Build a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) App (web search then answer question)
Build a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) App
https://python.langchain.com/docs/tutorials/rag/
One of the most powerful applications enabled by LLMs is sophisticated question-answering (Q&A) chatbots. These are applications that can answer questions about specific source information. These applications use a technique known as Retrieval Augmented Generation, or RAG.
This is a multi-part tutorial:
- Part 1 (this guide) introduces RAG and walks through a minimal implementation.
- Part 2 extends the implementation to accommodate conversation-style interactions and multi-step retrieval processes.
This tutorial will show how to build a simple Q&A application over a text data source. Along the way we’ll go over a typical Q&A architecture and highlight additional resources for more advanced Q&A techniques. We’ll also see how LangSmith can help us trace and understand our application. LangSmith will become increasingly helpful as our application grows in complexity.
If you're already familiar with basic retrieval, you might also be interested in this high-level overview of different retrieval techniques.
Note: Here we focus on Q&A for unstructured data. If you are interested for RAG over structured data, check out our tutorial on doing question/answering over SQL data.
Overview
A typical RAG application has two main components:
Indexing: a pipeline for ingesting data from a source and indexing it. This usually happens offline.
Retrieval and generation: the actual RAG chain, which takes the user query at run time and retrieves the relevant data from the index, then passes that to the model.
Note: the indexing portion of this tutorial will largely follow the semantic search tutorial.
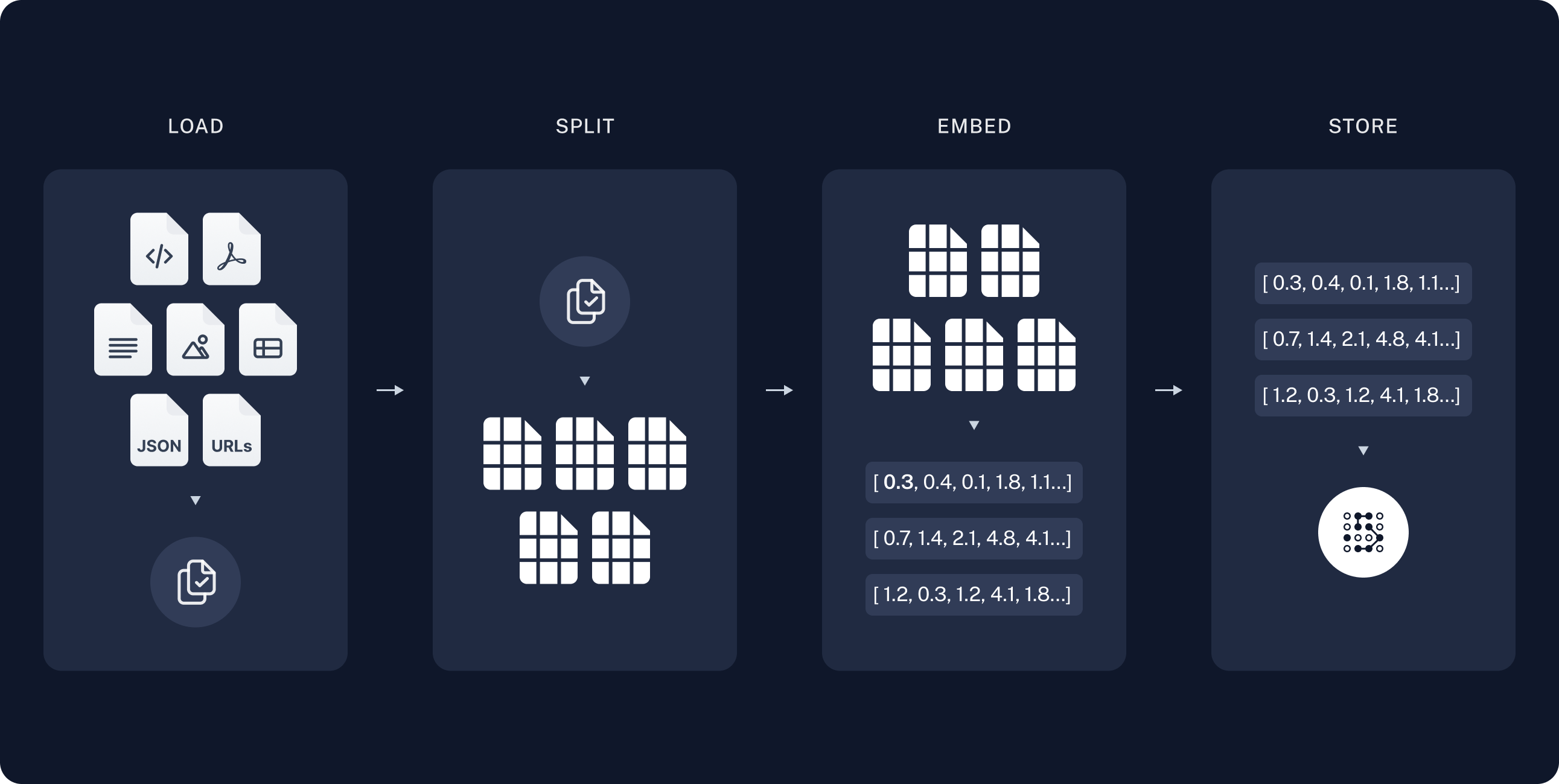
The most common full sequence from raw data to answer looks like:
Indexing
- Load: First we need to load our data. This is done with Document Loaders.
