Python基础学习day02
一、Python的基本数据类型
数字 字符串 列表 元组 字典 布尔值
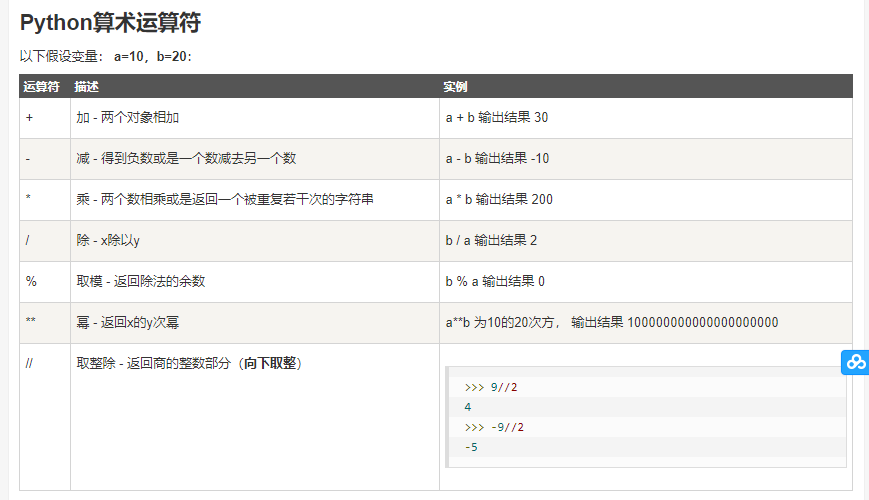
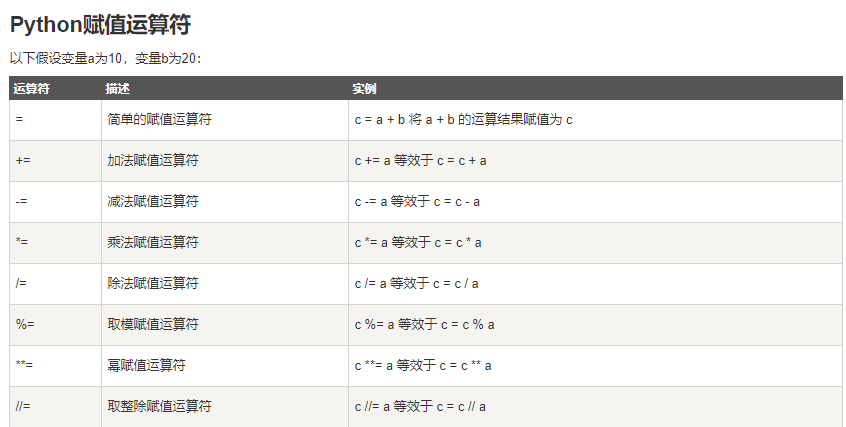
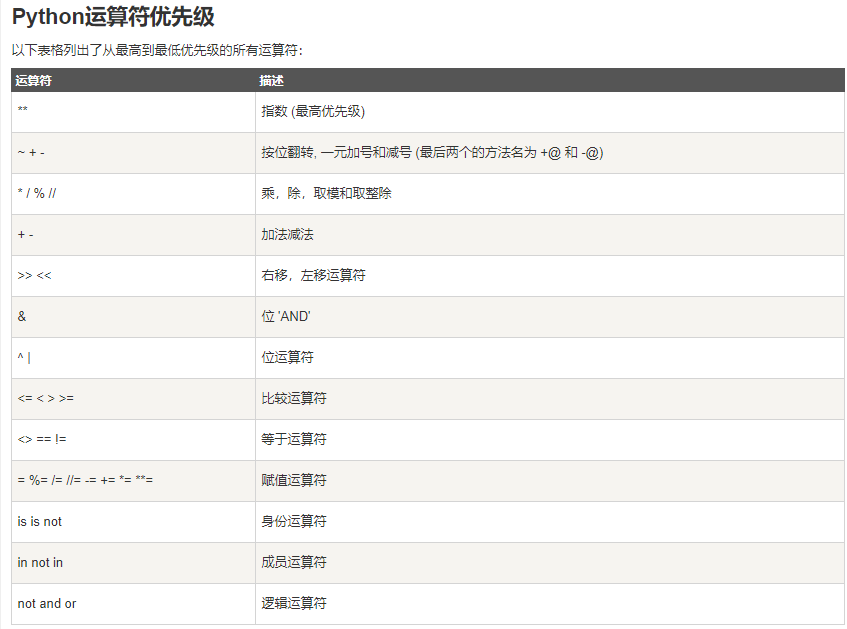
二、基本运算符(借鉴与菜鸟教程)

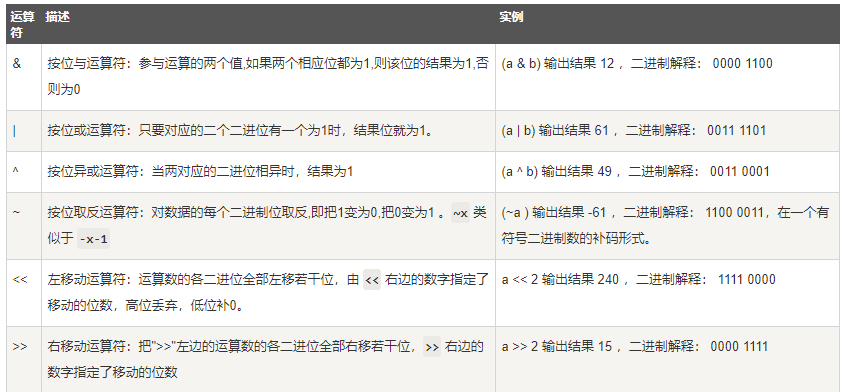
Python位运算符

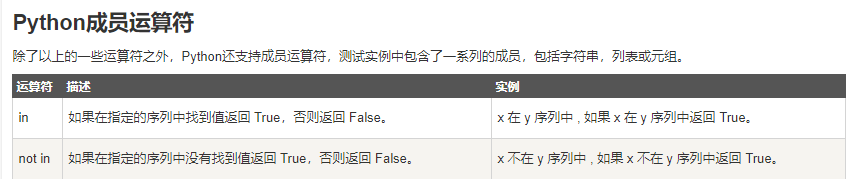

三、数字(int)
----int 将数字符串转换为数字
例: a = "123"
b = int(a)
print(b)
输出结果: 123
-----bit_length 当前数字的二进制,至少用n位表示
例: a = 1
print(a.bit_length) # 结果 1 1
例: a = 2 #二进制为:10
print(a.bit_length) #结果 2
例 : a =5 #二进制 :101
print(a.bit_length) #结果 3
四、字符串魔法(str )
***在pycharm软件中,可以通过输入str然后使用快捷键 Ctrl+b 查看字符串有哪些功能
----capitalize() 字符串首字母大写
例 : test = "alex"
v = test.capitalize()
print(v)
输出结果:Alex
-----casefold() 将字符串中的所有字符转换为小写字母,很多未知的对相应变小写
例 : test = "ALex"
print(test.casefold())
输出结果: alex
---islower() 判断字符串中的字母是否全部是小写字母
---lower() 将字符串中的大写字母全部转换为小写字母
---isupper() 判断字符串中的字母是否全部是大写字母
---upper() 将字符串中的小写字母全部转换为大写字母
例: test = "AjLD"
print(test.islower()) # 结果为False
print(test.lower()) # 结果为ajld
print(test.isupper()) #结果为False
print(test.upper()) #结果为 AJLD
----swapcase() 字符串大小写转换
例: test = "alsx"
print(test.swapcase()) #结果为 ALSX
例: test = "ALSX"
print(test.swapcase()) #结果为alsx
----find() 从开始往后找,找到第一个之后,获取其位置,并返回找到的位置的下标,如果没有找到,就返回-1
例 : test = "alexalex"
v = test.find('ex',5,8)
print(v) #结果6
----index() 从开始往后找,找到之后返回子序列在字符串中的下标,反之没有找到子序列则报错
例: test = "alesdd"
v = test.index('sw')
print(v) # 结果 报错
-----format() format_map() 格式化,将一个字符串中的zhan'wei占位符替换为指定的值
例: test = "I am {name},age{a}"
v = test.format(name="mary", age = 19)
print(v) #结果 I am mary , age 19
例 : test = "I am {0},age{1}"
v = test.format("alex",20)
print(v) # 结果 I am alex ,age 20
例 : test = "I am {name} , age {a}"
v = test.format_map({'name':'mary','age':20})
