25-x 第二十五章 总结与测验
至此,我们对C++继承与虚函数的探索之旅已然结束。亲爱的读者,不必忧虑,随着我们继续前行,C++还有诸多领域等待我们去探索。
章节总结
C++允许将基类指针和引用指向派生对象。当需要编写能处理任何基类派生对象的函数或数组时,此特性尤为实用。
若无虚函数,指向派生类的基类指针和引用仅能访问基类的成员变量及函数版本。
虚函数是一种特殊函数,它会解析为基类与派生类之间存在的最高派生版本函数(称为重写函数)。要被视为重写函数,派生类函数必须与虚基类函数具有相同的签名和返回类型。唯一例外是协变返回类型:当基类函数返回基类指针或引用时,重写函数可返回派生类指针或引用。
若需确保函数被重写,应使用重写限定符。
最终限定符可用于禁止函数重写或类继承。
若需使用继承,应将析构函数设为虚函数,以便删除基类指针时调用正确的析构函数。
可通过作用域解析运算符直接指定所需函数版本来绕过虚函数解析,例如:base.Base::getName()。
当编译器遇到直接函数调用时发生早期绑定,此时编译器或链接器可直接解析函数调用。当调用函数指针时发生晚期绑定。此类情况下,需运行时才能确定调用哪个函数。虚函数通过晚期绑定和虚函数表来确定调用哪个函数版本。
使用虚函数存在代价:虚函数调用耗时更长,且虚函数表的存在会使每个包含虚函数的对象增加一个指针的大小。
通过在虚函数原型末尾添加“= 0”,可将虚函数定义为纯虚函数/抽象函数。包含纯虚函数的类称为抽象类,不可实例化。继承纯虚函数的类必须具体实现这些函数,否则也将被视为抽象类。纯虚函数可以拥有函数体,但仍被视为抽象函数。
接口类是指不含成员变量且所有函数均为纯虚函数的类,其名称通常以大写字母I开头。
虚拟基类是指无论被对象继承多少次,都仅需包含一次的基类。
当派生类被赋值给基类对象时,基类仅接收派生类基部分的副本,此现象称为对象切片。
动态转换可将基类对象指针转换为派生类对象指针,此操作称为向下转换。转换失败时将返回空指针。
为继承类重载<<运算符的最简方法是:在最基类中实现重载的<<运算符,再通过调用虚成员函数完成输出操作。
测验时间
以下每个程序都存在某种缺陷。请检查每个程序(通过目视检查,而非编译运行),找出程序的问题所在。每个程序的预期输出应为“Derived”。
1a)
#include <iostream>
class Base
{
protected:
int m_value;
public:
Base(int value)
: m_value{ value }
{
}
const char* getName() const { return "Base"; }
};
class Derived : public Base
{
public:
Derived(int value)
: Base{ value }
{
}
const char* getName() const { return "Derived"; }
};
int main()
{
Derived d{ 5 };
Base& b{ d };
std::cout << b.getName() << '\n';
return 0;
}
解决方案:
基类方法 Base::getName() 未被声明为虚函数,因此 b.getName() 不会解析为派生类方法 Derived::getName()。
b)
#include <iostream>
class Base
{
protected:
int m_value;
public:
Base(int value)
: m_value{ value }
{
}
virtual const char* getName() { return "Base"; }
};
class Derived : public Base
{
public:
Derived(int value)
: Base{ value }
{
}
virtual const char* getName() const { return "Derived"; }
};
int main()
{
Derived d{ 5 };
Base& b{ d };
std::cout << b.getName() << '\n';
return 0;
}
解决方案
基类Base::getName()是非常量函数,而派生类Derived::getName()是常量函数,因此Derived::getName()不被视为重写。
c)
#include <iostream>
class Base
{
protected:
int m_value;
public:
Base(int value)
: m_value{ value }
{
}
virtual const char* getName() { return "Base"; }
};
class Derived : public Base
{
public:
Derived(int value)
: Base{ value }
{
}
const char* getName() override { return "Derived"; }
};
int main()
{
Derived d{ 5 };
Base b{ d };
std::cout << b.getName() << '\n';
return 0;
}
解决方案:
d被赋值给b,导致d被切片。
d)
#include <iostream>
class Base final
{
protected:
int m_value;
public:
Base(int value)
: m_value{ value }
{
}
virtual const char* getName() { return "Base"; }
};
class Derived : public Base
{
public:
Derived(int value)
: Base{ value }
{
}
const char* getName() override { return "Derived"; }
};
int main()
{
Derived d{ 5 };
Base& b{ d };
std::cout << b.getName() << '\n';
return 0;
}
解决方案
