第五模块 WEB开发基础之JavaScript
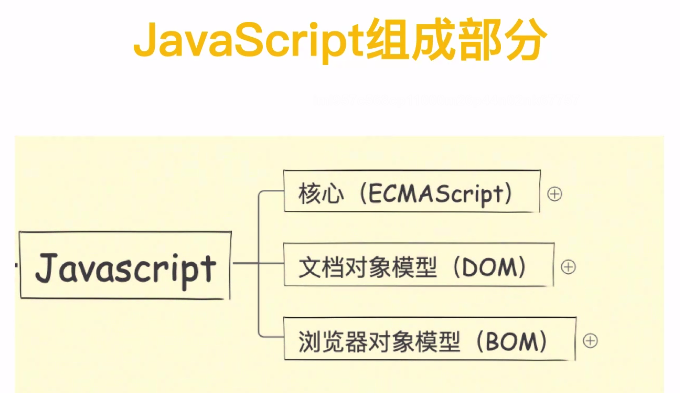
1. JavaScript介绍
ECMAScript是一种语言标准, JavaScript是对ECMAScript的一种实现.
可以将ECMAScript看作JavaScript.
现在, 大部分浏览器上运行的是2011年(ES5)和2015年(ES6)发布的版本.
主要学习ES5, 然后完善补充ES6.
2. 如何在网页中插入JavaScript
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>js文件的引入</title>
<!-- 方式一(内部js):
通过script引入, 可以放在head标签中,
也可以放在body标签中,也可以放在外面,
只要它在当前的整个文档中就行. -->
<script type="text/javascript">
<!-- 编写js代码 -->
</script>
<!-- 方式二(外接js):
通常在开发项目中使用 -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/index.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
3. 变量
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>变量</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
//单行注释, 快捷键: ctrl+?
/*
多行注释: 快捷键: ctrl+shift+?
*/
// 方式一:
// 变量初始化
var x = 30;
var name = '王思聪';
// 方式二:
// 声明变量:
var y;
// 变量赋值:
y = 50;
/*
规则:
1. 必须使用字母, 下划线(_), $开始;
2. 多个英文字母, 通常采用驼峰体;
3. 不能使用js中的关键字和保留字来进行命名;
4. 严格区分大小写;
5. 可以对变量进行重新赋值;
*/
</script>
</body>
</html>
4. 基本变量类型
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
基本变量类型
</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 变量类型
// 基本的数据类型
// number, string, boolean, undefined, null
// 引用的数据类型
// object, array, function
// 小数,整数,正数和负数都属于number类型
var a = 3;
var b = 1.23;
var c = -1;
// typeof来检查当前变量的数据类型
alert(typeof a);
alert(typeof b);
alert(typeof c);
// 字符串 'abc123' "cds78"
// boolean 0(假 false) 1(真 true)
var c = 3 < 4;
alert(c);
alert(typeof c);
// undefined
// 声明了变量, 但是未赋值, 就是undefined.
var x;
// null
var y = null;
</script>
</body>
</html>
5. 算数运算符
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>运算符-算数运算符</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var x = 10;
var y = 4;
var sum = x + y;
var en = x - y;
var or = x * y;
var ll = x / y;
// 取余
var op = x % y;
</script>
</body>
</html>
6. 赋值运算符
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>运算符-递增,递减,赋值运算符</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// ++
// --
var x = 10;
x++;
alert(x);
// 赋值运算符
var a = 4;
var b = 5;
a = b;
var c = 10;
c = c + 5;
c += 5;
c -= 5;
c *= 5;
c /= 5;
</script>
</body>
</html>
7. 字符串
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>字符串</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 注意字符串的嵌套问题
// 可以加\进行转译
var str = "I'm \"MJJ\"";
// 字符串的拼接
var one = "hello";
var two = "world";
var both = one + " " + two;
</script>
</body>
</html>
8. 数字和字符串转换
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>数字和字符串转换</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 隐式转换: 数值转为字符串
/*当字符串和数字相加时, 不会报错, 会自动将数字转化为字符串.*/
var a = "mjj" + 521;
// 结果: mjj520, 类型是string
// 字符串转数字
var num = "" + 234;
var nNum = Number(num);
alert(typeof nNum);
// 数字转字符串
var nnNum = num.toString();
//注意: '2323fff'不能转化为数字.
