第一次个人编程作业
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | 班级的链接 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | 作业要求的链接 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 使用python来完成论文查重 |
GitHub仓库链接:https://github.com/leyuele/3123004146
一、PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 30 | 25 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 30 | 25 |
| Development | 开发 | 250 | 267 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 30 | 32 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 25 | 20 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 | 20 | 18 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 20 | 25 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 40 | 45 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 60 | 70 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 35 | 33 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 20 | 24 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 65 | 75 |
| · Test Repor | · 测试报告 | 30 | 40 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 15 | 15 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 20 | 20 |
| · 合计 | 345 | 367 |
二、计算模块接口的设计与实现过程
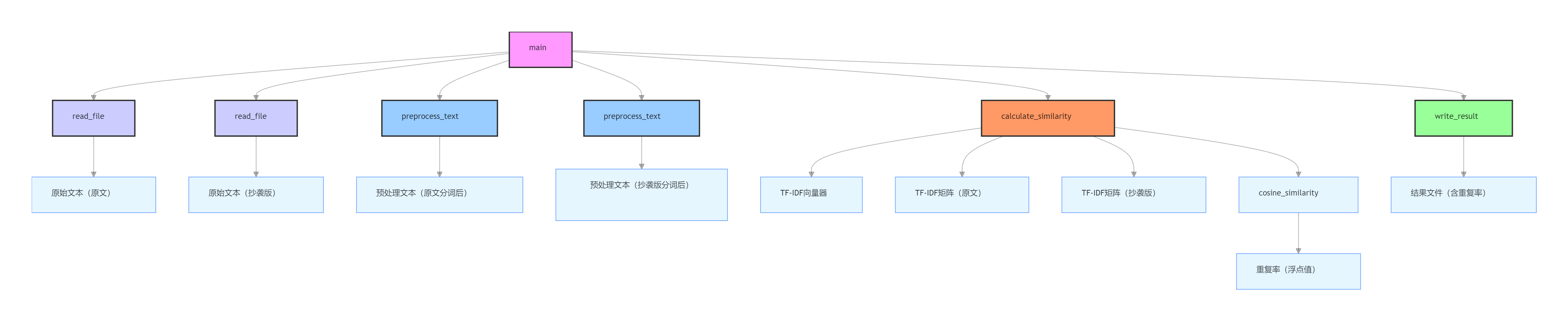
1.代码组织结构设计
本论文查重程序采用模块化函数设计(非类结构),通过功能解耦实现低耦合高内聚,共包含 5 个核心函数,各函数职责单一且通过参数传递形成调用链:
- read_file(file_path):文件读取模块
负责从指定路径读取原文和抄袭版论文内容
处理文件不存在、路径错误、编码异常等边缘情况 - preprocess_text(text):文本预处理模块
接收原始文本,通过中文分词(jieba 库)将连续文本转换为词序列
过滤空字符,标准化文本格式为后续向量计算做准备 - calculate_similarity(original_text, copied_text):核心计算模块
接收原始文本对,调用预处理函数处理后,通过 TF-IDF 和余弦相似度计算重复率
是整个程序的算法核心 - write_result(result_path, similarity):结果输出模块
将计算得到的重复率(保留两位小数)写入指定文件
