Map (C++)
map 类
用于存储和检索集合中的数据,此集合中的每个元素均为包含数据值和排序键的元素对。 键的值是唯一的,用于自动排序数据。
可以直接更改映射中的元素值。 键值是常量,不能更改。 必须先删除与旧元素关联的键值,才能为新元素插入新键值。
|
构造特定大小的列表、包含具有特定值的元素的列表、包含特定 allocator 的列表或作为其他某个映射的副本的列表。 |
Map是c++的一个标准容器,她提供了很好一对一的关系,在一些程序中建立一个map可以起到事半功倍的效果,总结了一些map基本简单实用的操作! 1. map最基本的构造函数; map<string , int >mapstring; map<int ,string >mapint; map<sring, char>mapstring; map< char ,string>mapchar; map<char ,int>mapchar; map<int ,char >mapint;
2. map添加数据;
map<int ,string> maplive; 1.maplive.insert(pair<int,string>(102,"aclive")); 2.maplive.insert(map<int,string>::value_type(321,"hai")); 3, maplive[112]="April";//map中最简单最常用的插入添加! 3,map中元素的查找:
find()函数返回一个迭代器指向键值为key的元素,如果没找到就返回指向map尾部的迭代器。
map<int ,string >::iterator l_it;; l_it=maplive.find(112); if(l_it==maplive.end()) cout<<"we do not find 112"<<endl; else cout<<"wo find 112"<<endl; 4,map中元素的删除: 如果删除112; map<int ,string >::iterator l_it;; l_it=maplive.find(112); if(l_it==maplive.end()) cout<<"we do not find 112"<<endl; else maplive.erase(l_it); //delete 112; 5,map中 swap的用法: Map中的swap不是一个容器中的元素交换,而是两个容器交换; For example: #include <map> #include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( ) { map <int, int> m1, m2, m3; map <int, int>::iterator m1_Iter;
m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 1, 10 ) ); m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 2, 20 ) ); m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 3, 30 ) ); m2.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 10, 100 ) ); m2.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 20, 200 ) ); m3.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 30, 300 ) );
cout << "The original map m1 is:"; for ( m1_Iter = m1.begin( ); m1_Iter != m1.end( ); m1_Iter++ ) cout << " " << m1_Iter->second; cout << "." << endl;
// This is the member function version of swap //m2 is said to be the argument map; m1 the target map m1.swap( m2 );
cout << "After swapping with m2, map m1 is:"; for ( m1_Iter = m1.begin( ); m1_Iter != m1.end( ); m1_Iter++ ) cout << " " << m1_Iter -> second; cout << "." << endl; cout << "After swapping with m2, map m2 is:"; for ( m1_Iter = m2.begin( ); m1_Iter != m2.end( ); m1_Iter++ ) cout << " " << m1_Iter -> second; cout << "." << endl; // This is the specialized template version of swap swap( m1, m3 );
cout << "After swapping with m3, map m1 is:"; for ( m1_Iter = m1.begin( ); m1_Iter != m1.end( ); m1_Iter++ ) cout << " " << m1_Iter -> second; cout << "." << endl; }
6.map的sort问题: Map中的元素是自动按key升序排序,所以不能对map用sort函数: For example: #include <map> #include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( ) { map <int, int> m1; map <int, int>::iterator m1_Iter;
m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 1, 20 ) ); m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 4, 40 ) ); m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 3, 60 ) ); m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 2, 50 ) ); m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 6, 40 ) ); m1.insert ( pair <int, int> ( 7, 30 ) );
cout << "The original map m1 is:"<<endl; for ( m1_Iter = m1.begin( ); m1_Iter != m1.end( ); m1_Iter++ ) cout << m1_Iter->first<<" "<<m1_Iter->second<<endl; } The original map m1 is: 1 20 2 50 3 60 4 40 6 40 7 30 请按任意键继续. . .
