17-1 std::array 介绍
在第16.1节——容器与数组介绍中,我们介绍了容器和数组。简而言之:
容器为一组无名对象(称为元素)提供存储空间。
数组将元素连续分配在内存中,并允许通过下标快速直接访问任意元素。
C++ 常用三种数组类型:std::vector、std::array 和 C 风格数组。
在第16.10节——std::vector的动态调整与容量中,我们提到数组可分为两类:
固定长度数组(也称固定大小数组)要求在实例化时确定数组长度,且长度不可更改。C风格数组和std::array均属于此类。
动态数组可在运行时调整大小。std::vector 属于动态数组。
前一章重点探讨了 std::vector,因其速度快、使用相对简单且用途广泛。这使其成为我们需要数组容器时的首选类型。
那么为什么不把动态数组用于所有场景呢?
动态数组功能强大且便捷,但正如生活中的一切事物,它们在提供便利的同时也存在取舍。
- std::vector 的性能略逊于固定大小数组。在大多数情况下你可能不会察觉差异(除非你编写了粗糙的代码导致大量意外的重新分配)。
- std::vector 仅在极有限的场景下支持 constexpr。
在现代 C++ 中,后者才是真正关键的特性。constexpr 数组能编写更健壮的代码,同时还能获得编译器的更高优化。只要能使用 constexpr 数组就应优先采用——若需要 constexpr 数组,std::array 便是首选容器类。
最佳实践:
constexpr 数组使用 std::array,非 constexpr 数组使用 std::vector。
定义 std::array
std::array 在
其中一个区别在于声明方式:
#include <array> // for std::array
#include <vector> // for std::vector
int main()
{
std::array<int, 5> a {}; // a std::array of 5 ints
std::vector<int> b(5); // a std::vector of 5 ints (for comparison)
return 0;
}
我们的 std::array 声明包含两个模板参数。第一个参数 (int) 是类型模板参数,用于定义数组元素的类型。第二个参数 (5) 是整型非类型模板参数,用于定义数组长度。
相关内容:
我们在第 11.9 课——非类型模板参数中介绍了非类型模板参数。
std::array 的长度必须是常量表达式
与可在运行时调整大小的 std::vector 不同,std::array 的长度必须是常量表达式。通常情况下,长度参数的值应为整数常量、constexpr 变量或无作用域枚举器。
#include <array>
int main()
{
std::array<int, 7> a {}; // Using a literal constant
constexpr int len { 8 };
std::array<int, len> b {}; // Using a constexpr variable
enum Colors
{
red,
green,
blue,
max_colors
};
std::array<int, max_colors> c {}; // Using an enumerator
#define DAYS_PER_WEEK 7
std::array<int, DAYS_PER_WEEK> d {}; // Using a macro (don't do this, use a constexpr variable instead)
return 0;
}
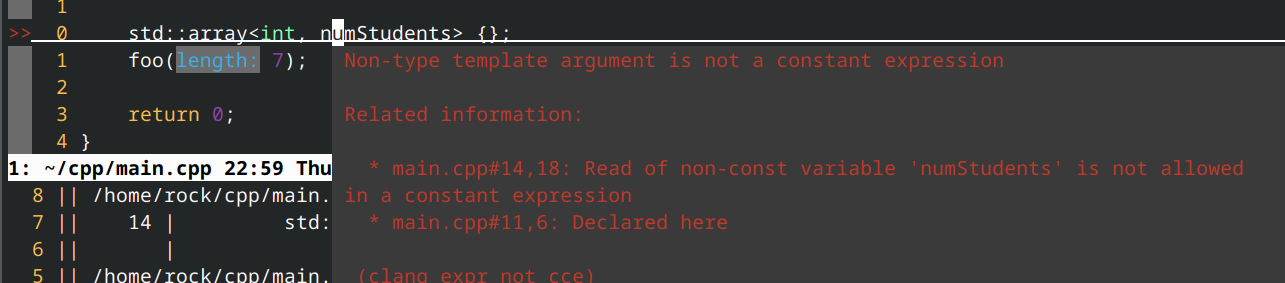
请注意,长度不能使用非常量变量和运行时常量:
#include <array>
#include <iostream>
void foo(const int length) // length is a runtime constant
{
std::array<int, length> e {}; // error: length is not a constant expression
}
int main()
{
// using a non-const variable
int numStudents{};
std::cin >> numStudents; // numStudents is non-constant
std::array<int, numStudents> {}; // error: numStudents is not a constant expression
foo(7);
return 0;
}