print(v) #结果 I am mary , age 20
-----isalnum() 判断字符传中是否只包含字母或数字
例: test = "alex22+"
print(test.isalnum()) #结果 False
------isalpha() 判断字符串中是否只有字母,汉字
例: test = "aldks223"
print(test.isalpha()) # 结果 False
-------isdecimal() 判断字符串中只是数字 不包括汉字
--------isdigit() 判断字符串中只是数字 不包括汉字,但是可以包括特殊的数字
--------isnumeric() 判断字符串中只是数字 包括汉字
--------expandtabs() 断句
例 :
testt = "djskldfj\tdsjklfd\tdsjldfj"
print(testt.expandtabs(20))
输出结果:
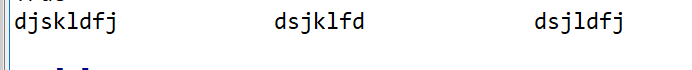
---------isidentifier() 字母 数字 下划线 标识符: def class
例 : a = "def"
print(a.isidentifier()) #结果 True
---------isprintable() 判断字符串是否存在不可见的字符
例: test = "djskld\t"
print(test.isprintable()) #结果 False
---------isspace() 判断字符串中是否全部为空格
例 : test = " "
print(test.isspace()) # 结果为 True
---------istitle() 判断字符串是否为标题
---------title() 将字符串转换为标题的形式,并输出转换后的结果
例: test = "Return the home "
print(test.istitle()) # False
print(test.title()) # Return The Home
---------join() 将字符串中的每一个元素按照指定分割符进行拼接
例: test = "你是风儿我是沙"
t = '*'
print(t.join(test)) # 你*是*风*儿*我*是*沙
---------填充
------ljust() 将内容放置在左边,用指定字符将指定字符串长度填充完整
例 : test = "djsd"
print(test.ljust(20,'*')) #djsd****************
-------rjust() 将内容放置在右边,用指定字符将指定字符串长度填充完整
例: test = "mary"
print(test.rjust(10,'&')) #&&&&&&mary
--------center()设置宽度,并将内容居中,指定字符或不指定字符(默认使用空格填充剩余长度)进行填充
例:test = "alex"
print(test.center(10,'*')) #***alex***
---------zfill() 只用0填充,指定字符串长度,将字符串放在最右边,在左边用0进行填充字符串
例:tts = "mary"
print(tts.zfill(20)) # 0000000000000000mary
---------去除字符串空格
------strip() 去除字符串左右两边的空格
------lstrip() 去除字符串左边的空格
------rstrip() 去除字符串右边的空格
---------替换
------maketrans() translate()
例 :
vb = "asidufkasd:didfj:adddsodis"
m = str.maketrans("auid","1234")
new_v = vb.translate(m)