7, map的基本操作函数: C++ Maps是一种关联式容器,包含“关键字/值”对 begin() 返回指向map头部的迭代器 clear() 删除所有元素 count() 返回指定元素出现的次数 empty() 如果map为空则返回true end() 返回指向map末尾的迭代器 equal_range() 返回特殊条目的迭代器对 erase() 删除一个元素 find() 查找一个元素 get_allocator() 返回map的配置器 insert() 插入元素 key_comp() 返回比较元素key的函数 lower_bound() 返回键值>=给定元素的第一个位置 max_size() 返回可以容纳的最大元素个数 rbegin() 返回一个指向map尾部的逆向迭代器 rend() 返回一个指向map头部的逆向迭代器 size() 返回map中元素的个数 swap() 交换两个map upper_bound() 返回键值>给定元素的第一个位置 value_comp() 返回比较元素value的函数
map<Key, Data, Compare, Alloc>
map是一种关联容器,存储相结合形成的一个关键值和映射值的元素。Map 是一种Pair Associative Container,意味着它的值类型为 pair<const Key, Data>. 而且也是 Unique Associative Container, 也就是任何两个元素没有相同的key值。
map具有重要的属性,就是在map对象中插入一个新元素不指向现有元素的迭代器失效。从map上删除一个元素,也没有任何迭代器失效,除非,当然,实际上指向正在被删除的元素的迭代器。
1、例子
- struct ltstr
- {
- bool operator()(const char* s1, const char* s2) const
- {
- return strcmp(s1, s2) < 0;
- }
- };
- int main()
- {
- map<const char*, int, ltstr> months;
- months["january"] = 31;
- months["february"] = 28;
- months["march"] = 31;
- months["april"] = 30;
- months["may"] = 31;
- months["june"] = 30;
- months["july"] = 31;
- months["august"] = 31;
- months["september"] = 30;
- months["october"] = 31;
- months["november"] = 30;
- months["december"] = 31;
- cout << "june -> " << months["june"] << endl;
- map<const char*, int, ltstr>::iterator cur = months.find("june");
- map<const char*, int, ltstr>::iterator prev = cur;
- map<const char*, int, ltstr>::iterator next = cur;
- ++next;
- --prev;
- cout << "Previous (in alphabetical order) is " << (*prev).first << endl;
- cout << "Next (in alphabetical order) is " << (*next).first << endl;
- }
2、定义形式
- template < class Key, class T, class Compare = less<Key>,
- class Allocator = allocator<pair<const Key,T> > > class map;
3、模板参数具有以下涵义: key:关键值的类型。在map对象中的每个元素是通过该关键值唯一确定元素的。 T:映射值的类型。在map中的每个元素是用来储存一些数据作为其映射值。 compare:Comparison类:A类键的类型,它有两个参数,并返回一个bool。表达comp(A,B),comp是这比较类A和B是关键值的对象,应返回true,如果是在早先的立场比B放置在一个严格弱排序操作。这可以是一个类实现一个函数调用运算符或一个函数的指针(见一个例子构造)。默认的对于<KEY>,返回申请小于操作符相同的默认值(A <B)。 Map对象使用这个表达式来确定在容器中元素的位置。以下这个规则在任何时候都排列在map容器中的所有元素。 Allocator:用于定义存储分配模型分配器对象的类型。默认情况下,分配器类模板,它定义了最简单的内存分配模式,是值独立的
- map<Key,T>::iterator it;
- (*it).first; // 指向key值(of type Key)
- (*it).second; // 映射的值(of type T)
- (*it); // the "element value" (of type pair<const Key,T>)
也可以如下表达:
- it->first; // same as (*it).first (the key value)
- it->second; // same as (*it).second (the mapped value)
4、成员变量和成员函数
| Member | Where defined | Description |
|---|---|---|
| key_type | Associative Container | map中的key类型 |
| data_type | Pair Associative Container | key关联的值类型 |
| value_type | Pair Associative Container | 对象类型, pair<const key_type, data_type>,存储在map中 |
| key_compare | Sorted Associative Container | Function object 通过顺序比较 |
| value_compare | Sorted Associative Container | Function object that compares two values for ordering. |
| pointer | Container | Pointer to T. |
| reference | Container | Reference to T |
| const_reference | Container | Const reference to T |
| size_type | Container | An unsigned integral type. |
| difference_type | Container | A signed integral type. |
| iterator | Container | Iterator used to iterate through a map. [1] |
| const_iterator | Container | Const iterator used to iterate through a map. |
| reverse_iterator | Reversible Container | Iterator used to iterate backwards through a map.[1] |
| const_reverse_iterator | Reversible Container | Const iterator used to iterate backwards through amap. |
| iterator begin() | Container | Returns an iterator pointing to the beginning of the map. |
| iterator end() | Container | Returns an iterator pointing to the end of themap. |
| const_iterator begin() const | Container | Returns a const_iterator pointing to the beginning of themap. |
| const_iterator end() const | Container | Returns a const_iterator pointing to the end of the map. |
| reverse_iterator rbegin() | Reversible Container | Returns a reverse_iterator pointing to the beginning of the reversed map. |
| reverse_iterator rend() | Reversible Container | Returns a reverse_iterator pointing to the end of the reversed map. |
| const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const | Reversible Container | Returns a const_reverse_iterator pointing to the beginning of the reversed map. |
| const_reverse_iterator rend() const | Reversible Container | Returns a const_reverse_iterator pointing to the end of the reversed map. |
| size_type size() const | Container | Returns the size of the map. |
| size_type max_size() const | Container | Returns the largest possible size of the map. |
| bool empty() const | Container | true if the map's size is 0. |
| key_compare key_comp() const | Sorted Associative Container | Returns the key_compare object used by the map. |
| value_compare value_comp() const | Sorted Associative Container | Returns the value_compare object used by themap. |
