扫描线算法 学习笔记
概述
一种算法,常用于计算几何。大致思路是在其中一维维护一根扫描线,用一个数据结构维护被这条线所截的另一维信息。
例题
面积并是扫描线的一个比较典的应用。
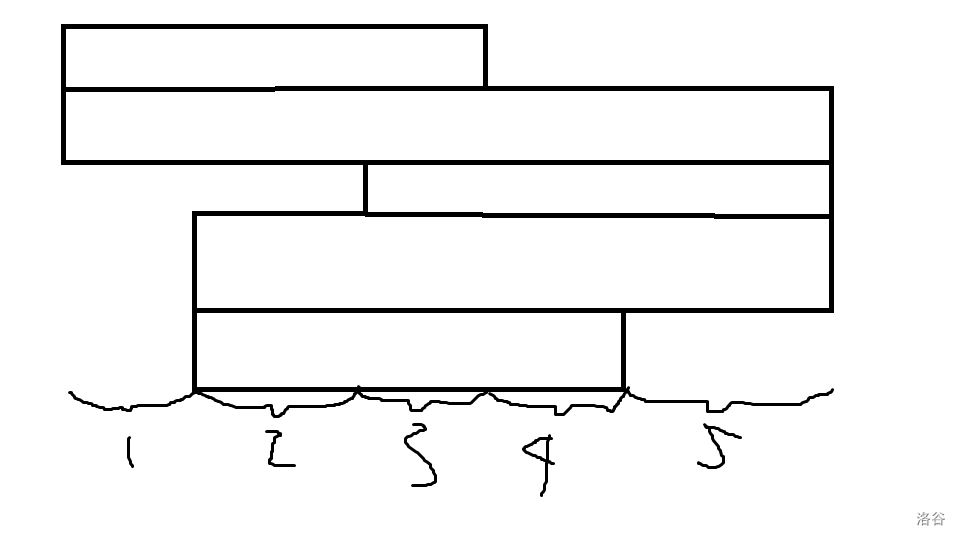
假设有一根横向的扫描线从下往上扫,遇到一个矩形的上下边会停止,这根线会把矩形的并分成若干矩形,高为相邻两条边的高度差,宽为矩形的并覆盖扫描线的长度。
用线段树维护这个过程。维护上下边的端点之间的部分(不是端点),遇到一条上边为区间加一,下边为区间减一,要维护全局有几个位置不为 \(0\)。
对于线段树上的每个节点,维护两个值:当前区间被覆盖的次数、当前区间有几个位置不为 \(0\)。由于只需要用到根节点的值,考虑标记永久化。在 pushup 操作中,如果当前节点有标记,就把值赋值为区间长,否则用子节点更新。修改时一路 pushup 就好了。
口胡一个正确性证明:
这棵树出现错误的更新,有两种情况:区间被覆盖,但 tag 为 \(0\);区间没被覆盖,但 \(tag\) 不为 \(0\)。
对于第一种情况,这个区间的祖先被覆盖时出现。但由于只用根节点的信息,在 pushup 到这个祖先时往上会变成正确的。
对于第二种情况,如果删的是祖先,那么不会用到这个节点的信息;如果删的是儿子,那么由于加边和删边成对,不会改变这个区间的实际被覆盖情况。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,temp[200005],cnt,p[200005];
long long ans;
struct seg{
int l,r,h,v;
}a[200005];
bool cmp(seg a,seg b){
return a.h<b.h;
}
template<typename T>struct node{
T v;
int tag;
};
template<typename T,int maxn>struct SMT{
node<T>tr[maxn];
void pushup(int pos,int nl,int nr){
if(tr[pos].tag)tr[pos].v=p[nr+1]-p[nl];
else if(nl==nr)tr[pos].v=0;
else tr[pos].v=tr[pos<<1].v+tr[pos<<1|1].v;
}
void build(int pos,int nl,int nr){
tr[pos].v=tr[pos].tag=0;
if(nl!=nr){
int mid=(nl+nr)>>1;
build(pos<<1,nl,mid),build(pos<<1|1,mid+1,nr);
}
}
void add(int pos,int nl,int nr,int gl,int gr,int k){
if(gl<=nl&&nr<=gr){
tr[pos].tag+=k,pushup(pos,nl,nr);
return;
}
int mid=(nl+nr)>>1;
if(gl<=mid)add(pos<<1,nl,mid,gl,gr,k);
if(gr>mid)add(pos<<1|1,mid+1,nr,gl,gr,k);
pushup(pos,nl,nr);
}
};
SMT<long long,800005>t;
int main(){
cin>>n;
for(int i=1,t1,t2,t3,t4;i<=n;i++)cin>>t1>>t2>>t3>>t4,a[i]=seg{t1,t3,t2,1},a[n+i]=seg{t1,t3,t4,-1};
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)temp[i]=a[i].l,temp[n+i]=a[i].r;
sort(temp+1,temp+2*n+1),cnt=unique(temp+1,temp+2*n+1)-temp-1;
for(int i=1,r;i<=n;i++){
r=lower_bound(temp+1,temp+cnt+1,a[i].l)-temp,p[r]=a[i].l,a[i].l=a[n+i].l=r;
r=lower_bound(temp+1,temp+cnt+1,a[i].r)-temp,p[r]=a[i].r,a[i].r=a[n+i].r=r;
}
sort(a+1,a+2*n+1,cmp),t.build(1,1,cnt-1);
for(int i=1;i<2*n;i++)t.add(1,1,cnt-1,a[i].l,a[i].r-1,a[i].v),ans+=t.tr[1].v*(a[i+1].h-a[i].h);
return cout<<ans<<'\n',0;
}
求周长并时分别计算横边和竖边。横边的贡献为当前扫描线被覆盖的长度与上一次的长度之差(对应内凹和外凸),竖边的贡献则为扫描线被覆盖的连续段数乘高度差再乘 \(2\)。因此要多维护连续段数。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,temp[10005],cnt,p[10005];
long long ans;
struct seg{
int l,r,h,v;
}a[10005];