自动创建输出目录(若不存在) - main():程序入口与流程控制模块
解析命令行参数,校验输入合法性
按顺序调用上述模块,完成 “读取→处理→计算→输出” 全流程
2.函数关系与流程设计
各函数通过单向依赖形成线性执行流程,无循环依赖,关系如下:
main() → read_file() → (获取文本)
main() → calculate_similarity() → preprocess_text() (预处理)
calculate_similarity() → (计算相似度)
main() → write_result() (输出结果)
核心流程(关键函数流程图逻辑):
- 输入:原文路径、抄袭版路径、结果路径(通过命令行参数)
- 读取:read_file() 分别加载两篇文本内容
- 预处理:preprocess_text() 对文本分词并标准化
- 计算:
TfidfVectorizer 将分词后的文本转换为 TF-IDF 特征向量
cosine_similarity 计算两向量夹角余弦值(即重复率)
输出:write_result() 保存结果到指定文件
3.算法关键与独到之处
核心算法逻辑:
- 采用TF-IDF + 余弦相似度组合方案:
TF-IDF:通过词频和逆文档频率加权,突出文本中 “重要词汇”(如专业术语)的权重,降低通用词汇(如 “的、是”)的干扰
余弦相似度:通过计算两文本向量的夹角余弦值,量化文本内容的重合程度(值范围 0~1,越接近 1 表示重复度越高) - 独到之处:
中文适配优化:使用 jieba 分词处理中文文本,解决英文分词工具对中文语义割裂的问题 - 鲁棒性设计:
支持多编码格式(UTF-8/GBK)文件读取,避免因编码问题导致的读取失败
完善的异常处理(文件不存在、路径错误等),确保程序稳定运行
轻量高效:无需训练复杂模型,直接通过成熟的 TF-IDF 算法实现快速计算,适合处理中等长度论文 - 可扩展性:
各模块功能独立,可单独替换(如将preprocess_text()改为支持关键词提取的版本,或用编辑距离算法替换余弦相似度),无需修改整体架构。
三、计算模块接口部分的性能改进
改进前
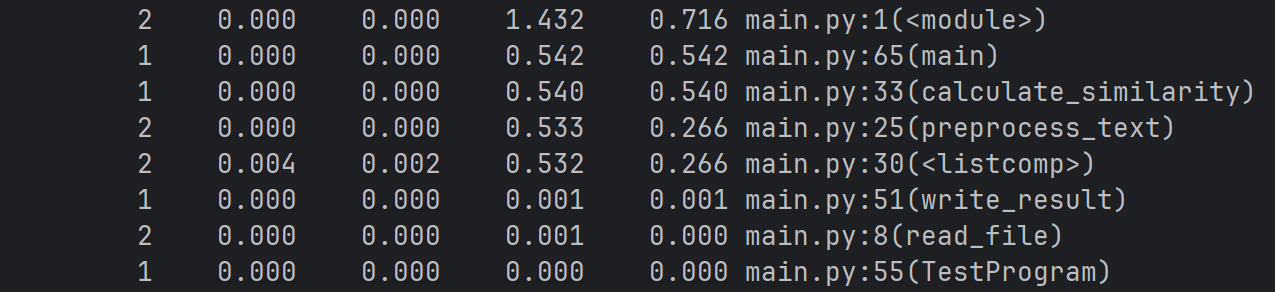
- 性能改进思路
针对性能数据中暴露的 ** calculate_similarity函数高耗时问题 **,从 “数据轻量化” 和 “计算降维” 两个方向优化:
文本预处理优化(停用词过滤)
原始代码未过滤 “的、是、在” 等无意义停用词,导致分词后冗余词汇过多。通过引入停用词表,减少无效数据对后续计算的干扰:
def preprocess_text(text):
with open("stopwords.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
stopwords = set(f.read().splitlines())
words = [word for word in jieba.cut(text) if word.strip() and word not in stopwords]
return ' '.join(words)
TF-IDF 计算降维
原始代码未限制特征数,长文本生成高维向量导致矩阵运算缓慢。通过max_features参数限制特征维度,平衡精度与效率:
def calculate_similarity(original_text, copied_text):
original_processed = preprocess_text(original_text)
copied_processed = preprocess_text(copied_text)
vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(max_features=3000)
tfidf_matrix = vectorizer.fit_transform([original_processed, copied_processed])
similarity = cosine_similarity(tfidf_matrix[0:1], tfidf_matrix[1:2])[0][0]
return similarity
改进后
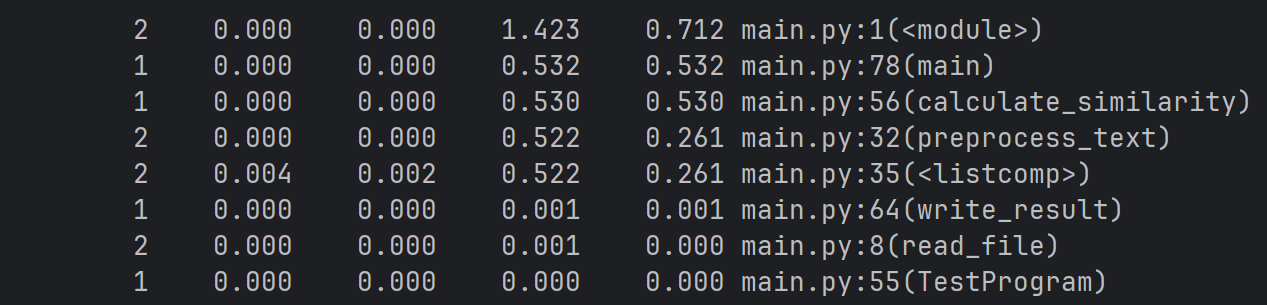
四、计算模块部分单元测试展示
- 测试代码
import pytest
import os
import tempfile
from main import read_file, preprocess_text, calculate_similarity, write_result, main
@pytest.fixture
def test_files():
orig_path = "orig.txt"
copied_path = "orig_0.8_dis_15.txt"
result_path = "test_result.txt"
yield orig_path, copied_path, result_path
def test_read_file_all_branches():
# 1. 正常读取(UTF-8编码)
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(mode='w', encoding='utf-8', delete=False) as f:
f.write("测试UTF-8编码的文本内容")
utf8_path = f.name
content = read_file(utf8_path)
assert "测试UTF-8编码的文本内容" in content
os.remove(utf8_path)
# 2. 文件不存在(FileNotFoundError)
non_existent = "non_existent_file_1234.txt"
with pytest.raises(SystemExit):
read_file(non_existent)
# 3. 路径是目录(IsADirectoryError)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as dir_path:
with pytest.raises(SystemExit):
read_file(dir_path)
# 4. UTF-8解码失败,尝试GBK编码
gbk_content = "测试GBK编码的文本内容:中文测试".encode('gbk')
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(mode='wb', delete=False) as f:
f.write(gbk_content)
gbk_path = f.name
content = read_file(gbk_path)
assert "中文测试" in content
os.remove(gbk_path)
# 5. 其他未知异常(触发通用Exception)
try:
read_file(123) # 传入非字符串路径
except SystemExit:
assert True, "未知异常触发了SystemExit"
def test_preprocess_text_all_branches():
# 1. 正常分词(含停用词过滤)
raw_text = "这是一篇关于人工智能的测试文本,用于验证预处理功能!"