//虽然用Number()转化后得到number类型的数据, 但结果为NaN(not a number).
</script>
</body>
</html>
9. 数组
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>数组array</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 1. 创建
var shopping = ['香蕉','苹果','橘子']
// 类型是object. array属于object.
// array中可以存放各种类型的数据. 存在索引: 0, 1, 2...
//检查>>>console中可以打印结果
// console.log(shopping);
// 2. 访问
var lst = ['tree', 1, 5, 'good'];
var item1 = lst[0];
console.log(item1);
// 3. 修改
lst[0] = '大树';
// 4. 访问数组的长度
console.log("数组的长度是:" + lst.length);
</script>
</body>
</html>
10. 条件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>条件判断</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
if(true){
do onething
}
else{
do another thing
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
11. if...else...语句
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>if...else...</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
//单条件
var distance = 10;
var nowDistance = 5
if (nowDistance <= distance){
console.log("自动驾驶");
}else{
console.log("人为驾驶");
}
//多条件
var weather = "snow";
if (weather === "sunny"){
console.log('出去玩');
}else if (weather === "rain"){
console.log("呆在家里");
}else if (weather==="snow"){
console.log('滑雪');
}else{
console.log("输入的天气有错");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
12. 逻辑运算符
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>比较运算符</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// === 和 !==
// === 同时比较值和数据类型
// == 和 !=
// == 仅比较数值
// 推荐使用 ===
// > < >= <=
</script>
</body>
</html>
13. 逻辑运算符
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>逻辑运算符</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var weather = "sunny";
var temp = 32;
if (weather === "sunny" && temp > 30){
console.log("在家吹空调, 吃西瓜.")
}
// 逻辑运算符: &&(and) //(or) !(not)
</script>
</body>
</html>
14. switch语句
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>switch语句</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 在多个条件进行判断时建议使用switch语句.
// switch后的变量与case后的值进行匹配, 匹配成功后运行后面的代码.
// 如果没有写break, 则会继续运行后面的代码.
var weather = "sunny";
switch(weather){
case 'sunny':
alert(1);
break;
case 'rain':
alert(2);
break;
default:
alert(3);
break;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
15. 三元运算符
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>三元运算符</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// if...else...
/*if(true){
...
}else{
...
}*/
// 以上代码比较繁琐, 可以使用三元运算进行简化
// 条件 ? run this code : run another code;
var result = 1>2 ? '真的':'假的';
console.log(result);
</script>
</body>
</html>
16. for循环介绍和应用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>for循环</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
/*for(初始化条件;结束的条件;递增的条件){
run code
}*/
var i;
var sum = 0;
for(i = 1; i <= 10000; i++){
sum += i;
}
console.log(sum);
var shopping = ['香蕉', '苹果', '牛奶']
var j;
for(j=0;j<shopping.length;j++){
var str = '<h1>' + shopping[j] +'</h1>';
document.write(str);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
17. break和continue
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>break和continue语句</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
//break可以跳出当前循环
var x = 0;
for(;;){
if(x > 100){
break;
}
x++;
}
// continue 跳出当前循环, 下次循环继续执行.
var sum = 0;
for(var i = 1;i <= 10; i++){
if(i === 8){
continue;
}
sum += i;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
18. while循环
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>while循环</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
/*初始化条件
while(判断循环结束条件){
run code
递增条件
}*/
var i = 1;
var sum = 0;
while(i < 100){
sum += i;
i += 2;
}
document.write(sum);
</script>
</body>
</html>
19. do-while
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>do-while循环</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
//先执行后判断
var sum = 0;
var i = 1;
do{
sum += i;
i++;
}while(i <= 100);
</script>
</body>
</html>
20. 函数的定义
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>函数的定义</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 函数: 封装代码, 解决反复重复的问题
function f(){
xxx;
xxx;
xxx;
}
f();
</script>
</body>
</html>
21. 函数传参
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>函数传参</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 函数: 封装代码, 解决反复重复的问题
function f(参数1, 参数2, 参数3){
xxx;
xxx;
xxx;
}
f(参数1, 参数2, 参数3);
// 如果不传参数, 则参数就是undefinded.