基类已被声明为最终类,因此派生类无法从其派生。这将导致编译错误。
e)
#include <iostream>
class Base
{
protected:
int m_value;
public:
Base(int value)
: m_value{ value }
{
}
virtual const char* getName() { return "Base"; }
};
class Derived : public Base
{
public:
Derived(int value)
: Base{ value }
{
}
virtual const char* getName() = 0;
};
const char* Derived::getName()
{
return "Derived";
}
int main()
{
Derived d{ 5 };
Base& b{ d };
std::cout << b.getName() << '\n';
return 0;
}
解决方案:
派生类::getName() 是一个纯虚函数(带有函数体),因此派生类是一个抽象类,无法被实例化。
f)
#include <iostream>
class Base
{
protected:
int m_value;
public:
Base(int value)
: m_value{ value }
{
}
virtual const char* getName() { return "Base"; }
};
class Derived : public Base
{
public:
Derived(int value)
: Base{ value }
{
}
virtual const char* getName() { return "Derived"; }
};
int main()
{
auto* d{ new Derived(5) };
Base* b{ d };
std::cout << b->getName() << '\n';
delete b;
return 0;
}
解决方案
该程序实际输出了正确结果,但存在另一个问题。我们正在删除基类指针 b,但基类从未添加过虚析构函数。因此程序仅删除了派生对象的基类部分,而派生部分则作为内存泄漏残留。
2a) 创建一个名为 Shape 的抽象类。该类应包含三个函数:一个纯虚函数 print(该函数接受并返回 std::ostream&),一个重载的 operator<<,以及一个空的虚析构函数。
解决方案:
class Shape
{
public:
virtual std::ostream& print(std::ostream& out) const = 0;
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const Shape& p)
{
return p.print(out);
}
virtual ~Shape() = default;
};
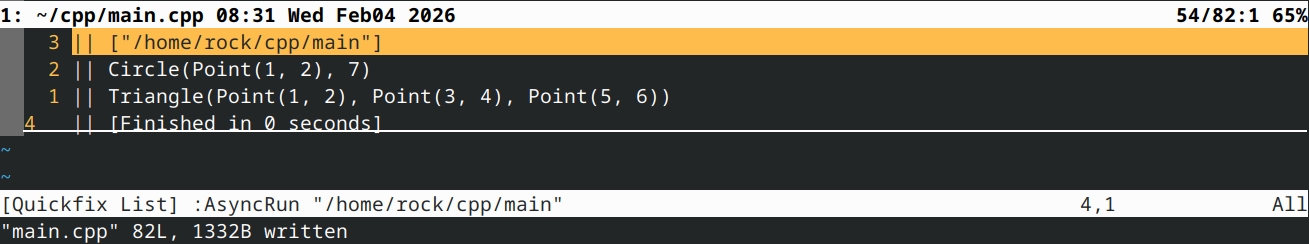
2b) 从Shape类派生出两个子类:三角形和圆形。三角形应包含3个顶点作为成员。圆形应包含一个中心点和一个整数半径。重写print()函数,使以下程序运行:
int main()
{
Circle c{ Point{ 1, 2 }, 7 };
std::cout << c << '\n';
Triangle t{Point{ 1, 2 }, Point{ 3, 4 }, Point{ 5, 6 }};
std::cout << t << '\n';
return 0;
}
这应该输出:
Circle(Point(1, 2), radius 7)
Triangle(Point(1, 2), Point(3, 4), Point(5, 6))
以下是一个可供使用的Point类:
class Point
{
private:
int m_x{};
int m_y{};
public:
Point(int x, int y)
: m_x{ x }, m_y{ y }
{
}
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const Point& p)
{
return out << "Point(" << p.m_x << ", " << p.m_y << ')';
}
};
解决方案
#include <iostream>
class Point
{
private:
int m_x{};
int m_y{};
public:
Point(int x, int y)
: m_x{ x }, m_y{ y }
{
}
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const Point& p)
{
return out << "Point(" << p.m_x << ", " << p.m_y << ')';
}
};
class Shape
{
public:
virtual std::ostream& print(std::ostream& out) const = 0;
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const Shape& p)
{
return p.print(out);
}
virtual ~Shape() = default;
};
class Triangle : public Shape
{
private:
Point m_p1;
Point m_p2;
Point m_p3;
public:
Triangle(const Point& p1, const Point& p2, const Point& p3)
: m_p1{ p1 }, m_p2{ p2 }, m_p3{ p3 }
{
}
std::ostream& print(std::ostream& out) const override
{
return out << "Triangle(" << m_p1 << ", " << m_p2 << ", " << m_p3 << ')';
}
};
class Circle : public Shape
