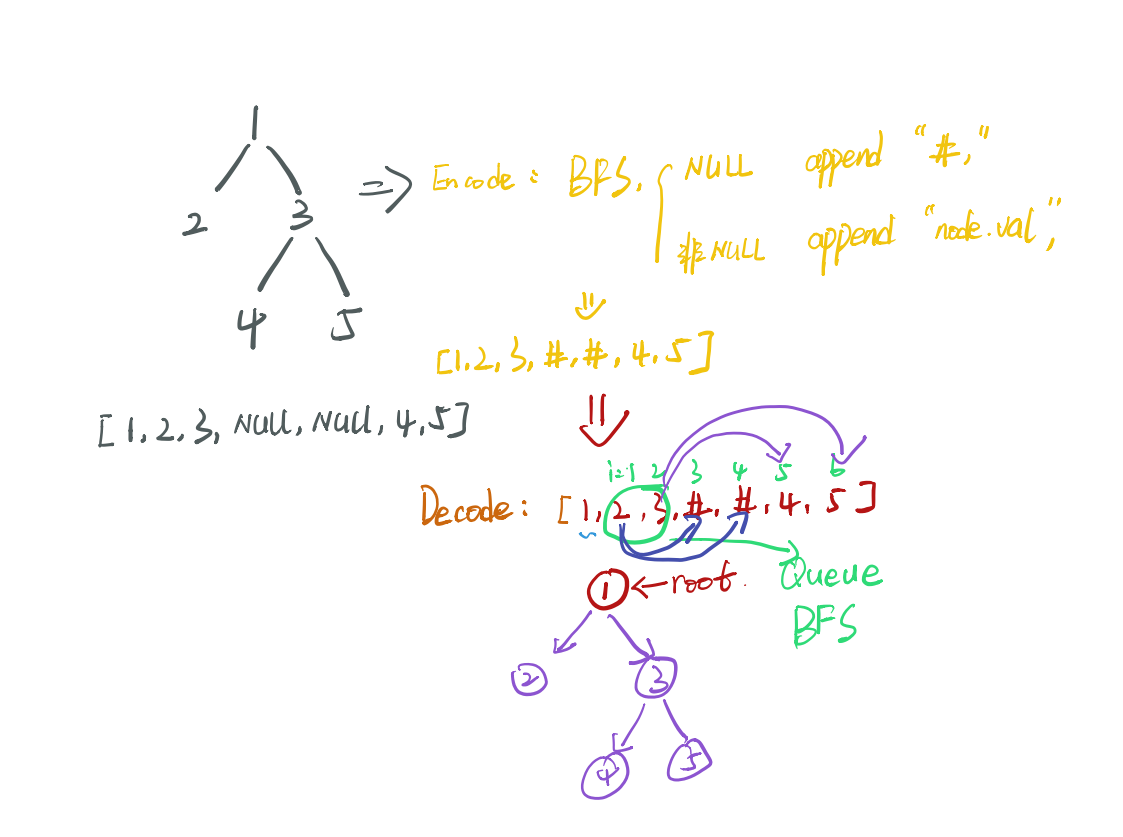
代码总结:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Codec {
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return "#";
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(node == null){
res.append("#,");
continue;
}
res.append(node.val + ",");
queue.add(node.left);
queue.add(node.right);
}
return res.toString();
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
if(data == "#") return null;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
String[] values = data.split(",");
// 第一个节点
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(values[0]));
queue.add(node);
for(int i =1; i < values.length; i++){
TreeNode treeNode = queue.poll();
if(!"#".equals(values[i])){
treeNode.left = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(values[i]));
queue.add(treeNode.left);
}
if(!"#".equals(values[++i])){
treeNode.right = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(values[i]));
queue.add(treeNode.right);
}
}
return node;
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号