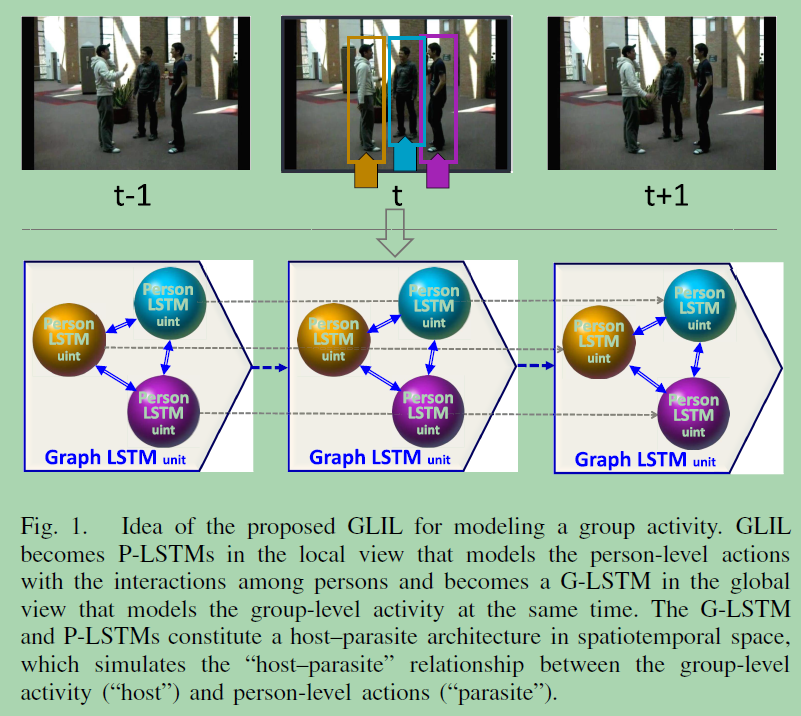
Host–Parasite(主从关系): Graph LSTM-in-LSTM for Group Activity Recognition
This article aims to tackle the problem of group activity recognition in the multiple-person scene.
1)以往模型忽略:most long short-term memory (LSTM)-based methods first learn the person-level action representations by several LSTMs and then integrate all the person-level action representations into the following LSTM to learn the group-level activity representation.
从个体动作层面-->到群体层面。a two-stage strategy。在对话中也是这样,HRED。
但是忽略了时空层面的主从关系?
which neglects the “host-parasite” relationship between the group-level activity (“host”) and person-level actions (“parasite”) in spatiotemporal space.
2)propose a novel graph LSTM-in-LSTM (GLIL) for group activity recognition by modeling the person-level actions and group-level activity simultaneously.
“host-parasite” architecture, which can be seen as several person LSTMs (P-LSTMs) in the local view or a graph LSTM(G-LSTM) in the global view.
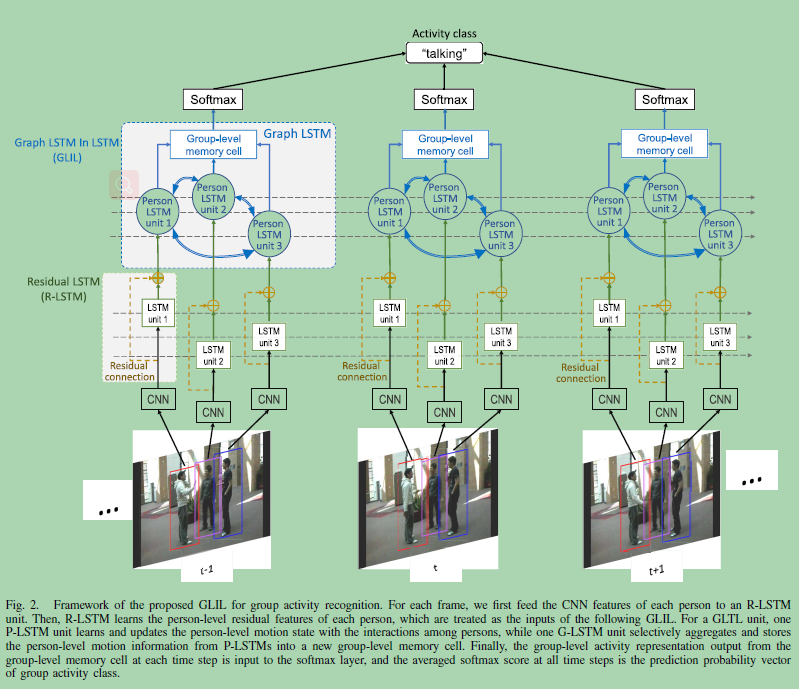
The training framework of GLIL is shown in Fig. 2, which stacks:
- a pretrained CNN, :extract the static features (i.e., CNN features) of each person on the person’s bounding boxes.
