软工第一周作业
一、通过实验了解double在进行四则运算时的精度规则
(1)源码
1 package day1; 2 3 public class TestDouble { 4 public static void main(String args[]) { 5 System.out.println("0.05 + 0.01 = " + (0.05 + 0.01)); 6 System.out.println("1.0 - 0.42 = " + (1.0 - 0.42)); 7 System.out.println("4.015 * 100 = " + (4.015 * 100)); 8 System.out.println("123.3 / 100 = " + (123.3 / 100)); 9 } 10 }
(2)运行结果
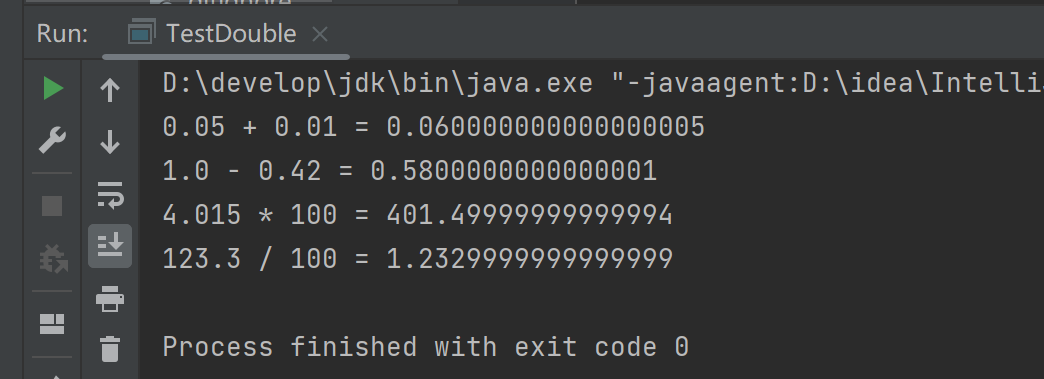
(3)总结
double类型元素在进行“+”,“-”运算时,会产生精度上的误差,但比较小;
double类型元素再进行“*”,“/”运算时,也会产生精度上的误差,相比加减来说误差较大;
二、精度丢失的解决方法
(1)使用java库中的BigDecimal进行操作,使用类中对应的方法对相应数字进行计算,(应把对应的value值转换为String类型 进行操作)如果不使用String类型,结果仍有精度丢失
(2)常用的加减乘除在该类中方法对应为:
加------f1.add(f2);
减------f1.subtract(f2);
乘------f1.multiply(f2);
除------f1.divide(f2);
此处的f1,f2均为BigDecimal类型数据
(3)源码
1 package day1; 2 3 4 import java.math.BigDecimal; 5 6 public class TestBigDecimal 7 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) 9 { 10 BigDecimal f1 = new BigDecimal("0.05"); 11 BigDecimal f2 = BigDecimal.valueOf(0.01); 12 BigDecimal f3 = new BigDecimal(0.05); 13 System.out.println("下面使用String作为BigDecimal构造器参数的计算结果:"); 14 System.out.println("0.05 + 0.01 = " + f1.add(f2)); 15 System.out.println("0.05 - 0.01 = " + f1.subtract(f2)); 16 System.out.println("0.05 * 0.01 = " + f1.multiply(f2)); 17 System.out.println("0.05 / 0.01 = " + f1.divide(f2)); 18 