Temporal + LangGraph: A Two-Layer Architecture for Multi-Agent Coordination
Temporal + LangGraph: A Two-Layer Architecture for Multi-Agent Coordination
https://www.anup.io/temporal-langgraph-a-two-layer-architecture-for-multi-agent-coordination/

The Two-Layer Architecture
Keeping these layers separate turned out to be critical.
Temporal: The Orchestration Layer
Temporal is a workflow engine. You write workflows as code. Temporal handles persisting state between steps, retrying failed operations with backoff, enforcing timeouts, and letting you query what's happening. If your worker crashes mid-workflow, Temporal picks up where it left off.
Think of Temporal workflows as deterministic replay machines. That framing helped me understand them. They don't run your code directly. Instead, they record what happened and replay from any checkpoint. That's why they're good for orchestrating unreliable things like LLM calls.
LangGraph: The Agent Layer
LangGraph gives you state machines for agent logic. You define nodes (functions), edges (transitions), and a state schema. It handles running nodes in parallel when you want that. It's built around the idea that agents accumulate state as they work.
I use TypedDict for state schemas. You get autocomplete and it catches typos. More on that later.
Why Keep Them Separate?
Temporal answers "did this complete, and if not, what do we do about it?" LangGraph answers "given this state, what should the agent do next?" These are different questions.
I tried combining them early on. It got messy fast. Retry logic bled into agent logic. I couldn't tell where state lived. Separating them cleaned everything up.
But wait, doesn't LangGraph have its own durable execution now?
Yes. LangGraph 1.0 (released October 2025) includes built-in persistence and durable execution. So why use Temporal?
Temporal is battle-tested across thousands of production deployments for mission-critical workflows. It gives you superior observability through the Temporal Web UI, native support for workflows spanning days or weeks, and a proven track record handling infrastructure failures. LangGraph's durable execution is newer and purpose-built for AI agents, but Temporal's maturity matters when you need rock-solid reliability.
A Grid Dynamics case study validates this: they migrated from LangGraph-only to Temporal after finding that LangGraph's Redis-based state management created issues with lifecycle management and debugging. Temporal's event history made state persistence automatic and debugging straightforward.
Temporal and OpenAI Launch AI Agent Durability with Public Preview Integration
https://www.infoq.com/news/2025/09/temporal-aiagent/
https://github.com/temporalio/sdk-python/blob/main/temporalio/contrib/openai_agents/README.md
Temporal has unveiled a public preview integration with the OpenAI Agents SDK, introducing durable execution capabilities to AI agent workflows built using OpenAI's framework. This collaboration enables developers to build AI agents that automatically handle real-world operational challenges, such as LLM rate limits, network disruptions, and unexpected crashes, without adding complexity to their code.
At the core of this integration is Temporal’s strength in orchestrating distributed, fault-tolerant systems. OpenAI agents, when wrapped in Temporal workflows, benefit from built-in retry logic, state persistence, and crash recovery, allowing developers to define the "happy path" and rely on Temporal to manage error handling and workflow consistency.
Traditionally, AI agents, whether built with LangChain, LlamaIndex, or the OpenAI SDK, run as stateless processes, meaning a failure mid-execution forces a complete restart and wastes compute and token costs. With Temporal, every agent interaction, including large language model (LLM) calls, tool executions, and external API requests, is captured as part of a deterministic workflow. This approach allows the system to automatically replay and restore the agent’s exact state after a crash, timeout, or network failure, dramatically increasing reliability and operational efficiency.
https://github.com/temporalio/sdk-python/blob/main/temporalio/contrib/openai_agents/README.md
In Temporal's durable execution implementation, a program that crashes or encounters an exception while interacting with a model or API will retry until it can successfully complete.
Temporal relies primarily on a replay mechanism to recover from failures. As the program makes progress, Temporal saves key inputs and decisions, allowing a re-started program to pick up right where it left off.