</script>
</body>
</html>
22. 函数返回值和函数表达式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>函数返回值</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
function addition(a,b){
var sum = a + b;
return sum;
}
var sum = addition(3,2);
console.log(sum);
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>函数表达式</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var division = function(a, b){
return a / b;
}
var result = division(6,2);
console.log(result);
</script>
</body>
</html>
23. 函数作用域和全局污染
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>函数作用域</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 定义在函数外部的变量称为全局作用域
// 定义在函数内部的变量称为局部作用域
var a = 1;
console.log(a);
function add(){
var b = 3;
console.log(a);
}
add();
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>全局污染</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/first.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/second.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
/*first.js或second.js中的代码如下:
var name = "mjj";
function hello(){
alert("hello " + name);
}*/
hello();
// 如果引入的两个js中, 同时存在相同的函数, 且使用相同的全局变量, 后面的会覆盖掉前面的, 则会导致全局污染.
// 为了防止出现全局污染的问题, 则应在函数内部定义变量.
(function(){
var name = "mjj";
var hello = function(){
alert("hello" + name);
}
})
// 这种情况下, hello是局部变量, 如果在全局调用的话, 则调用不到, 如果想进行调用, 则需要使用以下方法:
(function(){
var name = 'mjj';
var hello = function(){
alert ("hello" + name);
}
window.first = hello;
})
// 调用方式如下:
first();
</script>
</body>
</html>
24. 对象object讲解
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>object</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 万事万物皆对象(属性和方法)
// 字面量创建
var person = {
name : "mjj",
age: 18,
gender: "female",
fav: function(){
alert("爱好打球");
}
}
console.log(person.name);
console.log(person.fav());
</script>
</body>
</html>
25. 内置对象array
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>内置对象array</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// array的创建方式1:
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]
// array的创建方式2(构造函数):
var colors = new Array();
// 这种创建方式等价于以下方式:
var colors2 = [];
// 以下方法可以提高准确性.
if (Array.isArray(colors)){
colors[0] = 'red';
console.log(colors[0]);
console.log(colors.length);
}
if (Array.isArray(colors)){
colors[0] = "red";
colors[1] = "blue";
colors[2] = "green";
// 将array转化为string
var a = colors.toString();
console.log(a);
console.log(colors);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
26. 数组的join方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>数组的join方法</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 将数组转化为字符串的三种方法: toString toLocaleString join('分隔符')
var arr = [1,2,3];
var a = arr.toString();
var b = arr.toLocaleString();
console.log(a);
// 结果:1,2,3
console.log(b);
// 结果:1,2,3
// 如果数组中存放的是函数对象, 那么toString和toLocaleString方法得到的结果则不同. 通常使用的是toString来实现数组转字符串.
// 使用指定的分隔符分隔字符串.
var colors = ['red', 'blue', 'green'];
var a = colors.join(',');
console.log(a);
// 结果为字符串, 以逗号分隔: red,blue,green
// toString和toLocalString方法默认使用逗号将元素隔开, join方法可以指定分隔符, 例如|等.
</script>
</body>
</html>
27. 数组的栈方法和队列方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>数组的栈方法和队列方法</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 栈: 后进先出
// push() 在末尾追加, 返回数组的长度
// pop() 删除最后一项元素, 返回删除的最后一项元素
var colors = ['red','blue','green']
var newlength = colors.push('purple');
// 返回的是列表的长度.