System.out.println("下面使用double作为BigDecimal构造器参数的计算结果:"); 19 System.out.println("0.05 + 0.01 = " + f3.add(f2)); 20 System.out.println("0.05 - 0.01 = " + f3.subtract(f2)); 21 System.out.println("0.05 * 0.01 = " + f3.multiply(f2)); 22 System.out.println("0.05 / 0.01 = " + f3.divide(f2)); 23 } 24 }
(4)运行结果
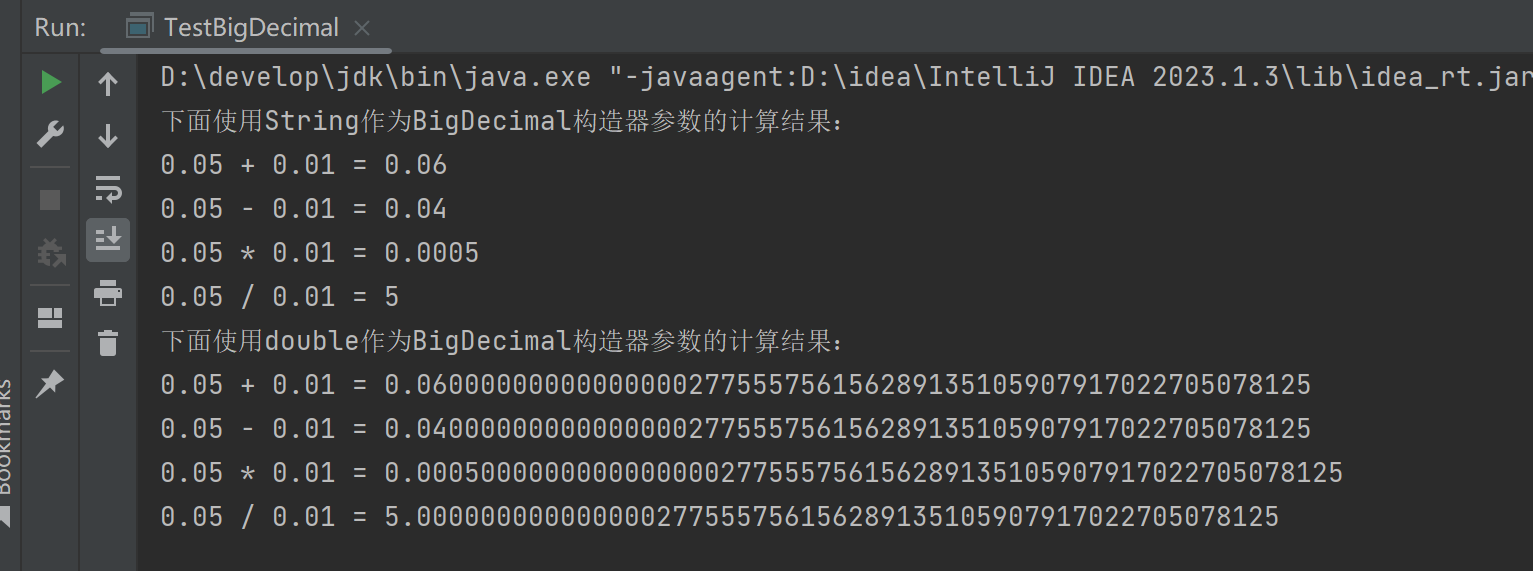
(5)总结
在遇到精度丢失的问题时,使用BigDecimal类,转化为String类型进行计算;
三、字符串拼接问题
(1)问题

(2)源码
1 package day1; 2 3 public class StringTest { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 int x=10; 6 int y=20; 7 System.out.println("X+Y="+x+y); 8 System.out.println("X+Y="+(x+y)); 9 System.out.println(x+y+"=X+Y"); 10 } 11 }
(3)运行结果
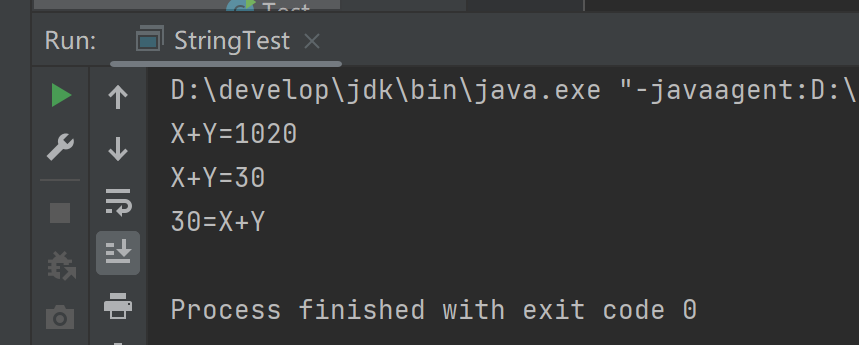
(4)分析与总结
当一个字符串后遇到“+”时,为字符串拼接操作
当一个字符串+另一个字符串时,同样为字符串拼接
当int+一个字符串时,结果仍为字符串拼接
当int+int,结果为两数相加
四、随机生成六位验证码问题
(1)问题
随机生成六位验证码
(2)源码
1 package xunlian; 2 3 import java.util.Random; 4 5 public class lianxi { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 Random r=new Random(); 8 String res=""; 9 for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) { 10 int a=r.nextInt(26)+97; 11 char c=(char)(a); 12 res=res+c; 13 } 14 System.out.println(res); 15 } 16 }
(3)运行结果
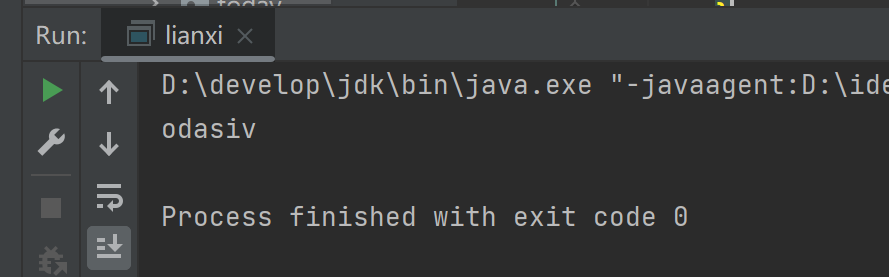
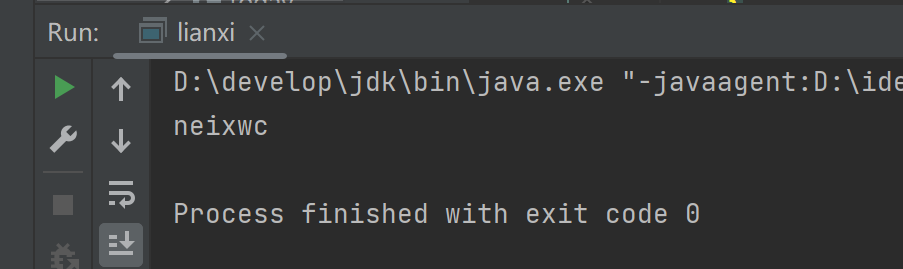
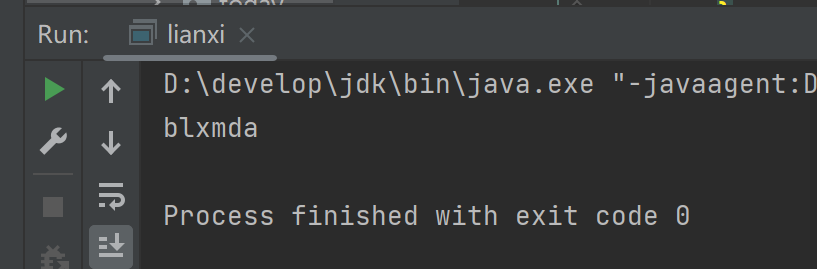
(4)总结
使用Random生成随机数,因为需要26位字母,在ASCII表中查找其对应的ASCII表中的值,随机生成,最后拼接进行输出