print(new_v)
输出结果:
1s342fk1s4:434fj:1444so43s
-----replace()
例:
tt = "aldds"
v1 = tt.replace('s','dd')
print(v1)
输出结果 : aldddd
---------分割
-----split() 对字符串整体进行分割,必须指定分割字符为哪个,也可以指定用几个指定字符进行分割字符串
-----rsplit() 从右边开始,找到指定字符进行分割字符串
------partition() 找到第一个指定字符进行分割
------rpartition() 从字符串的右边开始,找到第一个指定字符进行分割字符串
例:
estt = "adjskldjsfldsjk"
vs = testt.partition('s')#找到第一个‘s’进行分割
print(vs)
vs1 = testt.rpartition('s')#从字符串的右边开始,找到第一个‘s’进行分割
print(vs1)
vs2 = testt.split('s',3)#3为指定几个‘s’进行分割
print(vs2)
vs3 = testt.rsplit('s',3)#从右边开始,找到‘s’进行分割,指定为找到3个‘s’
print(vs3)
输出结果:
('adj', 's', 'kldjsfldsjk')
('adjskldjsfld', 's', 'jk')
['adj', 'kldj', 'fld', 'jk']
['adj', 'kldj', 'fld', 'jk']
-------splitlines() 只能根据True False 来决定结果是否输出换行符
例:
tt2 = "aaaadksl\nadjslddjs\nmdsldjl"
print(tt2.splitlines(True)) #结果显示换行符
print(tt2.splitlines(False))#结果不显示换行符
输出结果:
['aaaadksl\n', 'adjslddjs\n', 'mdsldjl']
['aaaadksl', 'adjslddjs', 'mdsldjl']
--------判断字符串是以哪个字符开头和结尾的
--------startswith() 判断字符串是以哪个字符开头的
---------endswith() 判断字符串是以哪个字符结尾的
例:
print(tt2.startswith('a')) #True
print(tt2.endswith('l'))#True
五、灰魔法
########灰魔法######
tests = "alex"
#索引,下标获取字符串中的某一个字符
print(tests[1])
#切片
vf = tests[0:1]#0=< <1 [0:-1]从开头到最后
print(vf)
#len 获取当前字符串中由几个字符组成
vf1 = len(tests)
print(vf1)
print("_".join('sasijjdisa'))
name1 = "zhengjianwen"
age1 = "18"
info = name1+age1
print(info)
#字符串一旦创建,不可修改
#一旦修改或者拼接,都会造成重新生成字符串
testd = "alexalex"
print(testd.replace("ex","bbbb",2))#基础魔法
ttt = "郑建文"
for item in ttt:
print(item)
range(100) #范围为0-99 帮助创建连续的数字
range (0,100,5)#通过设置步长来改变连续的数字的状态
#将文字对应的索引给打印出来
ttr = input(">>>")
for item in range(0,len(ttr)):
print(item, ttr[item])



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号