console.log(newlength);
// 结果: 4
console.log(colors);
// 结果: ["red", "blue", "green", "purple"]
var lastItem = colors.pop();
console.log(lastItem);
// 结果: purple
console.log(colors);
// 结果: ["red", "blue", "green"]
// 队列: 先进先出
// shift() 删除数组的第一个元素, 返回删除的元素
// unshift() 往数组的第一项添加元素, 返回添加后的数组的长度
var newlength2 = colors.unshift('yellow');
console.log(newlength2);
// 结果: 4
console.log(colors);
// 结果: ["yellow", "red", "blue", "green"]
var firstItem = colors.shift();
console.log(firstItem);
// 结果: yellow
console.log(colors);
// 结果: ["red", "blue", "green"]
</script>
</body>
</html>
28. 数组排序
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>数组排序</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
var values = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5,10, 18];
// 将数组中值的顺序进行反转
values.reverse();
console.log(values);
// 结果: [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
// 数组排序,默认按照ascii码升序,使用reverse进行降序排序
// 数组在排序之前,会将数值转化为字符串,然后进行排序
values.sort();
console.log(values);
// 结果: [1, 10, 18, 2, 3, 4, 5]
// 如果要比较两个数值的大小,则应采用以下方法:
function compare1(a,b){
if(a<b){
return -1;
}else if(a>b){
return 1;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
values.sort(compare1); //升序
console.log(values); // 结果: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 18]
// 将以上代码简写:
function compare11(a,b){
return a-b;
}
function compare2(a,b){
if(a>b){
return -1;
}else if(a<b){
return 1
}else{
return 0;
}
}
values.sort(compare2);
console.log(values); // 结果: [18, 10, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
// 将以上代码简写:
function compare22(a,b){
return b-a;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
29. 数组的操作方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>数组的操作方法</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
//1. concat() 对数组进行合并,得到新的数组,不会影响原来的数组
var colors = ['red','blue'];
colors.concat() // concat()中可以是一个数组或多个数组, 或者不是数组。
var newColors1 = colors.concat('green');
console.log(newColors1); //结果: ["red", "blue", "green"]
var newColors2 = colors.concat({"name":"张三"});
console.log(newColors2); // 结果:["red", "blue", Object]
var newColors3 = colors.concat({"name":"lisa"},[1,2]);
console.log(newColors3); // 结果:["red", "blue", Object, 1, 2]
//2. slice() 对数组进行分割,不会影响原来的数组,会返回新的数组.
var names = ['tom', 'sara','sunny','rita'];
// 一个参数,表示切割的步长
newNames1 = names.slice(1);
console.log(newNames1); // 结果:["sara", "sunny", "rita"]
//两个参数,第一个是起始位置,第二个是结束位置,且顾头不顾尾
newNames2 = names.slice(2,3);
console.log(newNames2); // 结果:["sunny"]
newNames3 = names.slice(-2, -1);
console.log(newNames3); // ["sunny"]
// 三个参数,第一个表示起始位置,第二个表示结束位置,第三个表示步长。
newNames4 = names.slice()
//3. splice() 对数组进行添加,删除或替换
//3.1 删除,两个参数
var fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange'];
// 从0开始删除两个元素,会影响原来的数组。
fruits.splice(0,2);
//3.2 插入, 三个参数
// 1表示从1开始,0表示不去删除元素,后面的表示插入的元素
fruits.splice(1,0,'sara','sunny');
//3.3 替换
// 删除一个元素,索引为1,然后添加第三个参数,表示替换。
fruits.splice(1,1,'rita');
</script>
</body>
</html>
30. 数组的位置方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>数组的位置方法</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 位置方法
// indexOf() 从前往后找
// lastIndexOf() 从后往前找
var names = ['alex', 'sunny', 'tom', 'alex', 'rita']
var ind = names.indexOf('sunny');
console.log(ind); // 1
var ind2 = names.lastIndexOf('alex');
console.log(ind2); // 3
// 下面的参数2表示从索引为2的位置进行查询
var ind3 = names.indexOf('alex',2);
console.log(ind3); // 3
var ind4 = names.lastIndexOf('alex',2);
console.log(ind4); // 0
// 注意:如果查不到结果就返回-1,查到结果就返回当前项的索引
</script>
</body>
</html>
31. 数组的迭代方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>数组的迭代方法</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
//1. filter() 将数组的元素进行过滤, 其中传入匿名函数
var numbers = [1,2,3,4,5,6,20]
var filterResult = numbers.filter(function(item,index,array){
return item > 10;
});
console.log(filterResult); // [20]
//2. map() 对数组的每一项进行操作, 其中传入匿名函数
var mapResult = numbers.map(function(item, index, array){
return item*2;
});
console.log(mapResult);// [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 40]
// 遍历
for(var i = 0; i < mapResult.length; i++){
console.log(mapResult[i]);
}
//3. forEach(),其中传入匿名函数
mapResult.forEach(function(item,index,array){
console.log(item);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
32. map方法的应用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>map方法的应用</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
var people = [
{
'name':"alex",
"age":18
},
{
'name':'apple',
'age':20
},
{
'name':'sunny',
'age':30
}
]
var names = people.map(
function(item,index,array){
return item.name;
}
)
console.log(names); // ["alex", "apple", "sunny"]
var ages = people.map(
function(item,index,array){
return item.age;
}
)
console.log(ages); // [18, 20, 30]
</script>
</body>
</html>
33. 字符串的字符方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>字符串的字符方法</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
/*
属性
length 获取字符串的长度
方法
charAt() 获取某个索引处的字符
charCodeAt() 获取某个索引处字符对应的编码(ascii码)
concat() 字符串拼接, 可以传多个参数,通常不使用这种方法. 通常使用+来做多个字符的拼接.
