机器学习基础(三)Logistic回归模型 分类: 机器学习 2015-01-18 10:50 85人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
Logistic回归模型是引入Logistic函数后对线性回归模型进行的归一化处理:
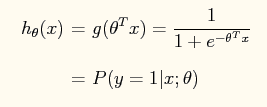
这样处理的结果是输出的结果在[0,1]之内,避免了某个特征影响过大。从概率的角度,我们可以将其理解为某个事件发生的可能性。
代价函数为:
![\begin{displaymath}J(\theta)=\frac{{1}}{m}\sum_{i=1}^{m}\left[-y^{(i)}\log(h_......(1-y^{(i)})\log(1-h_{\theta}(x^{(i)}))\right] \nonumber\par\end{displaymath}](http://openclassroom.stanford.edu/MainFolder/courses/DeepLearning/exercises/ex4/img8.png)
这个代价函数的推导涉及到极大似然估计,推导如下:
整合上面两式:
在独立同分布的前提下,似然函数:
取对数:
可以看出代价函数多了一步均值化处理。
对于Logistic回归模型的求解有两种方法:梯度下降法和牛顿法
梯度下降法求解
得到
这里我们可以看出Logistic函数本身也具有许多良好的性质,比如其导数:
牛顿法:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Newton%27s_method

牛顿法的迭代模型:
扩展到高维:

其中

![\begin{displaymath}H & = & \frac{1}{m}\sum_{i=1}^{m}\left[h_{\theta}(x^{(i)})\l......^{(i)})\right)x^{(i)}\left(x^{(i)}\right)^{T}\right] \nonumber\end{displaymath}](http://openclassroom.stanford.edu/MainFolder/courses/MachineLearning/exercises/ex4/img11.png)
参考资料:
http://www.netfoucs.com/article/yangliuy/62606.html
http://openclassroom.stanford.edu/MainFolder/DocumentPage.php?course=MachineLearning&doc=exercises/ex4/ex4.html
http://openclassroom.stanford.edu/MainFolder/CoursePage.php?course=MachineLearning
http://hi.baidu.com/hehehehello/item/40025c33d7d9b7b9633aff87#send
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号