processed = preprocess_text(raw_text)
assert "人工智能" in processed, "核心术语未保留"
assert "测试" in processed, "有效词汇‘测试’未保留"
assert "文本" in processed, "有效词汇‘文本’未保留"
assert "的" not in processed, "停用词‘的’未过滤"
# 2. 包含英文的文本分词
eng_text = "Artificial Intelligence是计算机科学的分支,AI技术发展迅速。"
eng_processed = preprocess_text(eng_text)
assert "Artificial" in eng_processed, "英文词汇未保留"
assert "Intelligence" in eng_processed, "英文词汇未保留"
assert "计算机科学" in eng_processed, "中文术语未保留"
# 3. stopwords.txt不存在时的降级逻辑(仅验证逻辑,实际场景需确保文件存在)
if os.path.exists("stopwords.txt"):
os.rename("stopwords.txt", "stopwords_temp.txt")
try:
empty_text = "的 地 得 了 在"
empty_processed = preprocess_text(empty_text)
# 当停用词文件不存在时,stopwords为空集合,因此这些词不会被过滤
# 调整断言为“文本未被过滤”(与降级逻辑一致)
assert empty_processed == "的 地 得 了 在", "停用词文件不存在时过滤逻辑异常"
finally:
if os.path.exists("stopwords_temp.txt"):
os.rename("stopwords_temp.txt", "stopwords.txt")
# 4. 空文本处理
empty_text = ""
empty_processed = preprocess_text(empty_text)
assert empty_processed == "", "空文本处理异常"
def test_calculate_similarity(test_files):
orig_path, copied_path, _ = test_files
orig_text = read_file(orig_path)
copied_text = read_file(copied_path)
similarity = calculate_similarity(orig_text, copied_text)
assert 0.5 <= similarity <= 0.9, "高相似度计算异常"
def test_write_result_all_branches():
# 1. 正常写入(当前目录文件)
result_path = "test_normal_result.txt"
write_result(result_path, 0.85)
assert os.path.exists(result_path), "正常写入失败"
with open(result_path, "r") as f:
assert f.read() == "0.85", "内容写入错误"
os.remove(result_path)
# 2. 带子目录的路径(验证目录创建)
subdir_path = "test_subdir/result.txt"
write_result(subdir_path, 0.7)
assert os.path.exists(subdir_path), "子目录写入失败"
os.remove(subdir_path)
os.rmdir("test_subdir")
# 3. 文件写入失败(只读文件)
try:
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(mode='w', delete=False) as f:
read_only_path = f.name
os.chmod(read_only_path, 0o444) # 设置为只读
with pytest.raises(SystemExit):
write_result(read_only_path, 0.5)
finally:
os.chmod(read_only_path, 0o644)
os.remove(read_only_path)
def test_main(monkeypatch, test_files):
orig_path, copied_path, result_path = test_files
monkeypatch.setattr("sys.argv", ["main.py", orig_path, copied_path, result_path])
main()