五、图形化界面实现两数相加
(1)源码
1 package day1; 2 3 // An addition program 4 5 import javax.swing.JOptionPane; // import class JOptionPane 6 7 public class Addition { 8 public static void main( String args[] ) 9 { 10 String firstNumber, // first string entered by user 11 secondNumber; // second string entered by user 12 int number1, // first number to add 13 number2, // second number to add 14 sum; // sum of number1 and number2 15 16 // read in first number from user as a string 17 firstNumber = 18 JOptionPane.showInputDialog( "Enter first integer" ); 19 20 // read in second number from user as a string 21 secondNumber = 22 JOptionPane.showInputDialog( "Enter second integer" ); 23 24 // convert numbers from type String to type int 25 number1 = Integer.parseInt( firstNumber ); 26 number2 = Integer.parseInt( secondNumber ); 27 28 // add the numbers 29 sum = number1 + number2; 30 31 // display the results 32 JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( 33 null, "The sum is " + sum, "Results", 34 JOptionPane.PLAIN_MESSAGE ); 35 36 System.exit( 0 ); // terminate the program 37 } 38 }
(2)运行结果
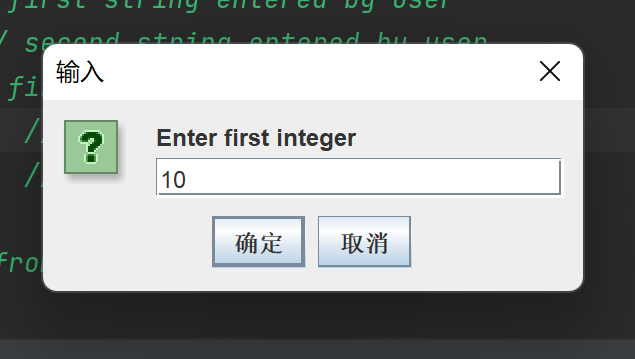
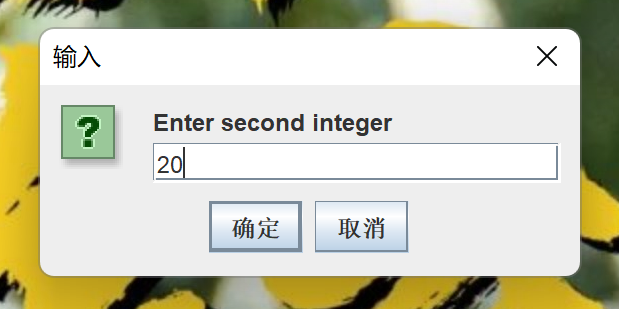
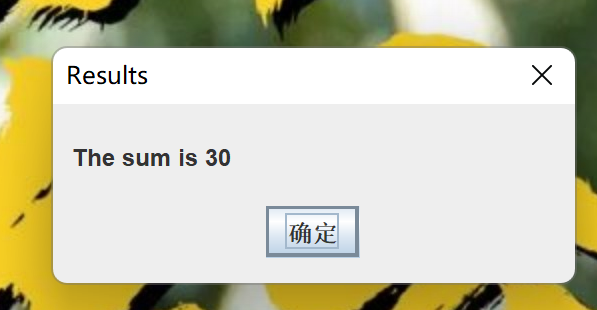
(3)总结
图形化界面的使用还需要再进一步学习



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号