bool cmp(seg a,seg b){
return a.h==b.h?a.v>b.v:a.h<b.h;
}
template<typename T>struct node{
T v1,v2;
int tag;
bool lf,rf;
};
template<typename T,int maxn>struct SMT{
node<T>tr[maxn];
void pushup(int pos,int nl,int nr){
if(tr[pos].tag)tr[pos].v1=p[nr+1]-p[nl],tr[pos].v2=tr[pos].lf=tr[pos].rf=1;
else{
if(nl==nr)tr[pos].v1=tr[pos].v2=tr[pos].lf=tr[pos].rf=0;
else{
tr[pos].v1=tr[pos<<1].v1+tr[pos<<1|1].v1;
tr[pos].lf=tr[pos<<1].lf,tr[pos].rf=tr[pos<<1|1].rf;
tr[pos].v2=tr[pos<<1].v2+tr[pos<<1|1].v2-(tr[pos<<1].rf&&tr[pos<<1|1].lf);
}
}
}
void build(int pos,int nl,int nr){
tr[pos].v1=tr[pos].v2=tr[pos].tag=tr[pos].lf=tr[pos].rf=0;
if(nl!=nr){
int mid=(nl+nr)>>1;
build(pos<<1,nl,mid),build(pos<<1|1,mid+1,nr);
}
}
void add(int pos,int nl,int nr,int gl,int gr,int k){
if(gl<=nl&&nr<=gr){
tr[pos].tag+=k,pushup(pos,nl,nr);
return;
}
int mid=(nl+nr)>>1;
if(gl<=mid)add(pos<<1,nl,mid,gl,gr,k);
if(gr>mid)add(pos<<1|1,mid+1,nr,gl,gr,k);
pushup(pos,nl,nr);
}
};
SMT<int,40005>t;
int main(){
cin>>n;
for(int i=1,t1,t2,t3,t4;i<=n;i++)cin>>t1>>t2>>t3>>t4,a[i]=seg{t1,t3,t2,1},a[n+i]=seg{t1,t3,t4,-1};
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)temp[i]=a[i].l,temp[n+i]=a[i].r;
sort(temp+1,temp+2*n+1),cnt=unique(temp+1,temp+2*n+1)-temp-1;
for(int i=1,r;i<=n;i++){
r=lower_bound(temp+1,temp+cnt+1,a[i].l)-temp,p[r]=a[i].l,a[i].l=a[n+i].l=r;
r=lower_bound(temp+1,temp+cnt+1,a[i].r)-temp,p[r]=a[i].r,a[i].r=a[n+i].r=r;
}
sort(a+1,a+2*n+1,cmp),t.build(1,1,cnt-1);
for(int i=1,l;i<=2*n;i++)l=t.tr[1].v1,t.add(1,1,cnt-1,a[i].l,a[i].r-1,a[i].v),ans+=2*t.tr[1].v2*(a[i+1].h-a[i].h)+abs(t.tr[1].v1-l);
return cout<<ans<<'\n',0;
}
一个细节:高度相同的边应先加后删。否则有 hack 2 0 0 4 4 0 4 4 8。此时两个矩形的上下边重合了,若先删会统计两次中间的边。
由于圆不会相交,圆的包含关系可以看做一个树形结构。如果一个圆到这棵树的根(最外面的平面),则加上这个圆的面积,否则减去。
建树时,考虑使用扫描线。用一条直线从下往上截这些圆,如果将一个圆分成左半圆弧和右半圆弧,扫描线交的半圆弧组成一个合法的括号序列。
用 set 维护这个序列,按照扫描线交圆弧的横坐标排序。当扫描线碰到圆的下方或上方时,插入或删除一对括号。插入前,二分出插入圆弧的后驱,若后驱为左括号,说明这两个圆为兄弟关系,否则为父节点。这就可以递推出圆区域被覆盖次数的奇偶性。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n;
long long ans,f[200005],x[200005],y[200005],r[200005],now;
struct seg{
int h,id;
bool operator<(seg a)const{
return h<a.h;
}
}p[400005];
struct cmp{
double calc(int a){
if(a>0)return x[a]+sqrt(r[a]*r[a]-(now-y[a])*(now-y[a]))+1e-6;
else return x[-a]-sqrt(r[-a]*r[-a]-(now-y[-a])*(now-y[-a]));