警告:
或许令人惊讶的是,std::array 数组可以定义为长度为 0:
#include <array>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::array<int, 0> arr {}; // creates a zero-length std::array
std::cout << arr.empty(); // true if arr is zero-length
return 0;
}
零长度的 std::array 是种特殊类,其本身不包含任何数据。因此,对零长度 std::array 调用任何访问数据的成员函数(包括 operator[])都会导致未定义行为。
可通过 empty() 成员函数检测 std::array 是否为零长度:若数组为零长度则返回 true,否则返回 false。
std::array 的聚合初始化
或许令人意外的是,std::array 属于聚合类型。这意味着它没有构造函数,而是通过聚合初始化进行初始化。简单回顾一下,聚合初始化允许我们直接初始化聚合的成员。为此,我们提供一个初始化列表,即用大括号括起的、以逗号分隔的初始化值列表。
相关内容:
我们在第13.8课——结构体聚合初始化中探讨过结构体的聚合初始化。
#include <array>
int main()
{
std::array<int, 6> fibonnaci = { 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5 }; // copy-list initialization using braced list
std::array<int, 5> prime { 2, 3, 5, 7, 11 }; // list initialization using braced list (preferred)
return 0;
}
这些初始化形式均按顺序初始化数组成员,从元素0开始。
若未指定初始化器定义std::array,元素将进行默认初始化。多数情况下,这会导致元素处于未初始化状态。
由于通常需要初始化元素,在未指定初始化器定义std::array时,应采用值初始化(使用空大括号)。
#include <array>
#include <vector>
int main()
{
std::array<int, 5> a; // Members default initialized (int elements are left uninitialized)
std::array<int, 5> b{}; // Members value initialized (int elements are zero initialized) (preferred)
std::vector<int> v(5); // Members value initialized (int elements are zero initialized) (for comparison)
return 0;
}
如果初始化列表中提供的初始化项数量超过定义的数组长度,编译器将报错。如果初始化列表中提供的初始化项数量少于定义的数组长度,则剩余未初始化的元素将按值初始化:
#include <array>
int main()
{
std::array<int, 4> a { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; // compile error: too many initializers
std::array<int, 4> b { 1, 2 }; // b[2] and b[3] are value initialized
return 0;
}

const 和 constexpr std::array
std::array 可以是 const:
#include <array>
int main()
{
const std::array<int, 5> prime { 2, 3, 5, 7, 11 };
return 0;
}
尽管 const std::array 的元素并未显式标记为 const,它们仍被视为 const(因为整个数组是 const)。
std::array 还完全支持 constexpr:
#include <array>
int main()
{
constexpr std::array<int, 5> prime { 2, 3, 5, 7, 11 };
return 0;
}
对 constexpr 的支持是使用 std::array 的关键原因。
最佳实践:
尽可能将 std::array 定义为 constexpr。如果您的 std::array 不是 constexpr,请考虑改用 std::vector。
std::array的类模板参数推导(CTAD)(C++17)
通过C++17的CTAD(类模板参数推导),编译器可从初始化列表中推导出std::array的元素类型和数组长度:
#include <array>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
constexpr std::array a1 { 9, 7, 5, 3, 1 }; // The type is deduced to std::array<int, 5>
constexpr std::array a2 { 9.7, 7.31 }; // The type is deduced to std::array<double, 2>
return 0;
}
在实际可行的情况下,我们推荐使用此语法。若编译器不支持C++17,则需显式提供类型和长度模板参数。
最佳实践:
使用类模板参数推导(CTAD)让编译器根据初始化表达式推导std::array的类型和长度。
CTAD不支持模板参数的部分省略(截至C++23版本),因此无法通过核心语言特性仅省略std::array的长度或类型参数:
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
constexpr std::array<int> a2 { 9, 7, 5, 3, 1 }; // error: too few template arguments (length missing)
constexpr std::array<5> a2 { 9, 7, 5, 3, 1 }; // error: too few template arguments (type missing)
return 0;
}


仅省略数组长度使用std::to_array (C++20)
然而,TAD(模板参数推导,用于函数模板解析)确实支持部分省略模板参数。自 C++20 起,可通过 std::to_array 辅助函数省略 std::array 的数组长度:
#include <array>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
constexpr auto myArray1 { std::to_array<int, 5>({ 9, 7, 5, 3, 1 }) }; // Specify type and size
constexpr auto myArray2 { std::to_array<int>({ 9, 7, 5, 3, 1 }) }; // Specify type only, deduce size
constexpr auto myArray3 { std::to_array({ 9, 7, 5, 3, 1 }) }; // Deduce type and size
return 0;
}
遗憾的是,使用 std::to_array 的开销比直接创建 std::array 更大,因为它需要创建一个临时 std::array 来进行复制初始化操作。因此,仅当无法从初始化表达式有效确定类型时才应使用 std::to_array,且在需要多次创建数组(例如循环内部)时应避免使用该函数。
例如,由于无法指定 short 类型的字面量,可通过以下方式创建 short 值的 std::array(无需显式指定数组长度):
#include <array>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
constexpr auto shortArray { std::to_array<short>({ 9, 7, 5, 3, 1 }) };
std::cout << sizeof(shortArray[0]) << '\n';
return 0;
}
使用下标运算符访问数组元素
与 std::vector 类似,访问 std::array 元素最常见的方式是使用下标运算符 (operator[]):
#include <array> // for std::array
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
constexpr std::array<int, 5> prime{ 2, 3, 5, 7, 11 };
std::cout << prime[3]; // print the value of element with index 3 (7)
std::cout << prime[9]; // invalid index (undefined behavior)
return 0;
}
请注意,operator[] 不会进行边界检查。若提供无效索引,将导致未定义行为。
我们将在下一课中探讨其他几种对 std::array 进行索引的方法。
测验时间
问题 #1
std::array 使用何种初始化方式?
显示答案
std::array 是聚合类型,因此它使用聚合初始化。
若未提供初始化值,为何需要显式对 std::array 进行值初始化?
显示答案
如果未提供初始化器,std::array 将默认初始化其成员。这将导致大多数类型的元素保持未初始化状态。
问题 #2
定义一个 std::array,用于存储全年每日最高温度(精确到十分之一度)。
显示解答
#include <array>
std::array<double, 365> highTemp {};
问题 #3
用以下值初始化 std::array:‘h’、'e'、‘l’、'l'、‘o’。输出索引为 1 的元素值。

显示解答
#include <array>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
constexpr std::array arr { 'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o' };
std::cout << arr[1] << '\n';
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号