slice()
substr()
substring()
indexOf()
lastIndexOf()
trim()
toLowerCase()
toLocaleLowerCase()
toUpperCase()
toLocaleUpperCase()
*/
var str = 'hello world';
console.log(str.length); //11
console.log(str.charAt(1)); //e
console.log(str.charCodeAt(1)); //101
console.log(str.concat('!')); //hello world!
</script>
</body>
</html>
34. 字符串的切片方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>字符串的切片方法</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
/*
属性
length 获取字符串的长度
方法
charAt() 获取某个索引处的字符
charCodeAt() 获取某个索引处字符对应的编码(ascii码)
concat() 字符串拼接, 可以传多个参数,通常不使用这种方法. 通常使用+来做多个字符的拼接.
slice()
substr()
substring()
indexOf()
lastIndexOf()
trim()
toLowerCase()
toLocaleLowerCase()
toUpperCase()
toLocaleUpperCase()
*/
var str = 'hello world';
console.log(str.length); //11
console.log(str.charAt(1)); //e
console.log(str.charCodeAt(1)); //101
console.log(str.concat('!')); //hello world!
//如果只传一个参数,slice(),substr()和substring()的效果一样, 不同的是第二个参数. 一个参数表示起始位置, 一直截到字符串末尾.
console.log(str.slice(2)); //llo world
console.log(str.substr(2));//llo world
console.log(str.substring(2)); //llo world
console.log(str.slice(2,4)); //ll 第一个参数是起始位置, 第二个参数是结束位置, 且顾头不顾尾.
console.log(str.substr(2,6)); //llo wo, 第一个参数是起始位置, 第二个参数表示返回的字符的个数, 第二个参数一定是个正数.
console.log(str.substring(2,4)); //ll 第一个参数是起始位置, 第二个参数是结束位置, 且顾头不顾尾.
</script>
</body>
</html>
35. 字符串的其他方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>字符串的切片方法</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
/*
属性
length 获取字符串的长度
方法
charAt() 获取某个索引处的字符
charCodeAt() 获取某个索引处字符对应的编码(ascii码)
concat() 字符串拼接, 可以传多个参数,通常不使用这种方法. 通常使用+来做多个字符的拼接.
slice()
substr()
substring()
indexOf()
lastIndexOf()
trim() 清除字符串前后的空格
toLowerCase() 全部转成小写, 常用
toLocaleLowerCase() 在特定地区有用
toUpperCase() 全部转成大写, 常用
toLocaleUpperCase() 在特定地区有用
*/
var str = 'hello world';
console.log(str.length); //11
console.log(str.charAt(1)); //e
console.log(str.charCodeAt(1)); //101
console.log(str.concat('!')); //hello world!
//如果只传一个参数,slice(),substr()和substring()的效果一样, 不同的是第二个参数. 一个参数表示起始位置, 一直截到字符串末尾.
console.log(str.slice(2)); //llo world
console.log(str.substr(2));//llo world
console.log(str.substring(2)); //llo world
console.log(str.slice(2,4)); //ll 第一个参数是起始位置, 第二个参数是结束位置, 且顾头不顾尾.
console.log(str.substr(2,6)); //llo wo, 第一个参数是起始位置, 第二个参数表示返回的字符的个数, 第二个参数一定是个正数.
console.log(str.substring(2,4)); //ll 第一个参数是起始位置, 第二个参数是结束位置, 且顾头不顾尾.
console.log(str.indexOf('o')); //4
console.log(str.lastIndexOf('o')); //7 从后往前找
console.log(str.indexOf('o',6)); //7, 从6开始往后找
console.log(str.lastIndexOf('o',6));//4, 从6往前找
var str1 = ' hello world ';
console.log(str.trim()); //hello world
console.log(str.toUpperCase()); //HELLO WORLD
</script>
</body>
</html>
36. 如何查找当前字符的所有位置
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>如何查找当前字符的所有位置</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
//查找e在str中的所有位置
var str = 'He unfolded the map and set it on the floor.'
var arr = [];
for(i=0; i<str.length; i++){
if(str[i]==='e'){
arr.push(i);
}
}
console.log(arr);
// [1, 9, 14, 25, 36]
</script>
</body>
</html>
37. date日期对象的创建方式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>date日期对象的创建方式</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
// UTC 1970.1.1 - 285616年
// Date日期对象, 其中可以传参数, 也可以不传参数.
