12.6.0 头文件
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
12.6.1 定义ResNet-18网络模型
# 定义ResNet-18网络模型
def resnet18(num_classes, in_channels=1):
"""稍加修改的ResNet-18模型"""
def resnet_block(in_channels, out_channels, num_residuals,first_block=False):
blk = []
for i in range(num_residuals):
if i == 0 and not first_block:
blk.append(d2l.Residual(in_channels, out_channels,use_1x1conv=True, strides=2))
else:
blk.append(d2l.Residual(out_channels, out_channels))
return nn.Sequential(*blk)
# 该模型使用了更小的卷积核、步长和填充,而且删除了最大汇聚层
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU())
net.add_module("resnet_block1", resnet_block(64, 64, 2, first_block=True))
net.add_module("resnet_block2", resnet_block(64, 128, 2))
net.add_module("resnet_block3", resnet_block(128, 256, 2))
net.add_module("resnet_block4", resnet_block(256, 512, 2))
net.add_module("global_avg_pool", nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1,1)))
net.add_module("fc", nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(),nn.Linear(512, num_classes)))
return net
net = resnet18(10)
# 获取GPU列表
devices = d2l.try_all_gpus()
12.6.2 利用多GPU来训练网络模型
def train(net, num_gpus, batch_size, lr):
# 下载fashion_mnist,并对数据集进行打乱和按批量大小进行切割的操作,得到可迭代的训练集和测试集(训练集和测试集的形式都为(特征数据集合,数字标签集合))
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
# 获取要求的GPU列表
devices = [d2l.try_gpu(i) for i in range(num_gpus)]
# 初始化全连接层和卷积层的权重
def init_weights(m):
if type(m) in [nn.Linear, nn.Conv2d]:
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.01)
net.apply(init_weights)
# 在多个GPU上设置模型
# 把模型参数拷贝到每个GPU上,把样本和标签均分到多个GPU上
net = nn.DataParallel(net, device_ids=devices)
# 定义梯度下降优化器
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr)
# 定义交叉熵损失函数
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 定义定时器和训练轮数
timer, num_epochs = d2l.Timer(), 10
# 定义动画,用来显示训练图像
animator = d2l.Animator('epoch', 'test acc', xlim=[1, num_epochs])
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# 开始一轮的训练过程
net.train()
timer.start()
for X, y in train_iter:
# 开始一个批量的训练过程
trainer.zero_grad()
X, y = X.to(devices[0]), y.to(devices[0])
# 更新模型参数
l = loss(net(X), y)
l.backward()
trainer.step()
timer.stop()
# 经过一轮的训练,记录下此时更新参数后的网络模型在测试集上的平均准确率
animator.add(epoch + 1, (d2l.evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, test_iter),))
# 输出最终的模型在测试集上的准确率、每轮训练的平均时间以及用到的GPU
print(f'测试精度:{animator.Y[0][-1]:.2f},{timer.avg():.1f}秒/轮,'f'在{str(devices)}')
12.6.3 使用单GPU和使用多GPU的训练结果对比
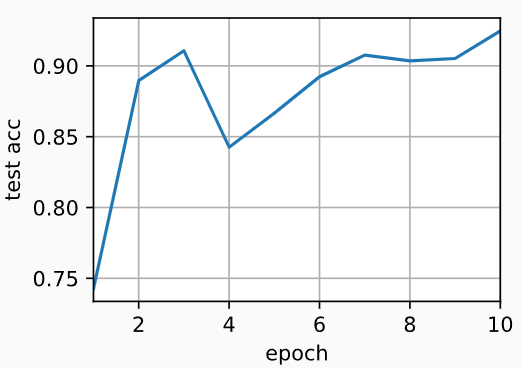
(1)单GPU
train(net, num_gpus=1, batch_size=256, lr=0.1)
# 输出:
# 测试精度:0.92,13.7秒/轮,在[device(type='cuda', index=0)]
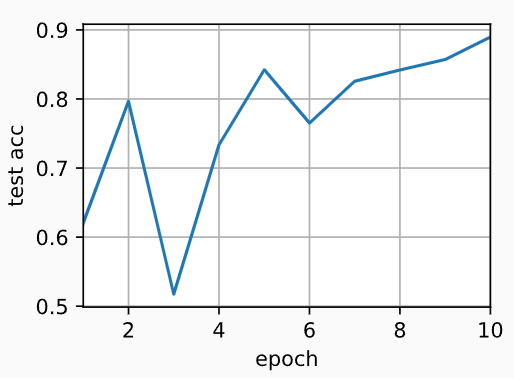
(2)双GPU
train(net, num_gpus=2, batch_size=512, lr=0.2)
# 输出:
# 测试精度:0.89,8.4秒/轮,在[device(type='cuda', index=0), device(type='cuda', index=1)]
本小节完整代码如下
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