- a residual LSTM (R-LSTM), :learn the person level residual features of each person from their static features;the person-level temporal features
- the GLIL,
- P-LSTM in GLIL learns and updates the person-level motion state of one person under the interaction with other persons,
- a G-LSTM in GLIL selectively aggregates the person-level motion information from P-LSTM into a new group-level memory cell over time.
Finally, we feed the group-level activity representation output from GLIL into the softmax layer at each time step and then average the outputs of all the softmax classifiers to infer the class of group activity.
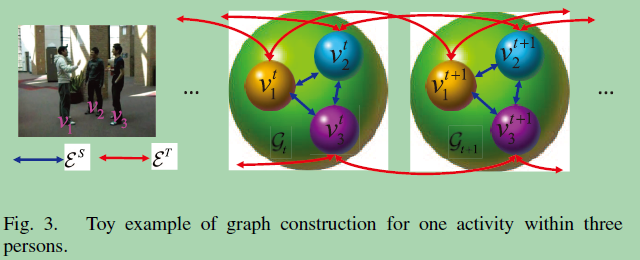
考虑了两种类型的邻居:in the spatial space and the temporal space?
1)时间维度上:有两条连边,与前一时刻和后一时刻。
2)空间维度上:有n-1条连边,与空间上的所有邻居结点。
本文最大的创新点在于:对于graph structure 的时空结构,设计了对于结点的LSTM更新(考虑了邻居结点的信息聚合(邻居信息的交互),对LSTM的影响,获得记忆状态和结点表示h);对于图结构的表示,设计了关于每个结点的记忆状态C的聚合(利用了上一时刻的隐状态计算和单人的行为和群体行为的相关性),然后得到整个图,即群体行为的表示h’。从而预测。
在空间维度上,利用的很充分,对于每个结点的表示更新都考虑了当前,上一时刻,邻居。
在时间维度上,利用了上一时刻的h,c
重点关注:
1)P-LSTMs: the interactions among persons under a new interaction gate
For a group activity, each video frame contains multiple-persons’ motion information, which is interrelated in both the spatial space and temporal space. In this article, we consider constructing a graph to explore such relations among persons’ motion. Specifically, the nodes of the graph can represent the state of data, and the edges can capture the spatiotemporal interactions among nodes.
对于一个群体活动,每个视频帧都包含着多人的运动信息,这些信息在空间空间和时间空间上都是相互关联的。在本文中,我们考虑构造一个图来探讨人的运动之间的这种关系。具体来说,图的节点可以代表数据的状态,图的边可以捕捉节点之间的时空交互。
we add a residual connection across the input and the output of LSTM
Such residual connection can provide better flexibility to deal with the gradient vanishing or exploding in the learning process
In the local view, GLIL becomes P-LSTMs that model the person-level motions by the neighboring interaction under an interaction gate.
