Threadlocal 特性
1.线程间共享变量:一个线程在设置threadlocal值之后,当前线程无论在哪里都可以从设置的threadlocal中获取值,解决值传递的问题。
2.不同线程间隔离:线程a在设置threadlocal值之后,线程b是无法获取线程a设置的值,解决了线程安全的问题。
Threadlocal 简单使用
public class ThreadLocalTest {
private static ThreadLocal<String> fruit = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void setFruit(String param) {
fruit.set(param);
}
public static String getFruit() {
return fruit.get();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread1 thread1 = new MyThread1();
MyThread2 thread2 = new MyThread2();
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
public static class MyThread1 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
setFruit("apple");
System.out.println("MyThread1 线程设置的水果:apple");
sleep(3000);
System.out.println("MyThread1 线程获取的水果:"+getFruit());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static class MyThread2 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
sleep(1000);
setFruit("orange");
System.out.println("MyThread2 线程设置的水果:orange");
sleep(1000);
System.out.println("MyThread2 线程获取的水果:"+getFruit());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
程序运行打印出结果
MyThread1 线程设置的水果:apple MyThread2 线程设置的水果:orange MyThread2 线程获取的水果:orange MyThread1 线程获取的水果:apple
由此可见之前叙述的两种特性。
深入threadlocal学习,拥有这两种特性的原因。
ThreadLocal.class set方法
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap map = this.getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
map.set(this, value);
} else {
this.createMap(t, value);
}
}
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
在使用set方法时,会获取到当前thread对象的引用,而this.getMap方法则是从当前对象中获取threadLocals参数,而此参数的类型为ThreadLocalMap,通过<key,value>的方式存储数据
此时key:当前threadlocal的引用。value则是要存储的数据
1.当前map 为空时,调用 this.createMap(t, value)
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
看下ThreadLocalMap
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
size = 1;
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
2.map中有数据,看下 map.set(this, value) 方法里具体操作。
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
综上两个方法可以看出threadlocal中处理key ,value的是用Entry 去接收的。
看下Entry.class
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
Entry是继承WeakReference,说明Entry 这边是一个虚引用,而虚引用在垃圾回收器线程扫描它所管辖的内存区域的过程中,一旦发现了只具有弱引用的对象,不管当前内存空间足够与否,都会回收它的内存。
get方法
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
remove方法
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
值得注意的是,在结合set,get 使用后,需要结合remove方法讲堆内存中的对象释放掉,不然会造成内存泄露。
下面看下内存图
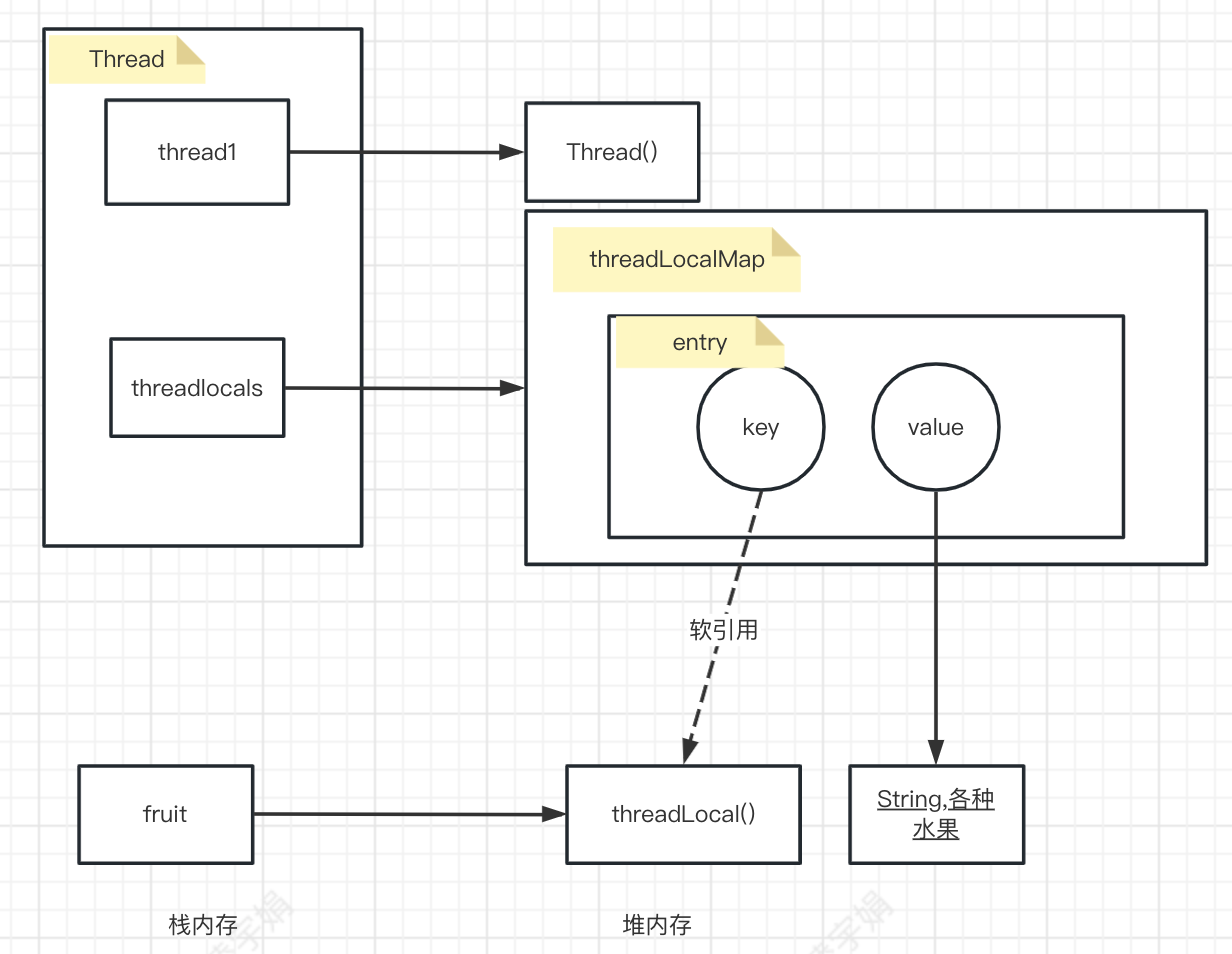
当前线程执行较长时间或者使用线程池时,由于线程一直都有引用时,fruit引用置null,此时threadLocal只有弱引用,此时会被gc回收,而回收之后key的值为null,而此时无法通过key访问value,此时gc无法回收value,造成内存泄漏。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号