LLama2源码分析——Rotary Position Embedding分析
参考:一文看懂 LLaMA 中的旋转式位置编码(Rotary Position Embedding)
原理推导参考自上文,以下结合huggingface代码分析公式计算过程
1 旋转角度计算
计算公式如下,其中d为词嵌入维度,这部分和论文原文一样
\[\theta_j=10000^{-2(j-1)/d},j\in [1,2,\ldots,d/2]
\]
# 计算词向量元素两两分组之后,每组元素对应的旋转角度
# 维度:[dim / 2]
inv_freq = 1.0 / (self.base ** (torch.arange(0, self.dim, 2).float().to(device) / self.dim))
2 计算整个seq的cos_sin矩阵
def _set_cos_sin_cache(self, seq_len, device, dtype):
self.max_seq_len_cached = seq_len
# 生成token长度序列
t = torch.arange(self.max_seq_len_cached, device=device, dtype=self.inv_freq.dtype)
# 计算两个矩阵的外积,结果维度[seq_len, dim // 2]
freqs = torch.einsum("i,j->ij", t, self.inv_freq)
# 类似[[0, 2, 4, ..., 0, 2, 4, ...], ...]形式,旋转角度两两一组相同
emb = torch.cat((freqs, freqs), dim=-1)
self.register_buffer("cos_cached", emb.cos().to(dtype), persistent=False)
self.register_buffer("sin_cached", emb.sin().to(dtype), persistent=False)
3 计算旋转式位置编码
\[\begin{aligned}f_q(x_m,m)&=(W_qx_m)e^{im\theta}
\\f_k(x_n,n)&=(W_kx_n)e^{in\theta}\end{aligned}
\]
公式根据欧拉公式转化后为
\[(q_{m}^{(1)}+iq_{m}^{(2)})*(\cos(m\theta)+i\sin(m\theta))
\]
展开后将结果重新表示为实数向量即为
\[q_me^{im\theta}=[q_m^{(1)}\cos(m\theta)-q_m^{(2)}\sin(m\theta),q_m^{(2)}\cos(m\theta)+q_m^{(1)}\sin(m\theta)]
\]
key的计算同理,以上公式是2维embedding的旋转编码计算,实际代码中是将高纬度的embedding两两分组按照上述公式计算,同一组内的旋转角度相同,此处Llama代码中的分组计算方式与论文原文有所区别,论文原文中是将embedding_dim维度(最后一维)的向量按照相邻两个位置数字为一组,可以按照如下代码理解
>>> a
tensor([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8],
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]])
>>> a.view(2, -1, 2)
tensor([[[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6],
[7, 8]],
[[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6],
[7, 8]]])
因此,单个token的位置编码是如下图方式计算
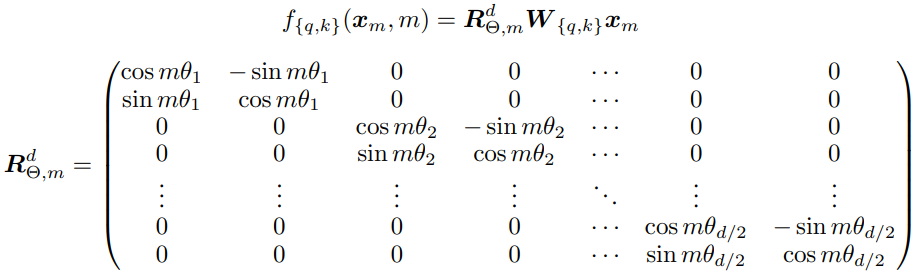
但以上的R矩阵比较稀疏,计算时浪费大量算力,因此Llama中采用不同的方式计算
- Llama源码中计算方法
\[\begin{pmatrix}
{q_0}\\{q_1}\\{\vdots}\\{q_{d/2-1}}\\{q_{d/2}}\\{q_{d/2+1}}\\{\vdots}\\{q_{d-1}}
\end{pmatrix}
\otimes
\begin{pmatrix}
\cos m\theta_0\\\cos m\theta_2\\\cos m\theta_4\\\vdots\\\cos m\theta_{d-2}\\\cos m\theta_0\\\cos m\theta_2\\\vdots\\\cos m\theta_{d-2}
\end{pmatrix}
+
\begin{pmatrix}
{-q_{d/2}}\\{-q_{d/2+1}}\\\vdots\\{-q_{d-1}}\\{q_{1}}\\{q_{2}}\\\vdots\\{q_{d/2-1}}
\end{pmatrix}
\otimes
\begin{pmatrix}
\sin m\theta_0\\\sin m\theta_2\\\sin m\theta_4\\\vdots\\\sin m\theta_{d-2}\\\sin m\theta_0\\\sin m\theta_2\\\vdots\\\sin m\theta_{d-2}
\end{pmatrix}
\]
def rotate_half(x):
"""Rotates half the hidden dims of the input."""
x1 = x[..., : x.shape[-1] // 2]
x2 = x[..., x.shape[-1] // 2 :]
return torch.cat((-x2, x1), dim=-1)
def apply_rotary_pos_emb(q, k, cos, sin, position_ids, unsqueeze_dim=1):
cos = cos[position_ids].unsqueeze(unsqueeze_dim)
sin = sin[position_ids].unsqueeze(unsqueeze_dim)
q_embed = (q * cos) + (rotate_half(q) * sin)
k_embed = (k * cos) + (rotate_half(k) * sin)
return q_embed, k_embed


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号