The key to making this work is to separate the applications repeatable (deterministic) and non-repeatable (non-deterministic) parts:
- Deterministic pieces, termed workflows, execute the same way when re-run with the same inputs.
- Non-deterministic pieces, termed activities, can run arbitrary code, performing I/O and any other operations.
Workflow code can run for extended periods and, if interrupted, resume exactly where it left off. Activity code faces no restrictions on I/O or external interactions, but if it fails part-way through it restarts from the beginning.
In the AI-agent example above, model invocations and tool calls run inside activities, while the logic that coordinates them lives in the workflow. This pattern generalizes to more sophisticated agents. We refer to that coordinating logic as agent orchestration.
As a general rule, agent orchestration code executes within the Temporal workflow, whereas model calls and any I/O-bound tool invocations execute as Temporal activities.
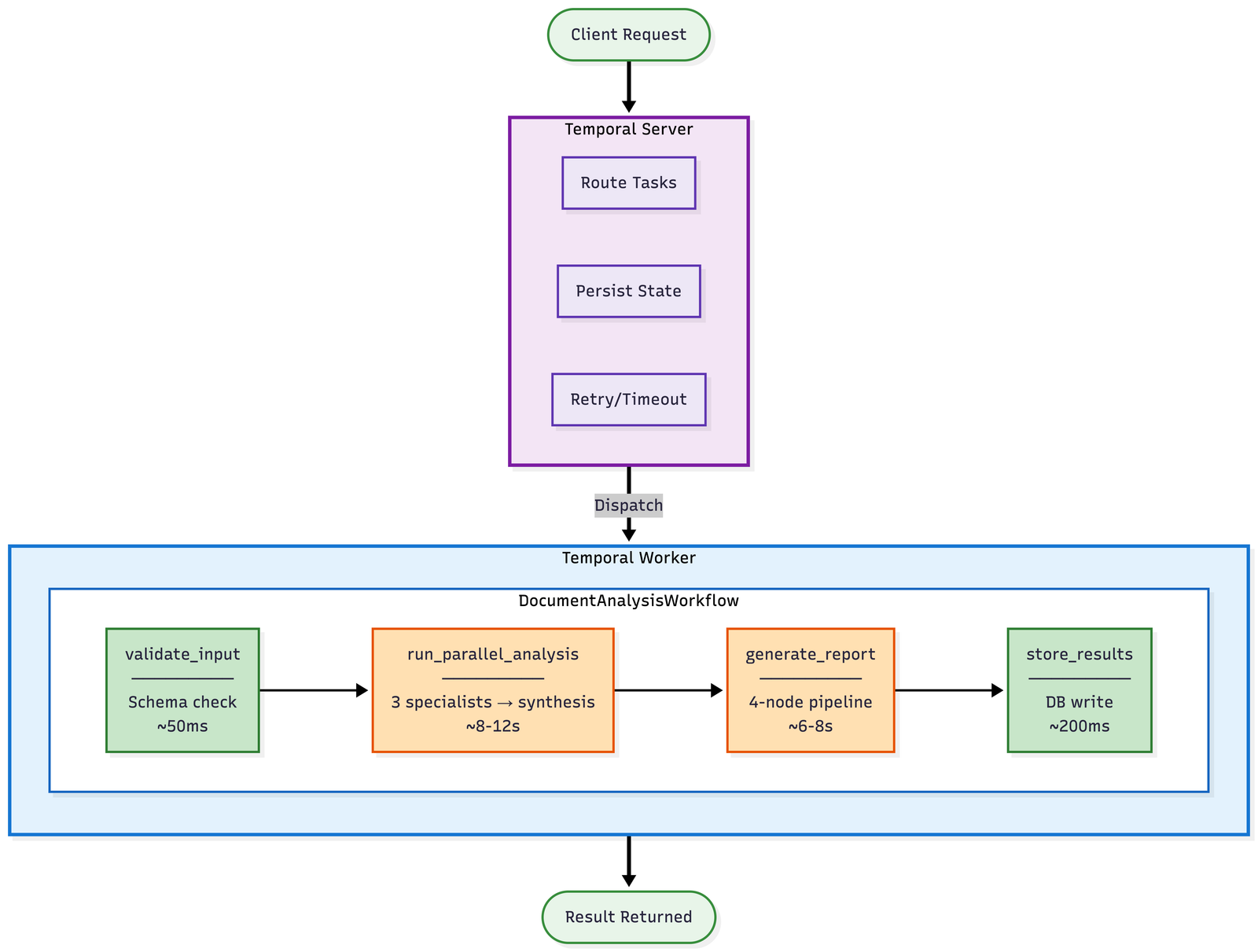
The diagram below shows the overall architecture of an agentic application in Temporal. The Temporal Server is responsible to tracking program execution and making sure associated state is preserved reliably (i.e., stored to a database, possibly replicated across cloud regions). Temporal Server manages data in encrypted form, so all data processing occurs on the Worker, which runs the workflow and activities.