// 方式1(常用)
var now = new Date();
console.log(now);
// Sun Sep 13 2020 12:05:39 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)
//方式2
var xmas = new Date('December 25,1995 13:30:00');
console.log(xmas);
// Mon Dec 25 1995 13:30:00 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)
//方式3
// 月份0-11
var xmas1 = new Date(1995,11,25);
console.log(xmas1);
//Mon Dec 25 1995 00:00:00 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)
//方式4
var xmas2 = new Date(1995,11,25,14,30,0);
console.log(xmas2);
//Mon Dec 25 1995 14:30:00 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)
</script>
</body>
</html>
38. Date的常用方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Date的常用方法</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
var now = new Date();
console.log(now.getDate());//13 获取日期(1-31)
console.log(now.getMonth());//9 获取月份(0-11)
console.log(now.getFullYear());//2020 获取年份
console.log(now.getDay());//0(星期天) 获取一星期中的第几天(0-6)
console.log(now.getHours()); //12 获取小时(0-23)
console.log(now.getMinutes());//28 获取分钟数(0-59)
console.log(now.getSeconds());//49 获取秒数(0-59)
</script>
</body>
</html>
39. 日期格式化方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>日期格式化方法</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
var now = new Date();
console.log(now.toDateString());
// Sun Sep 13 2020
console.log(now.toTimeString());
// 16:39:30 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)
console.log(now.toLocaleDateString());
// 2020-9-13 常用
console.log(now.toLocaleTimeString());
// 16:42:17 常用
console.log(now.toLocaleString());
// 2020-9-13 16:43:24 常用
console.log(now.toUTCString());
// Sun, 13 Sep 2020 08:45:02 GMT
</script>
</body>
</html>
40. 如何显示数字时钟的格式时间
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>如何显示数字时钟的格式时间</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
function nowNumTime(){
var now = new Date();
var hour = now.getHours();
var minute = now.getMinutes();
var second = now.getSeconds();
var temp = "" + (hour>12 ? hour-12 : hour);
if(hour === 0){
temp = "12";
}
temp = temp + (minute<10 ? ':0' : ':') + minute;
temp = temp + (second<10 ? ':0' : ':') + second;
temp = temp + (hour >= 12 ? ' P.M.' : ' A.M.');
return temp;
}
var time = nowNumTime();
console.log(time);
// 5:15:04 P.M.
</script>
</body>
</html>
41. 字符串和数值类型相互转换
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>字符串和数值类型相互转换</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
//1. 将数字字符串转化为整型
var str1 = '1.234555';
console.log(parseInt(str1));
// 1
var str2 = '1344dxdfdf009';
console.log(parseInt(str2));
// 1344
//2. 将数字字符串转化为浮点型
var str3 = '325.45667';
console.log(parseFloat(str3));
// 325.45667
console.log(Number(str3));
// 325.45667
var str4 = '3434dsfsg.543';
console.log(Number(str4));
// NaN
console.log(isNaN(Number(str4))); //检测结果是否为NaN
// true
//3. 将数值转化为字符串(强制类型转换)
var num1 = 124.34;
console.log(num1.toString());
//124.34
console.log(String(num1));
//124.34
//4. 隐式转换
console.log(''+ num1);
//124.34
console.log(''.concat(num1));
//124.34
//5. 按小数点后固定位数转换
console.log(num1.toFixed()); //124 四舍五入只保留整数
console.log(num1.toFixed(2));// 124.34
</script>
</body>
</html>
42. global对象的编码和解码方式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>global对象的编码和解码方法</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
//编码
// URI:统一资源标识符
var uri = 'http://www.aplend.cn/web index.html?name=alex';
console.log(encodeURI(uri));//对空格进行解析
//http://www.aplend.cn/web%20index.html?name=alex
console.log(encodeURIComponent(uri));//对空格,问号,冒号,斜杠等进行解析, 这种方法使用较多
//http%3A%2F%2Fwww.aplend.cn%2Fweb%20index.html%3Fname%3Dalex
//解码
var encodeuri1 = 'http://www.aplend.cn/web%20index.html?name=alex';
console.log(decodeURI(encodeuri1));// 只能解析空格
// http://www.aplend.cn/web index.html?name=alex
var encodeuri2 = 'http%3A%2F%2Fwww.aplend.cn%2Fweb%20index.html%3Fname%3Dalex';
console.log(decodeURIComponent(encodeuri2));
// http://www.aplend.cn/web index.html?name=alex
</script>
</body>
</html>
43. window对象讲解
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>window对象讲解</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
// js提供了一个window对象, 在目前的环境下, window对象就相当于global对象. 全局作用域下声明的变量或函数都成为了window对象的属性或方法.