邻居间的相互作用(通过一个来interaction gate呈现)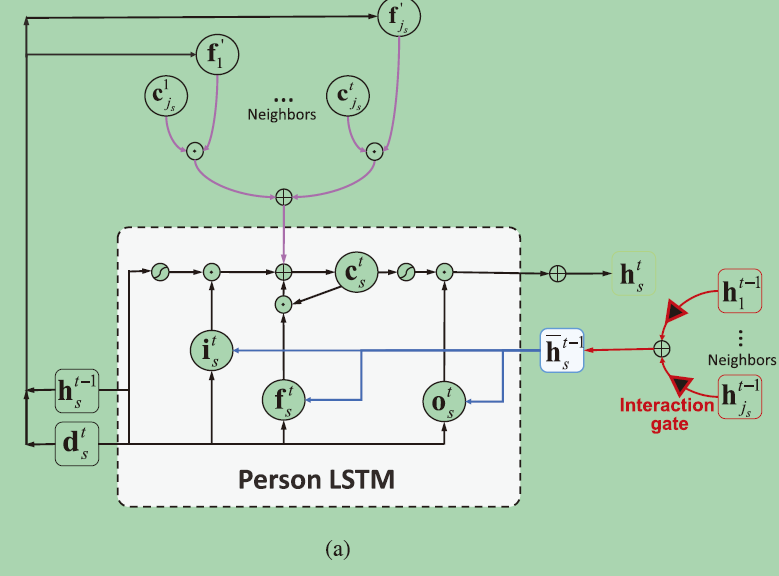


对Person-Level的动作表示:
三种输入:当前时刻的结点状态d, 上一时刻结点的隐藏层状态h,邻居结点的上一时刻状态的组合。
计算四个门: 输入门,遗忘门,输出门,邻居遗忘门。
最终计算:当前时刻的记忆状态:memory cell Ct,( cts is the person-level memory cell at time step t.)-->ht
将邻居的隐状态加权求和。Interaction Gate:利用两个人的特征相似度和位置相似度来衡量他们的互动。quantify the interaction between two persons at time step t

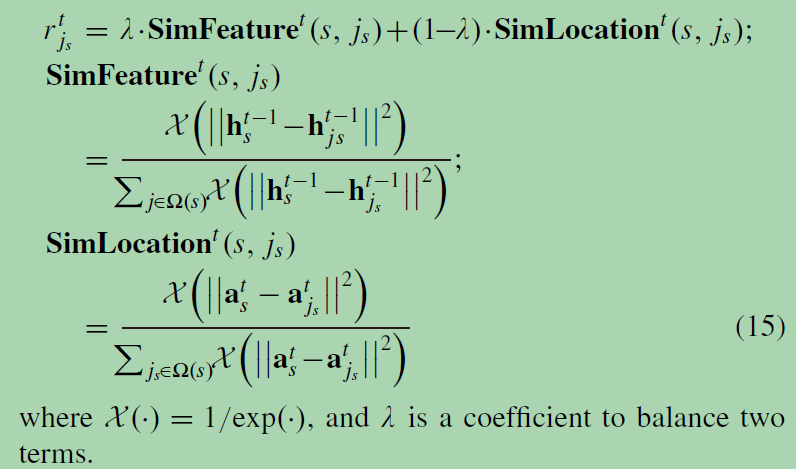
Host Architecture of GLIL
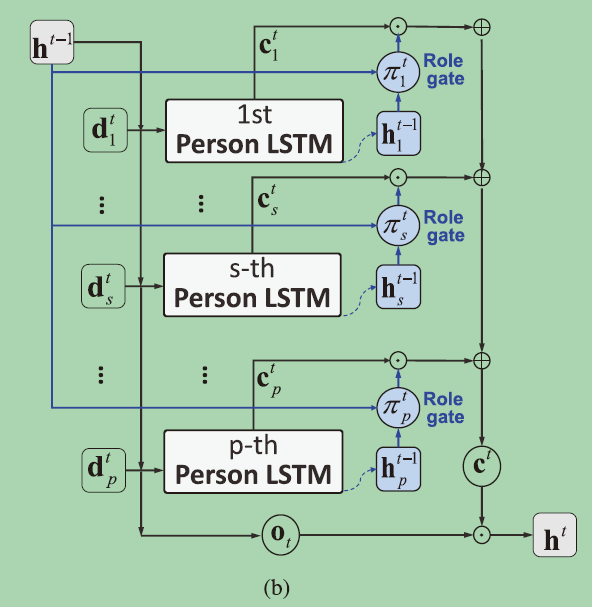
what type of person-level motion is useful to infer the class of group activity?
we can set a gate to control what types of person-level motion information would enter or leave the group-level memory cell over time.
we design a new role gate Pi_ts at time step t to allow the person-level motion of the sth person to enter or level group-level memory cell.
如何区别对待,衡量个人行为对群体行为的相关性,因此,我们测量了在前一个时间步上群体级活动表示和人级行动表示的标签推理的一致性->添加一个门:






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号