递归
递归(英语:Recursion),又译为递回,在数学与计算机科学中,是指在函数的定义中使用函数自身的方法。递归一词还较常用于描述以自相似方法重复事物的过程。例如,当两面镜子相互之间近似平行时,镜中嵌套的图像是以无限递归的形式出现的。
递归的要点:
1、找到相似性
2、设计出口
斐波那契数列是典型的递归案例:
 (初始值)
(初始值)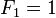 (初始值)
(初始值)- 对所有大于1的整数n:
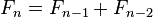 (递归定义)
(递归定义)
举例:
1、简单循环
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void fun(int begin, int end)
{
if(begin > end)
{
return;
}
else
{
cout << begin << endl;
fun(begin + 1, end);
}
}
int main()
{
fun(0, 9);
return 0;
}2、求和累加
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int fun(int begin, int end)
{
if(begin == end) return begin;
return begin + fun(begin+1, end);
}
int main()
{
cout << fun(1, 100) << endl;
return 0;
}3、字符串翻转
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
void fun(char *str, int begin, int end)
{
if(begin >= end) return;
char c = str[begin];
str[begin] = str[end];
str[end] = c;
fun(str, begin+1, end-1);
}
int main()
{
char str[] = "abcdef";
int length = strlen(str);
fun(str, 0, length - 1);
cout << str << endl;
return 0;
}4、输出全排列(STL中有next_permutation)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int n = 0;
void swap(int *a, int *b)
{
int m;
m = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = m;
}
void perm(int list[], int k, int m)
{
int i;
if(k > m)
{
for(i = 0; i <= m; i++)
{
cout << list[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
n++;
}
else
{
for(i = k; i <= m; i++)
{
swap(&list[k], &list[i]);
perm(list, k + 1, m);
swap(&list[k], &list[i]);
}
}
}
int main()
{
int list[] = {1, 2, 3};
perm(list, 0, 2);
cout << "total = " << n << endl;
return 0;
} Keep it simple!




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号