数据结构与算法系列—队列
队列的特点
先进先出
顺序队列
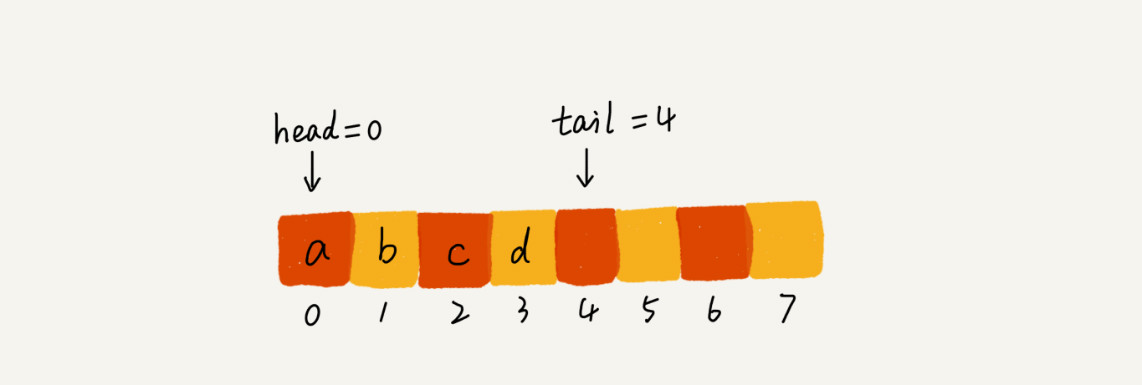
代码实现
package com.datastructure.queue;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* 数组实现顺序队列
*
* @Auther: dlm
* @Date: 2020/4/7 19:03
*/
public class ArrayQueue<T> {
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 1 << 3;
private int capacity; //队列大小
private T[] data; //存储数据
private int head; //队头下标
private int tail; //队尾下标
public ArrayQueue(int capacity){
this.capacity = capacity;
this.data = (T[])new Objects[capacity];
}
public ArrayQueue(){
this(DEFAULT_CAPACITY);
}
//入队
public boolean enqueue(T value){
//队满
if(tail == capacity)
return false;
//将元素放到队尾,之后tail向后移动一位
data[tail++] = value;
return true;
}
//出队
public T dequeue(){
//队空
if(head == tail)
return null;
//队头元素出队,之后head向后移动一位
T value = data[head++];
return value;
}
}
上面的代码中,其实还有一个问题,那就是不断的入队和出队会出现 tail = capacity 。
这时即使队列中还有空间,那么元素也不能入队了。这样会造成空间的浪费。
因此为了解决这个问题,当 tail = capacity 且 head != 0 时,
当再次发生入队操作时,先将所有元素整体向右移动。如下图:
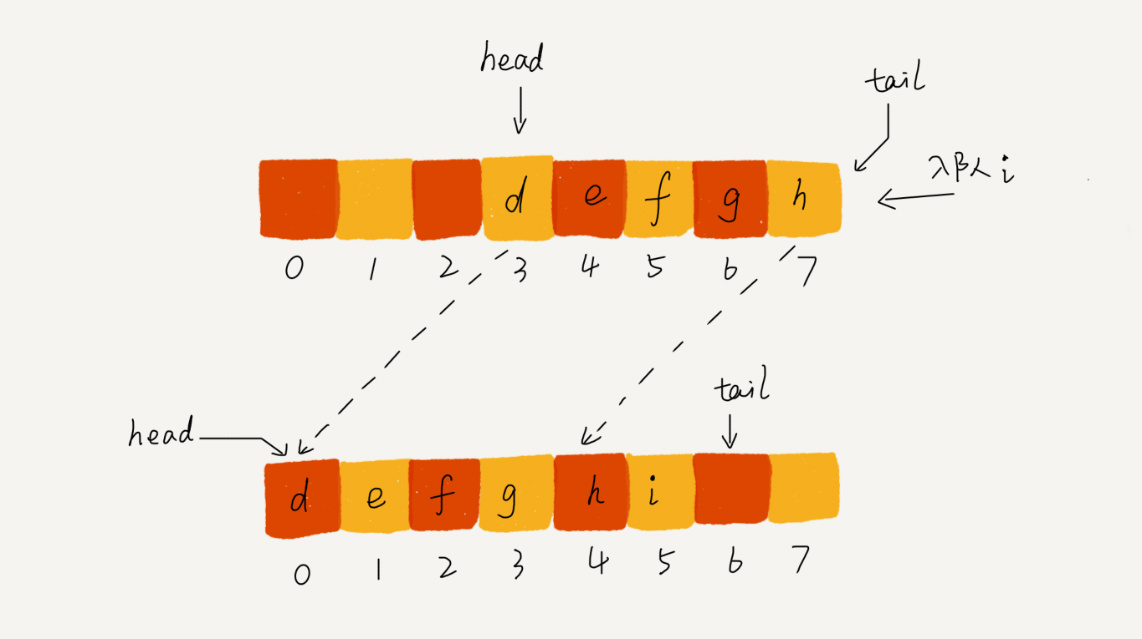
入队代码优化
//入队优化
public boolean enqueue_enhance(T value){
if(tail == capacity){