}
bool operator()(int a,int b){
return calc(a)<calc(b);
}
};
set<int,cmp>q;
int main(){
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>x[i]>>y[i]>>r[i],p[i]=seg{y[i]-r[i],i},p[n+i]=seg{y[i]+r[i],-i};
sort(p+1,p+2*n+1);
for(int i=1,t;i<=2*n;i++){
now=p[i].h,t=p[i].id;
if(t>0){
set<int,cmp>::iterator it=q.lower_bound(t);
f[t]=(it==q.end()?1:*it>0?-f[*it]:f[-*it]),ans+=f[t]*r[t]*r[t],q.insert(t),q.insert(-t);
}
else q.erase(t),q.erase(-t);
}
return cout<<ans<<'\n',0;
}
首先有结论:至多只会变色一次。
若点 \(A\) 在第二秒变色,那么它的某个方向上有一个点 \(B\) 在第一秒变色,而点 \(B\) 的这个方向上有一个初始就有的黑点,那么点 \(A\) 会在第一秒变色,矛盾。
处理所有平行于坐标轴且不经过其他黑点的线段,按 \(y\) 轴从小到大跑扫描线。用树状数组维护 \(x\) 轴信息,对于竖边,在下端点加一,上端点减一。此时树状数组存储的是上下都有点的位置,遇到横边就把答案加上这个区间的和。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,ans,temp[100005],cnt,vis1[100005],vis2[100005],l,r;
vector<int>t1[100005],t2[100005];
struct node{
int x,y;
}a[100005];
struct seg{
int l,r,y,f;
}q[300005];
bool cmp1(node a,node b){
return a.x==b.x?a.y<b.y:a.x<b.x;
}
bool cmp2(node a,node b){
return a.y==b.y?a.x<b.x:a.y<b.y;
}
bool cmp3(seg a,seg b){
return a.y==b.y?a.f<b.f:a.y<b.y;
}
template<typename T,int maxn>struct BIT{
T tr[maxn];
void add(int x,T k){
for(;x<=n;x+=(x&-x))tr[x]+=k;
}
T query(int x,T ans=0){
for(;x;x-=(x&-x))ans+=tr[x];
return ans;
}
};
BIT<int,100005>t;
int main(){
cin>>n,ans=n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>a[i].x>>a[i].y;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)temp[i]=a[i].x;
sort(temp+1,temp+n+1),cnt=unique(temp+1,temp+n+1)-temp-1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)a[i].x=lower_bound(temp+1,temp+cnt+1,a[i].x)-temp;
cnt=0,sort(a+1,a+n+1,cmp1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)if(a[i].x==a[i+1].x)q[++cnt]=seg{a[i].x,0,a[i].y,1},q[++cnt]=seg{a[i].x,0,a[i+1].y,-1};
sort(a+1,a+n+1,cmp2);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)if(a[i].y==a[i+1].y)q[++cnt]=seg{a[i].x,a[i+1].x,a[i].y,0};
sort(q+1,q+cnt+1,cmp3);
for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++){
if(q[i].f)t.add(q[i].l,q[i].f);
else ans+=t.query(q[i].r-1)-t.query(q[i].l);
}
return cout<<ans<<'\n',0;
}
一些细节:
-
只存不经过其他点的线段,否则会重复统计。所以对点排序时要双关键字排序。
-
遇到横边不能算两个端点。
-
竖边也不能算两个端点,因此当线段的纵坐标相同时,要先删,再统计,最后加。
[[计算几何]]



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号