var a = 3;
console.log(window.a);
function hello(){
alert(window.a);
}
window.hello();
// 在当前浏览器环境下, window对象等价于global对象. 全局作用域下声明的变量或函数都挂在window对象下. 在ECMAScript或JS中, 顶层对象就是window.
</script>
</body>
</html>
44. Math数学对象
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Math数学对象</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 属性(使用较少)
console.log(Math.E);
// 2.718281828459045
console.log(Math.LN2);
// 0.6931471805599453
console.log(Math.LN10);
// 2.302585092994046
console.log(Math.LOG2E);
// 1.4426950408889634
console.log(Math.LOG10E);
// 0.4342944819032518
console.log(Math.PI);
// 3.141592653589793
console.log(Math.SQRT2); //2的平方根
// 1.4142135623730951
console.log(Math.SQRT1_2); //2的平方根的倒数
// 0.7071067811865476
//方法
//1.max() min()
var max = Math.max(1,3,45,56,21);
console.log(max);
// 56
var min = Math.min(1,2,3,5,78);
console.log(min);
// 1
var arr = [1,23,45,67,87];
var max1 = Math.max.apply(null,arr);
console.log(max1);
// 87
//2.ceil() floor() round()
var num = 24.3;
console.log(Math.ceil(num)); //往前进一位, 向上取整
// 25
console.log(Math.floor(num)); //舍弃小数点后数字, 向下取整
// 24
console.log(Math.round(num)); //标准的四舍五入
//24
//3.随机数 random() 0=<random<1
console.log(Math.random());
// 0.5704137720924052
//3.1 获取min到max之间的整数(获取某个范围的随机整数)
function random(min,max){
return rint = Math.floor(Math.random() * (max-min) + min);
}
//3.2 获取随机颜色 rgba(0-255,0-255,0-255);
function randomColor(){
var r = random(0,256), g = random(0,256), b = random(0,256);
// 模板字符串``(位于tab键上方)
var result = `rgb(${r},${g},${b})`;
return result;
}
var rc = randomColor();
console.log(rc);
// document.body.style.backgroundColor = rc;
//3.3 随机验证码
function createCode(){
var code = '';
var codeLength = 4;
var randomCode = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,'A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H','I','J','K','L','M','N','O','P','Q','R','S','T','U','V','W','X','Y','Z'];
for(var i = 0; i < codeLength; i++){
var index = random(0,36);
code += randomCode[index];
}
return code;
}
var randomCode = createCode();
console.log(randomCode);
</script>
</body>
</html>
45. 随机对象
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>随机对象</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
//3.随机数 random() 0=<random<1
console.log(Math.random());
// 0.5704137720924052
//3.1 获取min到max之间的整数(获取某个范围的随机整数)
function random(min,max){
return rint = Math.floor(Math.random() * (max-min) + min);
}
//3.2 获取随机颜色 rgba(0-255,0-255,0-255);
function randomColor(){
var r = random(0,256), g = random(0,256), b = random(0,256);
// 模板字符串``(位于tab键上方)
var result = `rgb(${r},${g},${b})`;
return result;
}
var rc = randomColor();
console.log(rc);
// document.body.style.backgroundColor = rc;
//3.3 随机验证码
function createCode(){
var code = '';
var codeLength = 4;
var randomCode = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,'A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H','I','J','K','L','M','N','O','P','Q','R','S','T','U','V','W','X','Y','Z'];
for(var i = 0; i < codeLength; i++){
var index = random(0,36);
code += randomCode[index];
}
return code;
}
var randomCode = createCode();
console.log(randomCode);
</script>
</body>
</html>


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号