if(head == 0) // tail == capacity && head == 0 表示队满
return false;
//整体移动元素
for(int i = head;i < tail;i++){
data[i - head] = data[i];
}
//重置 head 和 tail
tail = tail - head;
head = 0;
}
//将元素放到队尾,之后tail向后移动一位
data[tail++] = value;
return true;
}
链式队列
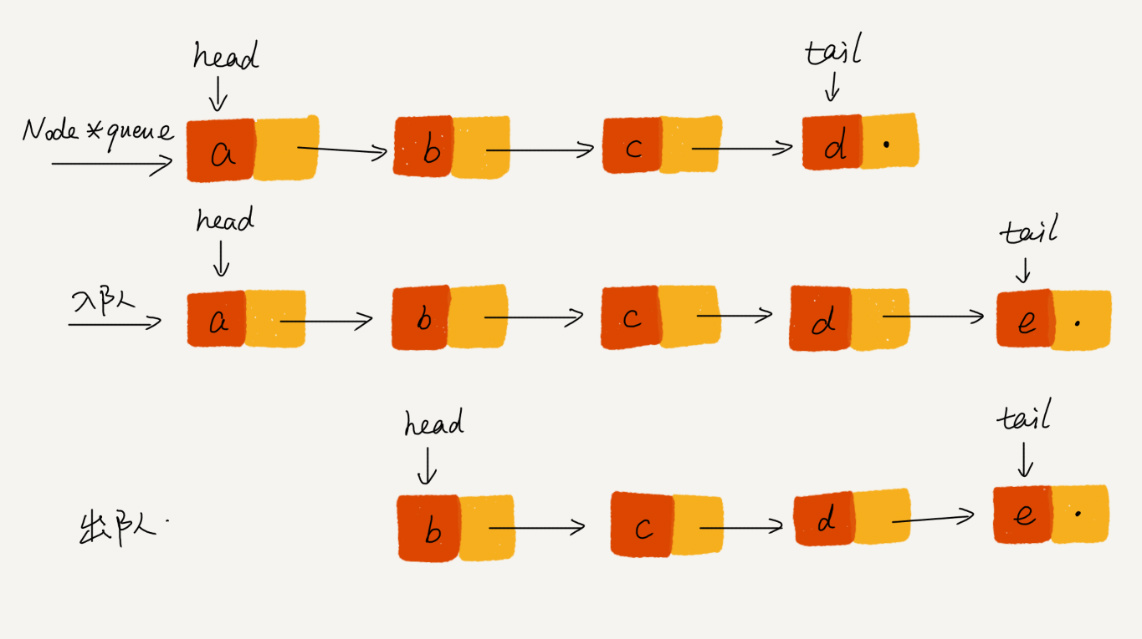
代码实现
package com.datastructure.queue;
/**
* 链表实现链式队列
*
* @Auther: dlm
* @Date: 2020/4/7 19:44
*/
public class LinkedListQueue<T> {
private Node head; //队头指针
private Node tail; //队尾指针
//入队
public boolean enqueue(T value){
Node newNode = new Node(value,null);
if(tail == null){ //队空
tail = newNode;
head = newNode;
}else {
tail.next = newNode;
tail = tail.next;
}
return true;
}
//出队
public T dequeue(){
//队空
if(head == null)
return null;
T value = (T)head.data;
head = head.next;
if(head == null){
tail = null;
}
return value;
}
public class Node<T>{
private T data;
private Node next;
public Node(T data,Node next){
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
public T getData(){
return this.data;
}
}
}
循环队列
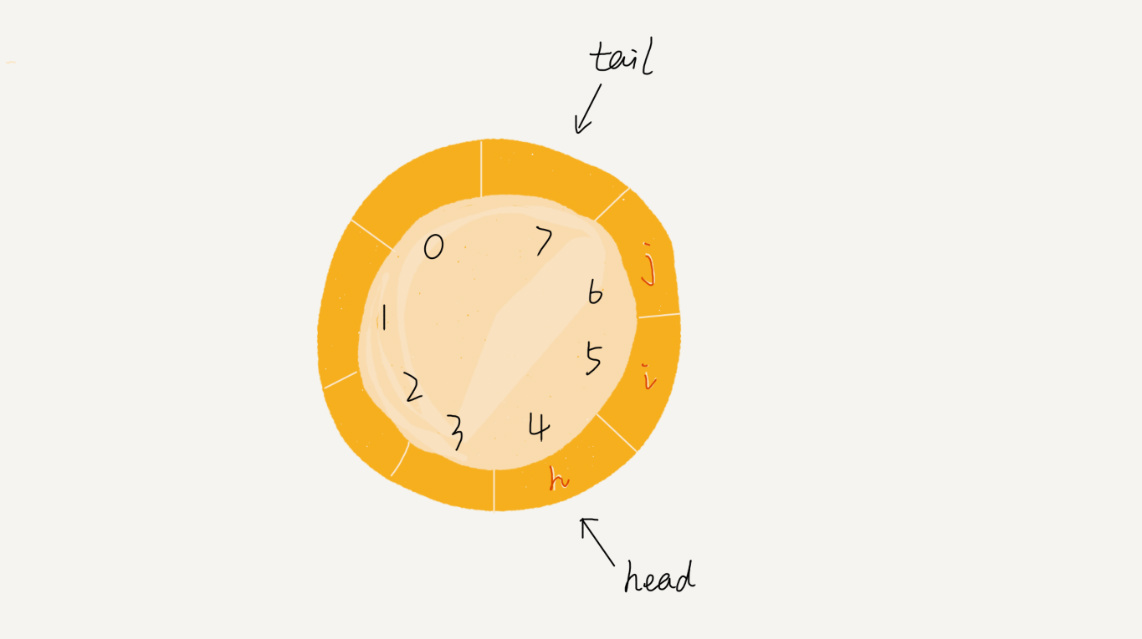
前面顺序队列中有移动数据的操作,这在无形之中肯定会增加时间复杂度。
循环队列就可以解决这个问题。
队空:head == tail