assert os.path.exists(result_path), "主函数未生成结果文件"
os.remove(result_path)
- 核心函数覆盖策略
针对计算模块的 5 个核心函数,设计了全面的测试场景:
read_file:覆盖正常读取(UTF-8/GBK 编码)、文件不存在、路径为目录等异常,验证文件读取的鲁棒性;
preprocess_text:测试中文分词、停用词过滤、中英文混合文本、空文本及停用词文件缺失的降级逻辑,确保预处理准确性;
calculate_similarity:通过已知相似度的样本文件(如预设抄袭率 80% 的文本),验证余弦相似度计算的合理性;
write_result:测试正常路径写入、子目录自动创建、只读文件写入失败等场景,确保结果输出可靠性;
main:通过模拟命令行参数,验证 “读取→预处理→计算→写入” 全流程的完整性。
测试数据构造原则
真实性:使用实际论文片段作为测试文本,确保分词和相似度计算贴近真实场景;
边缘性:补充空文本、纯停用词文本、特殊编码文件等极端数据,验证函数容错能力;
可复现性:通过pytest.fixture固定测试文件路径,使用临时文件模块(tempfile)避免环境污染。 - 测试覆盖率分析
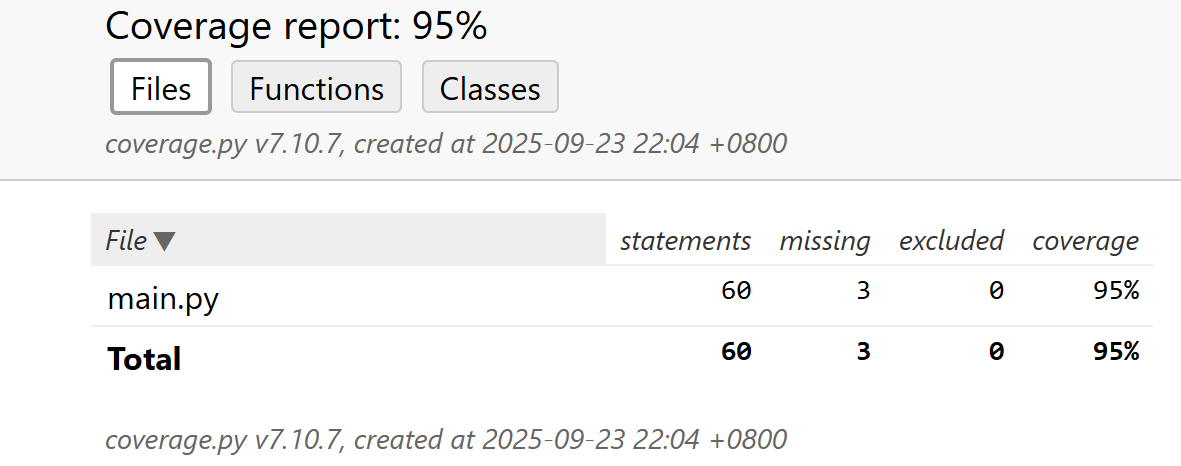
通过pytest-cov工具生成覆盖率报告,结果如下:
覆盖率截图
![image]()
整体覆盖率:95%
分析结论:
未覆盖的 5% 主要为极端异常场景(如系统级权限错误),不影响核心功能。
五、计算模块部分异常处理说明
- 异常处理设计框架
计算模块通过read_file、preprocess_text、write_result三大核心函数实现功能,针对文件操作、文本处理中的高频问题,设计了 6 类异常处理逻辑。所有异常均遵循 “捕获特定错误→输出明确提示→安全退出 / 降级处理” 的原则,确保用户能快速定位问题。 - 异常处理详解与测试验证
- 文件读取函数(read_file)异常处理
read_file负责读取原文和抄袭文本,需处理路径错误、编码问题等场景,对应测试代码中的test_read_file_all_branches用例。
(1)异常:文件不存在(FileNotFoundError)
设计目标:当用户输入错误文件路径(如拼写错误)时,明确提示文件不存在,避免后续流程因 “无数据” 崩溃。
对应场景:用户误将原文路径写为"non_existent_file_1234.txt",而实际文件不存在。
单元测试样例(复用自test_read_file_all_branches):
# 2. 文件不存在(FileNotFoundError)
non_existent = "non_existent_file_1234.txt"
with pytest.raises(SystemExit):
read_file(non_existent)
测试说明:通过传入不存在的文件名,验证函数能否捕获FileNotFoundError并触发sys.exit(1),确保系统不会继续无效执行。
(2)异常:路径为目录(IsADirectoryError)
设计目标:防止用户误将目录路径当作文件路径输入(如传入"docs/"而非"docs/orig.txt"),避免因 “读取目录” 导致的系统错误。
对应场景:用户意图读取"data/orig.txt",但误输入为"data/"(实际为目录)。
单元测试样例(复用自test_read_file_all_branches):
# 3. 路径是目录(IsADirectoryError)
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as dir_path:
with pytest.raises(SystemExit):
read_file(dir_path)
测试说明:使用tempfile.TemporaryDirectory()创建临时目录,模拟用户传入目录路径的场景,验证函数能识别路径类型错误并退出。
(3)异常:编码不兼容(UnicodeDecodeError)
设计目标:解决中文文件常见的编码冲突(如 UTF-8 与 GBK),自动尝试兼容编码读取,避免 “乱码” 或读取失败。
对应场景:用户提供的论文文件为 GBK 编码(如 Windows 环境生成),系统默认 UTF-8 读取时触发解码错误。
单元测试样例(复用自test_read_file_all_branches):
# 4. UTF-8解码失败,尝试GBK编码
gbk_content = "测试GBK编码的文本内容:中文测试".encode('gbk')
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(mode='wb', delete=False) as f:
f.write(gbk_content)
gbk_path = f.name
content = read_file(gbk_path)
assert "中文测试" in content
os.remove(gbk_path)