- Split: Text splitters break large
Documentsinto smaller chunks. This is useful both for indexing data and passing it into a model, as large chunks are harder to search over and won't fit in a model's finite context window.- Store: We need somewhere to store and index our splits, so that they can be searched over later. This is often done using a VectorStore and Embeddings model.
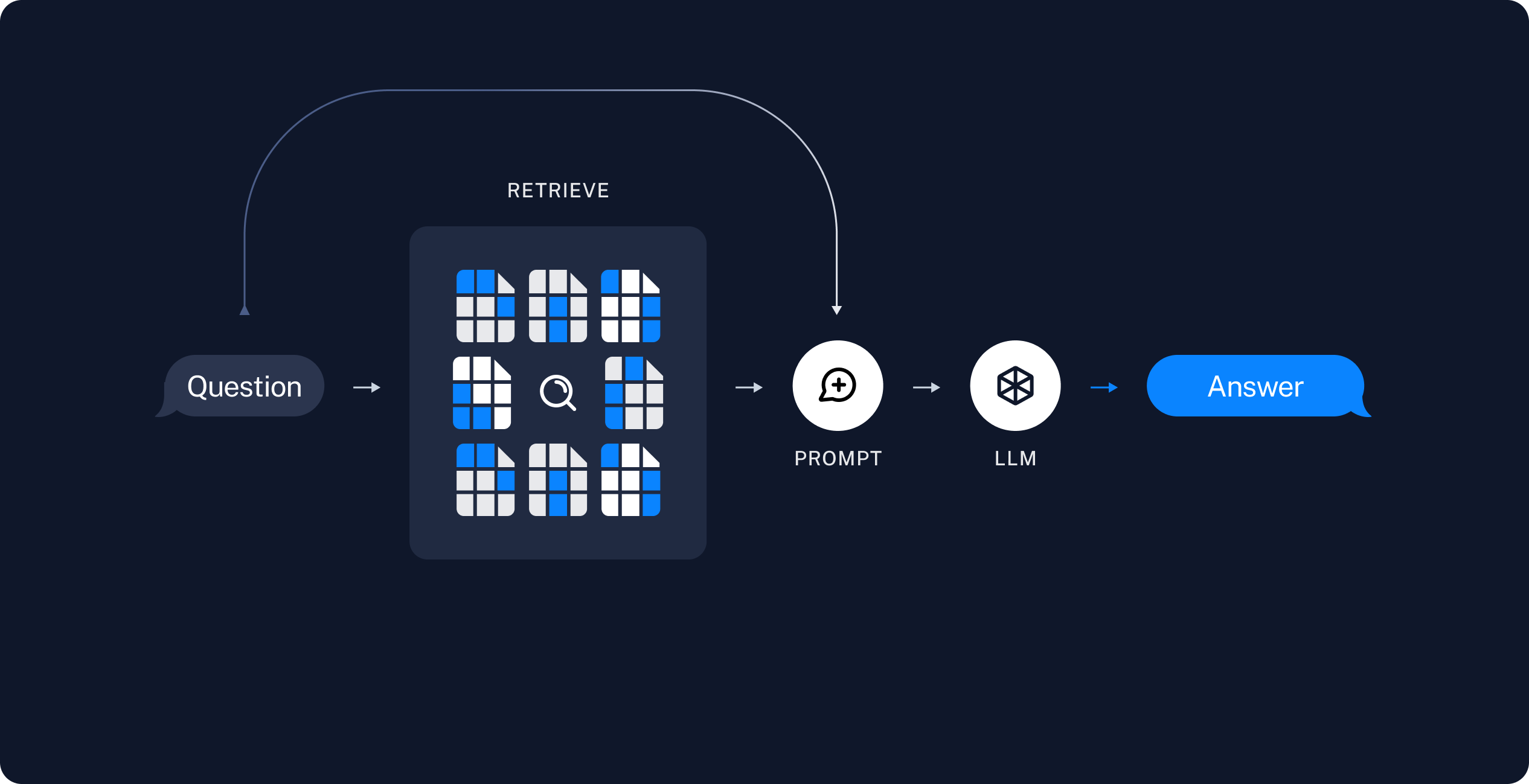
Retrieval and generation
- Retrieve: Given a user input, relevant splits are retrieved from storage using a Retriever.