队满:(tail + 1) % capacity = head
代码实现
package com.datastructure.queue;
/**
* 循环队列
*
* @Auther: dlm
* @Date: 2020/4/7 20:54
*/
public class CircularQueue<T>{
//默认容量
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 1 << 3;
//自定义容量
private int capacity;
//存储数据
private T[] data;
//队头下标
private int head;
//队尾下标
private int tail;
public CircularQueue(int capacity){
this.capacity = capacity;
this.data = (T[])new Object[capacity];
this.head = 0;
this.tail = 0;
}
public CircularQueue(){
this(DEFAULT_CAPACITY);
}
//入队
public boolean enqueue(T value){
//队满
if((tail + 1) % capacity == head )
return false;
data[tail] = value;
tail = (tail + 1) % capacity;
return true;
}
//出队
public T dequeue(){
//队空
if(head == tail)
return null;
T value = data[head];
head = (head + 1) % capacity;
return value;
}
}
阻塞队列和并发队列
阻塞队列和并发队列都是队列的高级结构,其底层都是队列这种数据结构。
阻塞队列:阻塞队列其实就是在队列基础上增加了阻塞操作。简单来说,就是在队列为空的时候,从队头取数据会被阻塞。因为此时还没有数据可取,
直到队列中有了数据才能返回;如果队列已经满了,那么插入数据的操作就会被阻塞,直到队列中有空闲位置后再插入数据,然后再返回。
并发队列:并发队列是线程安全的队列。最简单的实现方式就是在入队和出队时加上锁。
欢迎关注个人公众号,可直接扫描以下二维码或微信搜索“阿毛聊技术”。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号