{
private:
Point m_center;
int m_radius;
public:
Circle(const Point& center, int radius)
: m_center{ center }, m_radius{ radius }
{
}
std::ostream& print(std::ostream& out) const override
{
return out << "Circle(" << m_center << ", radius " << m_radius << ')';
}
};
int main()
{
Circle c{ Point{ 1, 2 }, 7 };
std::cout << c << '\n';
Triangle t{ Point{ 1, 2 }, Point{ 3, 4 }, Point{ 5, 6 } };
std::cout << t << '\n';
return 0;
}
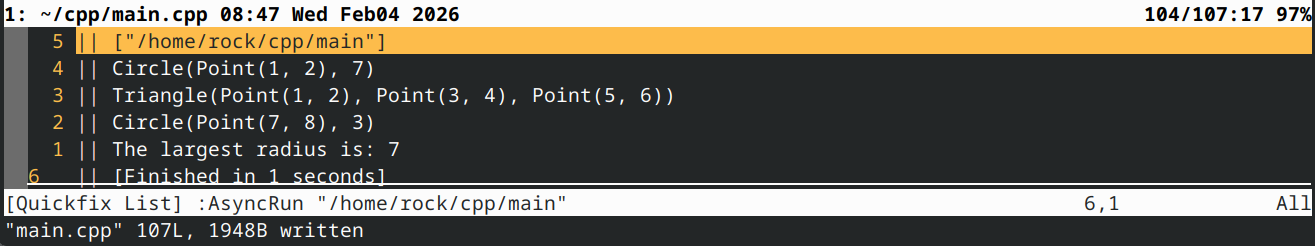
2c) 基于上述类(Point、Shape、Circle 和 Triangle),完成以下程序:
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::vector<Shape*> v{
new Circle{Point{ 1, 2 }, 7},
new Triangle{Point{ 1, 2 }, Point{ 3, 4 }, Point{ 5, 6 }},
new Circle{Point{ 7, 8 }, 3}
};
// print each shape in vector v on its own line here
std::cout << "The largest radius is: " << getLargestRadius(v) << '\n'; // write this function
// delete each element in the vector here
return 0;
}
该程序应输出以下内容:
Circle(Point(1, 2), radius 7)
Triangle(Point(1, 2), Point(3, 4), Point(5, 6))
Circle(Point(7, 8), radius 3)
The largest radius is: 7
提示:你需要在Circle类中添加一个getRadius()函数,并将Shape类型强制转换为Circle类型才能访问该函数。
解决方案
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm> // for std::max
class Point
{
private:
int m_x{};
int m_y{};
public:
Point(int x, int y)
: m_x{ x }, m_y{ y }
{
}
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const Point& p)
{
return out << "Point(" << p.m_x << ", " << p.m_y << ')';
}
};
class Shape
{
public:
virtual std::ostream& print(std::ostream& out) const = 0;
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const Shape& p)
{
return p.print(out);
}
virtual ~Shape() = default;
};
class Triangle : public Shape
{
private:
Point m_p1;
Point m_p2;
Point m_p3;
public:
Triangle(const Point& p1, const Point& p2, const Point& p3)
: m_p1{ p1 }, m_p2{ p2 }, m_p3{ p3 }
{
}
std::ostream& print(std::ostream& out) const override
{
return out << "Triangle(" << m_p1 << ", " << m_p2 << ", " << m_p3 << ')';
}
};
class Circle : public Shape
{
private:
Point m_center;
int m_radius{};
public:
Circle(const Point& center, int radius)
: m_center{ center }, m_radius{ radius }
{
}
std::ostream& print(std::ostream& out) const override
{
out << "Circle(" << m_center << ", radius " << m_radius << ')';
return out;
}
int getRadius() const { return m_radius; }
};
// h/t to reader Olivier for this updated solution
// assumes radiuses are >= 0
int getLargestRadius(const std::vector<Shape*>& v)
{
int largestRadius{ 0 };
// Loop through all the shapes in the vector
for (const auto* element : v)
{
// // Ensure the dynamic cast succeeds by checking for a null pointer result
if (auto* c { dynamic_cast<const Circle*>(element) })
{
largestRadius = std::max(largestRadius, c->getRadius());