+---------------------+
| Temporal Server | (Stores workflow state,
+---------------------+ schedules activities,
^ persists progress)
|
Save state, | Schedule Tasks,
progress, | load state on resume
timeouts |
|
+------------------------------------------------------+
| Worker |
| +----------------------------------------------+ |
| | Workflow Code | |
| | (Agent Orchestration Loop) | |
| +----------------------------------------------+ |
| | | | |
| v v v |
| +-----------+ +-----------+ +-------------+ |
| | Activity | | Activity | | Activity | |
| | (Tool 1) | | (Tool 2) | | (Model API) | |
| +-----------+ +-----------+ +-------------+ |
| | | | |
+------------------------------------------------------+
| | |
v v v
[External APIs, services, databases, etc.]
from dataclasses import dataclass from datetime import timedelta from temporalio import activity, workflow from temporalio.contrib import openai_agents from agents import Agent, Runner @dataclass class Weather: city: str temperature_range: str conditions: str @activity.defn async def get_weather(city: str) -> Weather: """Get the weather for a given city.""" return Weather(city=city, temperature_range="14-20C", conditions="Sunny with wind.") @workflow.defn class WeatherAgent: @workflow.run async def run(self, question: str) -> str: agent = Agent( name="Weather Assistant", instructions="You are a helpful weather agent.", tools=[ openai_agents.workflow.activity_as_tool( get_weather, start_to_close_timeout=timedelta(seconds=10) ) ], ) result = await Runner.run(starting_agent=agent, input=question) return result.final_output