# ------------------------------定义ResNet-18网络模型------------------------------------
# 定义ResNet-18网络模型
def resnet18(num_classes, in_channels=1):
"""稍加修改的ResNet-18模型"""
def resnet_block(in_channels, out_channels, num_residuals,first_block=False):
blk = []
for i in range(num_residuals):
if i == 0 and not first_block:
blk.append(d2l.Residual(in_channels, out_channels,use_1x1conv=True, strides=2))
else:
blk.append(d2l.Residual(out_channels, out_channels))
return nn.Sequential(*blk)
# 该模型使用了更小的卷积核、步长和填充,而且删除了最大汇聚层
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU())
net.add_module("resnet_block1", resnet_block(64, 64, 2, first_block=True))
net.add_module("resnet_block2", resnet_block(64, 128, 2))
net.add_module("resnet_block3", resnet_block(128, 256, 2))
net.add_module("resnet_block4", resnet_block(256, 512, 2))
net.add_module("global_avg_pool", nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1,1)))
net.add_module("fc", nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(),nn.Linear(512, num_classes)))
return net
net = resnet18(10)
# 获取GPU列表
devices = d2l.try_all_gpus()
# ------------------------------利用多GPU来训练网络模型------------------------------------
def train(net, num_gpus, batch_size, lr):
# 下载fashion_mnist,并对数据集进行打乱和按批量大小进行切割的操作,得到可迭代的训练集和测试集(训练集和测试集的形式都为(特征数据集合,数字标签集合))
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
# 获取要求的GPU列表
devices = [d2l.try_gpu(i) for i in range(num_gpus)]
# 初始化全连接层和卷积层的权重
def init_weights(m):
if type(m) in [nn.Linear, nn.Conv2d]:
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.01)
net.apply(init_weights)
# 在多个GPU上设置模型
# 把模型参数拷贝到每个GPU上,把样本和标签均分到多个GPU上
net = nn.DataParallel(net, device_ids=devices)
# 定义梯度下降优化器
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr)
# 定义交叉熵损失函数
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 定义定时器和训练轮数
timer, num_epochs = d2l.Timer(), 10
# 定义动画,用来显示训练图像
animator = d2l.Animator('epoch', 'test acc', xlim=[1, num_epochs])
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# 开始一轮的训练过程
net.train()
timer.start()
for X, y in train_iter:
# 开始一个批量的训练过程
trainer.zero_grad()
X, y = X.to(devices[0]), y.to(devices[0])
# 更新模型参数
l = loss(net(X), y)
l.backward()
trainer.step()
timer.stop()
# 经过一轮的训练,记录下此时更新参数后的网络模型在测试集上的平均准确率
animator.add(epoch + 1, (d2l.evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, test_iter),))
# 输出最终的模型在测试集上的准确率、每轮训练的平均时间以及用到的GPU
print(f'测试精度:{animator.Y[0][-1]:.2f},{timer.avg():.1f}秒/轮,'f'在{str(devices)}')
# ------------------------------使用单GPU和使用多GPU的训练结果对比------------------------------------
train(net, num_gpus=1, batch_size=256, lr=0.1)
# 输出:
# 测试精度:0.92,13.7秒/轮,在[device(type='cuda', index=0)]
train(net, num_gpus=2, batch_size=512, lr=0.2)
# 输出:
# 测试精度:0.89,8.4秒/轮,在[device(type='cuda', index=0), device(type='cuda', index=1)]



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号