- Generate: A ChatModel / LLM produces an answer using a prompt that includes both the question with the retrieved data
Once we've indexed our data, we will use LangGraph as our orchestration framework to implement the retrieval and generation steps.
import getpass import os if not os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY"): os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = getpass.getpass("Enter API key for OpenAI: ") from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings(model="text-embedding-3-large") from langchain_core.vectorstores import InMemoryVectorStore vector_store = InMemoryVectorStore(embeddings)
import bs4 from langchain import hub from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader from langchain_core.documents import Document from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter from langgraph.graph import START, StateGraph from typing_extensions import List, TypedDict # Load and chunk contents of the blog loader = WebBaseLoader( web_paths=("https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/",), bs_kwargs=dict( parse_only=bs4.SoupStrainer( class_=("post-content", "post-title", "post-header") ) ), ) docs = loader.load() text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=200) all_splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs) # Index chunks _ = vector_store.add_documents(documents=all_splits) # Define prompt for question-answering prompt = hub.pull("rlm/rag-prompt") # Define state for application class State(TypedDict): question: str context: List[Document] answer: str # Define application steps def retrieve(state: State): retrieved_docs = vector_store.similarity_search(state["question"]) return {"context": retrieved_docs} def generate(state: State): docs_content = "\n\n".join(doc.page_content for doc in state["context"]) messages = prompt.invoke({"question": state["question"], "context": docs_content}) response = llm.invoke(messages) return {"answer": response.content} # Compile application and test graph_builder = StateGraph(State).add_sequence([retrieve, generate]) graph_builder.add_edge(START, "retrieve") graph = graph_builder.compile()
RAG Bootcamp: Web Search
https://github.com/VectorInstitute/rag_bootcamp/tree/main/web_search
# Do a Google web search and parse the results into a big text string web_documents = [] for result_url in search(query, tld="com", num=5, stop=10, pause=2): response = requests.get(result_url) soup = BeautifulSoup(response.content, 'html.parser') web_documents.append(soup.get_text()) # Wrap text as Document object docs = [Document(page_content=web_txt, metadata={"source": "web"}) for web_txt in web_documents] print(f"Number of source documents: {len(docs)}") # Split the result text into smaller chunks text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=512, chunk_overlap=32) chunks = text_splitter.split_documents(docs) print(f"Number of text chunks: {len(chunks)}\n") model_kwargs = {'device': 'cuda', 'trust_remote_code': True} encode_kwargs = {'normalize_embeddings': True} # set True to compute cosine similarity print(f"Setting up the embeddings model...") embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings( model_name=EMBEDDING_MODEL_NAME, model_kwargs=model_kwargs, encode_kwargs=encode_kwargs, ) vectorstore = FAISS.from_documents(chunks, embeddings) retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": 5}) # Retrieve the most relevant context from the vector store based on the query retrieved_docs = retriever.invoke(query) rag_pipeline = RetrievalQA.from_llm(llm=llm, retriever=retriever) result = rag_pipeline.invoke(input=query) print(f"Result: \n\n{result['result']}")



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号