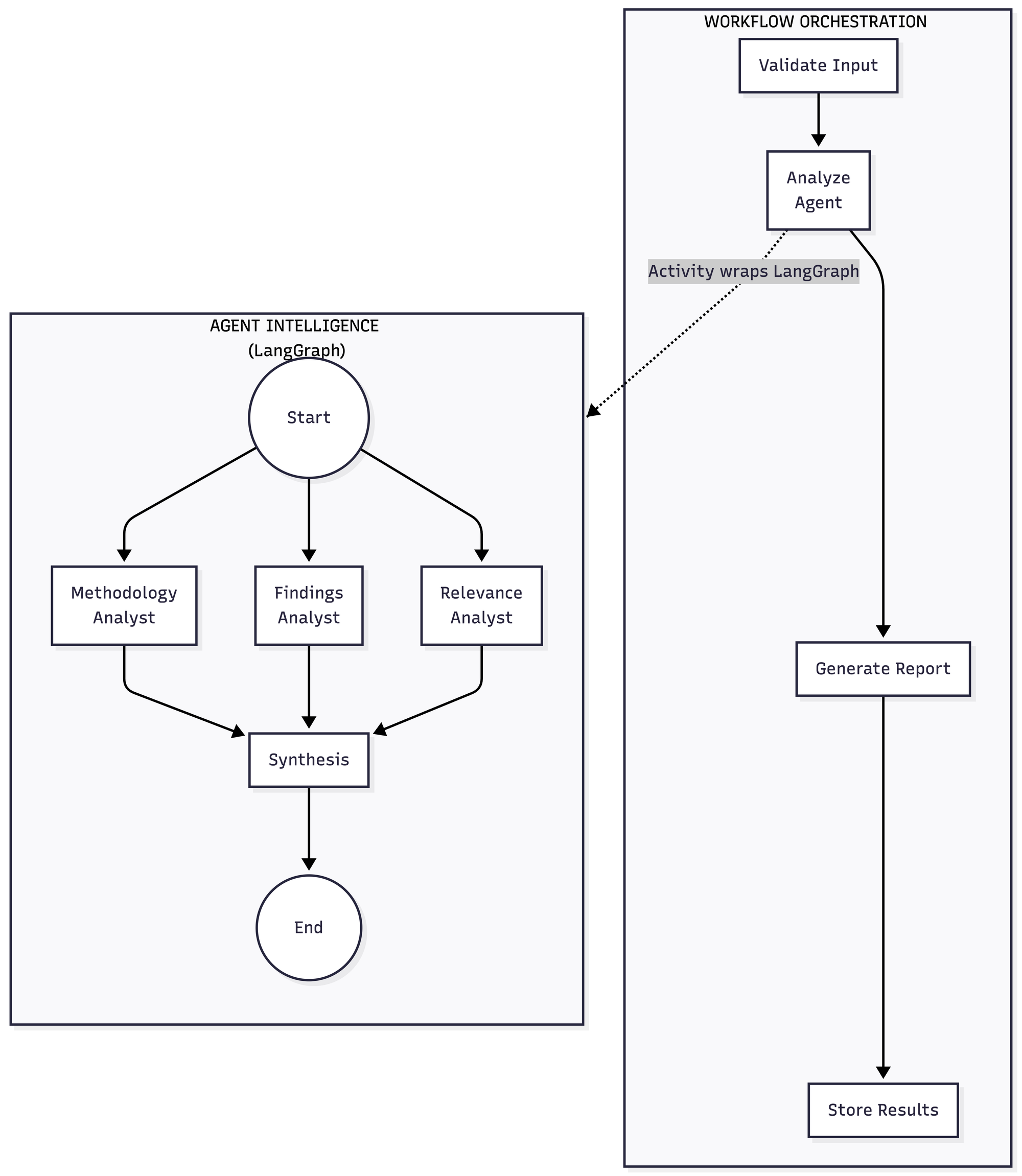
POC: Temporal + LangGraph Integration
https://github.com/fanqingsong/temporal-langgraph-poc
A proof-of-concept research assistant that demonstrates how to combine Temporal workflow orchestration with LangGraph's intelligent graph-based workflow management for building robust AI agent workflows.
Building production AI agent workflows requires both intelligent decision-making and distributed reliability:
- LangGraph: Excellent for AI agent logic but core is not distributed - runs on single processes without built-in scaling
- Temporal: World-class distributed orchestration that can make any workflow distributed
This POC shows how Temporal distributes LangGraph workflows to achieve intelligent AND scalable AI systems:
🤖 LangGraph (Intelligence) + ⚡ Temporal (Distribution) = 🚀 Scalable AI Workflows
Temporal Level: Orchestrates three main activities with durable execution, fault tolerance, and parallelization
LangGraph Level: Each Temporal activity contains its own StateGraph with nodes, edges, and conditional logic
https://github.com/fanqingsong/pydantic-ai-demos/tree/main
https://github.com/fanqingsong/temporal-data-pipeline-demo
https://github.com/fanqingsong/temporal-deep-research-demo
https://github.com/fanqingsong/temporal-ai-agent
https://github.com/temporal-community/openai-agents-demos
samples-python/langchain at main · temporalio/samples-python · GitHub



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号