}
}
return largestRadius;
}
int main()
{
std::vector<Shape*> v{
new Circle{Point{ 1, 2 }, 7},
new Triangle{Point{ 1, 2 }, Point{ 3, 4 }, Point{ 5, 6 }},
new Circle{Point{ 7, 8 }, 3}
};
for (const auto* element : v) // element will be a Shape*
std::cout << *element << '\n';
std::cout << "The largest radius is: " << getLargestRadius(v) << '\n';
for (const auto* element : v)
delete element;
return 0;
}
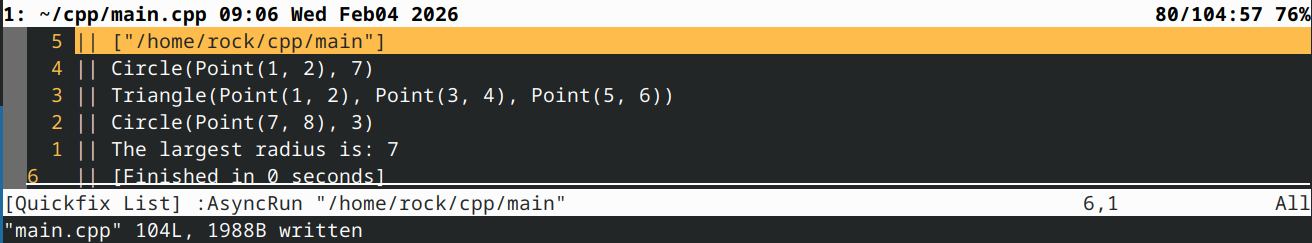
2d) 附加题:将先前解决方案更新为使用 std::vector<std::unique_ptr
感谢读者 surrealcereal 提供此思路。
显示提示
提示:您无法使用 std::initializer_list 初始化向量,因为这需要复制元素。
显示提示
提示:std::unique_ptr::get() 返回指向被管理的元素的指针。
显示解决方案
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm> // for std::max
#include <memory>
class Point
{
private:
int m_x{};
int m_y{};
public:
Point(int x, int y)
: m_x{ x }, m_y{ y }
{
}
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const Point& p)
{
return out << "Point(" << p.m_x << ", " << p.m_y << ')';
}
};
class Shape
{
public:
virtual std::ostream& print(std::ostream& out) const = 0;
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const Shape& p)
{
return p.print(out);
}
virtual ~Shape() = default;
};
class Triangle : public Shape
{
private:
Point m_p1;
Point m_p2;
Point m_p3;
public:
Triangle(const Point& p1, const Point& p2, const Point& p3)
: m_p1{ p1 }, m_p2{ p2 }, m_p3{ p3 }
{
}
std::ostream& print(std::ostream& out) const override
{
return out << "Triangle(" << m_p1 << ", " << m_p2 << ", " << m_p3 << ')';
}
};
class Circle : public Shape
{
private:
Point m_center;
int m_radius{};
public:
Circle(const Point& center, int radius)
: m_center{ center }, m_radius{ radius }
{
}
std::ostream& print(std::ostream& out) const override
{
out << "Circle(" << m_center << ", radius " << m_radius << ')';
return out;
}
int getRadius() const { return m_radius; }
};
int getLargestRadius(const std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Shape>>& v)
{
int largestRadius{ 0 };
// Loop through all the shapes in the vector
for (const auto& element : v)
{
// // Ensure the dynamic cast succeeds by checking for a null pointer result
if (auto *c { dynamic_cast<const Circle*>(element.get()) })
{
largestRadius = std::max(largestRadius, c->getRadius());
}
}
return largestRadius;
}
int main()
{
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Shape>> v;
v.reserve(3);
v.push_back(std::make_unique<Circle>(Point{1, 2}, 7));
v.push_back(std::make_unique<Triangle>(Point{1, 2}, Point{3, 4}, Point{5, 6}));
v.push_back(std::make_unique<Circle>(Point{7, 8}, 3));
for (const auto& element : v) std::cout << *element << '\n';
std::cout << "The largest radius is: " << getLargestRadius(v) << '\n';
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号