| map() | Container | Creates an empty map. |
| map(const key_compare& comp) | Sorted Associative Container | Creates an empty map, using comp as thekey_compare object. |
template <class InputIterator> map(InputIterator f, InputIterator l) |
Unique Sorted Associative Container | Creates a map with a copy of a range. |
template <class InputIterator> map(InputIterator f, InputIterator l, const key_compare& comp) |
Unique Sorted Associative Container | Creates a map with a copy of a range, using compas thekey_compare object. |
| map(const map&) | Container | The copy constructor. |
| map& operator=(const map&) | Container | The assignment operator |
| void swap(map&) | Container | Swaps the contents of two maps. |
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const value_type& x) |
Unique Associative Container | Inserts x into the map. |
iterator insert(iterator pos,
const value_type& x)
|
Unique Sorted Associative Container | Inserts x into the map, using pos as a hint to where it will be inserted. |
template <class InputIterator> void insert(InputIterator, InputIterator) [2] |
Unique Sorted Associative Container | Inserts a range into the map. |
| void erase(iterator pos) | Associative Container | Erases the element pointed to by pos. |
| size_type erase(const key_type& k) | Associative Container | Erases the element whose key is k. |
| void erase(iterator first, iterator last) | Associative Container | Erases all elements in a range. |
| void clear() | Associative Container | Erases all of the elements. |
| iterator find(const key_type& k) | Associative Container | Finds an element whose key is k. |
| const_iterator find(const key_type& k) const | Associative Container | Finds an element whose key is k. |
| size_type count(const key_type& k) | Unique Associative Container | Counts the number of elements whose key is k. |
| iterator lower_bound(const key_type& k) | Sorted Associative Container | Finds the first element whose key is not less thank. |
| const_iterator lower_bound(const key_type& k) const | Sorted Associative Container | Finds the first element whose key is not less thank. |
| iterator upper_bound(const key_type& k) | Sorted Associative Container | Finds the first element whose key greater than k. |
| const_iterator upper_bound(const key_type& k) const | Sorted Associative Container | Finds the first element whose key greater than k. |
pair<iterator, iterator> equal_range(const key_type& k) |
Sorted Associative Container | Finds a range containing all elements whose key is k. |
pair<const_iterator, const_iterator> equal_range(const key_type& k) const |
Sorted Associative Container | Finds a range containing all elements whose key is k. |
data_type& operator[](const key_type& k) [3] |
map | See below. |
bool operator==(const map&,
const map&)
|
Forward Container | Tests two maps for equality. This is a global function, not a member function. |
bool operator<(const map&,
const map&)
|
Forward Container | Lexicographical comparison. This is a global function, not a member function. |
- 下面展示了常用的一些方法。<p>// stu_map.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
- //
- #include "stdafx.h"
- #include <iostream>
- #include <map>
- using namespace std;
- bool fncomp(char lhs,char rhs)
- {
- return lhs<rhs;
- }
- struct classcomp
- {
- bool operator()(const char& lhs,const char& rhs)
- {
- return lhs<rhs;
- }
- };
- int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
- {
- map<char,int> mymap;
- mymap['a']=10;
- mymap['b']=60;
- mymap['c']=30;
- mymap['d']=90;
- mymap['e']=50;
- map<char,int> second(mymap);
- map<char,int> third(mymap.begin(),mymap.end());
- map<char,int,classcomp> fourth;
- bool(*fn_pt)(char,char)=fncomp;
- map<char,int,bool(*)(char,char)> fifth(fn_pt);
- map<char,int>::key_compare key_comp;
- map<char,int>::iterator it;
- it=mymap.begin();
- for (it;it!=mymap.end();it++)
- {
- cout<<it->first<<":"<<it->second<<endl;
- }
- cout<<"================================="<<endl;
- second.clear();
- second['a']=1002;
- second['b']=10023;
- while (!second.empty())
- {
- cout << second.begin()->first << " => ";
- cout << second.begin()->second << endl;
- second.erase(second.begin());
- }
- cout<<"================================="<<endl;
- mymap.insert(pair<char,int>('f',100) );
- mymap.insert(pair<char,int>('g',200) );
- cout<<"f => " <<mymap.find('f')->second<<endl;
- cout<<"g => " <<mymap.find('g')->second<<endl;
- cout<<"================================="<<endl;
- key_comp=mymap.key_comp();
- cout << "mymap contains:\n";
- char highest=mymap.rbegin()->first; // key value of last element
- it=mymap.begin();
- do {
- cout << (*it).first << " => " << (*it).second << endl;
- } while ( key_comp((*it++).first, highest) );
- cout << endl;
- return 0;
- }
- </p>
运行结果: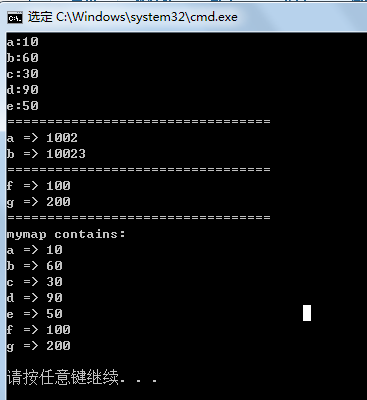


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号