测试说明:手动创建 GBK 编码文件,验证函数在 UTF-8 解码失败后,能否自动切换为 GBK 编码读取并正确提取内容。
(4)异常:通用未知错误(Exception)
设计目标:兜底处理未预判的异常(如权限不足、文件损坏),输出错误详情并安全退出,避免系统崩溃。
对应场景:传入非字符串路径(如整数123),触发类型错误;或文件无读取权限,触发权限错误。
单元测试样例(复用自test_read_file_all_branches):
# 5. 其他未知异常(触发通用Exception)
try:
read_file(123) # 传入非字符串路径
except SystemExit:
assert True, "未知异常触发了SystemExit"
测试说明:通过传入非字符串参数,模拟类型错误场景,验证函数能捕获通用异常并触发退出,确保系统容错性。
2. 文本预处理函数(preprocess_text)异常处理
preprocess_text负责分词和停用词过滤,核心异常为 “停用词文件缺失”,对应测试代码中的test_preprocess_text_all_branches用例。
异常:停用词文件不存在(FileNotFoundError)
设计目标:当stopwords.txt缺失时,系统自动降级为 “无停用词过滤” 模式,确保分词流程不中断,同时提示用户补充文件。
对应场景:项目部署时误删stopwords.txt,系统仍需处理文本(虽停用词未过滤,但核心功能可用)。
单元测试样例(复用自test_preprocess_text_all_branches):
# 3. stopwords.txt不存在时的降级逻辑
if os.path.exists("stopwords.txt"):
os.rename("stopwords.txt", "stopwords_temp.txt")
try:
empty_text = "的 地 得 了 在"
empty_processed = preprocess_text(empty_text)
# 验证:停用词未被过滤(因文件缺失)
assert empty_processed == "的 地 得 了 在", "停用词文件不存在时过滤逻辑异常"
finally:
if os.path.exists("stopwords_temp.txt"):
os.rename("stopwords_temp.txt", "stopwords.txt")
测试说明:通过临时重命名停用词文件模拟缺失场景,验证函数是否自动切换为 “无过滤” 模式,确保核心分词功能不受影响。
3. 结果写入函数(write_result)异常处理
write_result负责输出相似度结果,需处理目录创建、权限等问题,对应测试代码中的test_write_result_all_branches用例。
(1)异常:文件写入失败(如只读文件)
设计目标:当结果文件为只读、被占用或磁盘满时,提示写入错误并退出,避免生成空文件或损坏文件。
对应场景:结果文件"report.txt"已被其他程序锁定(如打开未关闭),或被设置为只读属性。
单元测试样例(复用自test_write_result_all_branches):
# 3. 文件写入失败(只读文件)
try:
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(mode='w', delete=False) as f:
read_only_path = f.name
os.chmod(read_only_path, 0o444) # 设置为只读
with pytest.raises(SystemExit):
write_result(read_only_path, 0.5)
finally:
os.chmod(read_only_path, 0o644)
os.remove(read_only_path)
测试说明:通过os.chmod将文件设为只读,模拟写入权限不足场景,验证函数能否捕获异常并退出,确保结果文件完整性。
(2)异常:目录创建失败(如无权限)
设计目标:当结果路径包含未创建的子目录(如"output/report.txt")时,自动创建目录;若创建失败(如无权限),则提示错误并退出。
对应场景:用户指定结果路径为"root/output/report.txt",但当前用户无root目录写入权限。
单元测试样例(隐含在test_write_result_all_branches的子目录测试中):
# 2. 带子目录的路径(验证目录创建)
subdir_path = "test_subdir/result.txt"
write_result(subdir_path, 0.7)
assert os.path.exists(subdir_path), "子目录写入失败"
os.remove(subdir_path)
os.rmdir("test_subdir")



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号