activation functions summary and comparision
written in the foreword
Any nonlinear function that has good derivative properties has the potential to become an activation function. So here, we will just compare some classic activation functions.
summary
| name | formula | digraph | attribution | advantage | disadvantage | usage | addition |
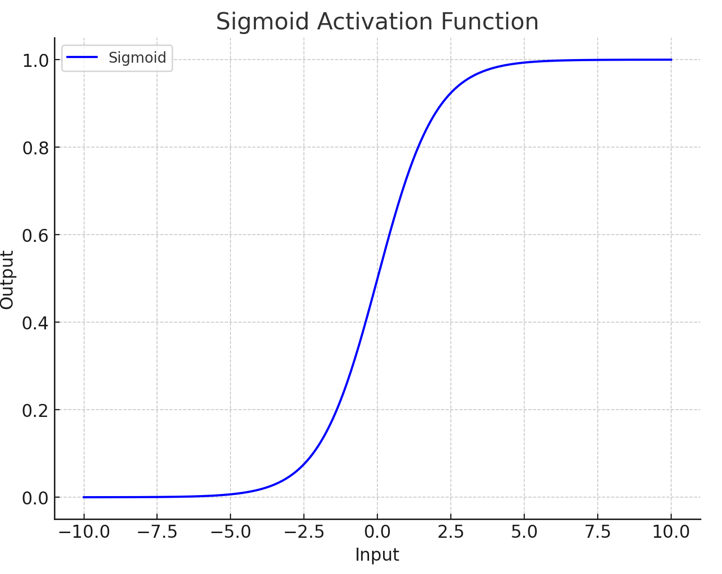
| sigmoid |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| tanh |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| softmax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ReLU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
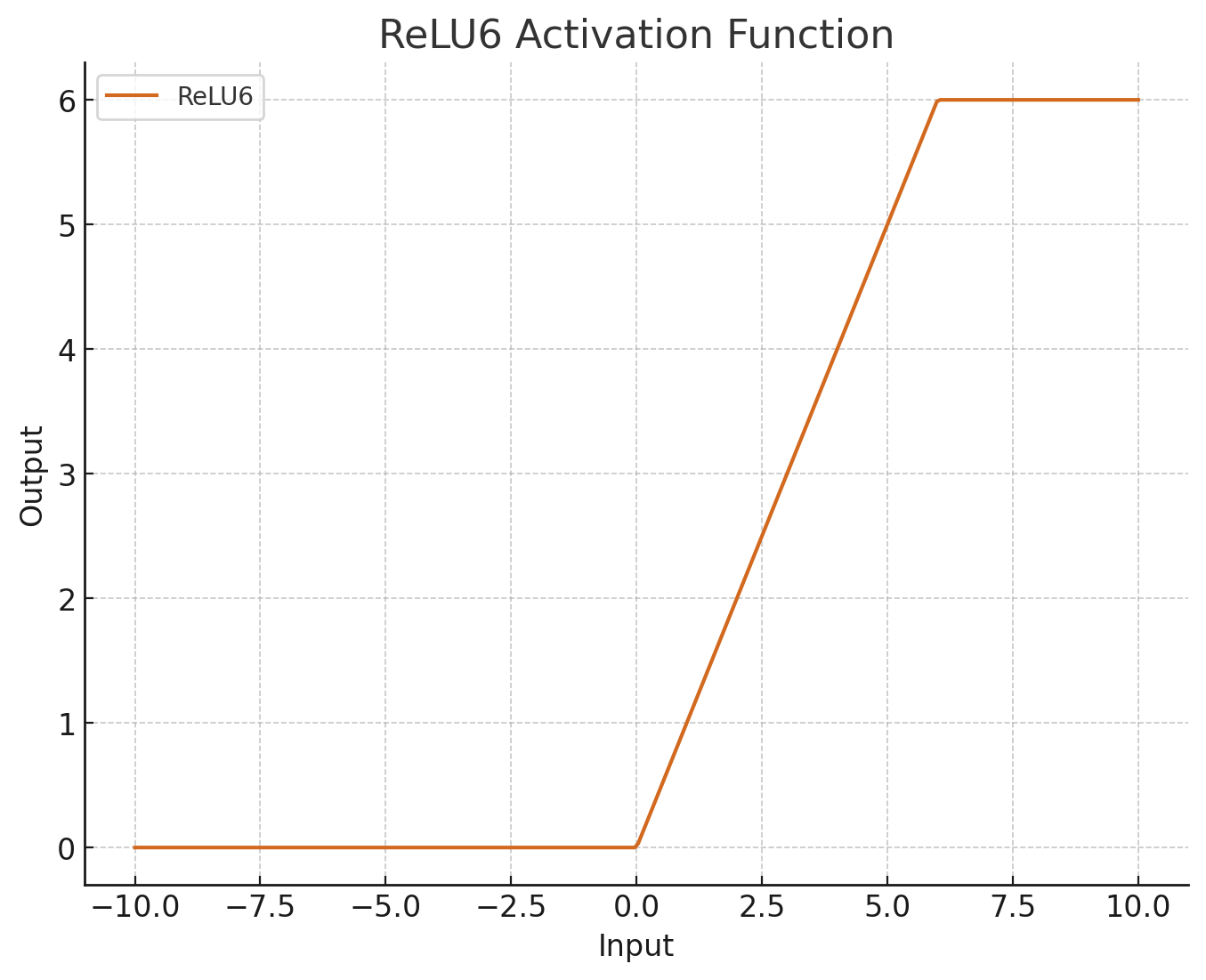
| ReLU6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
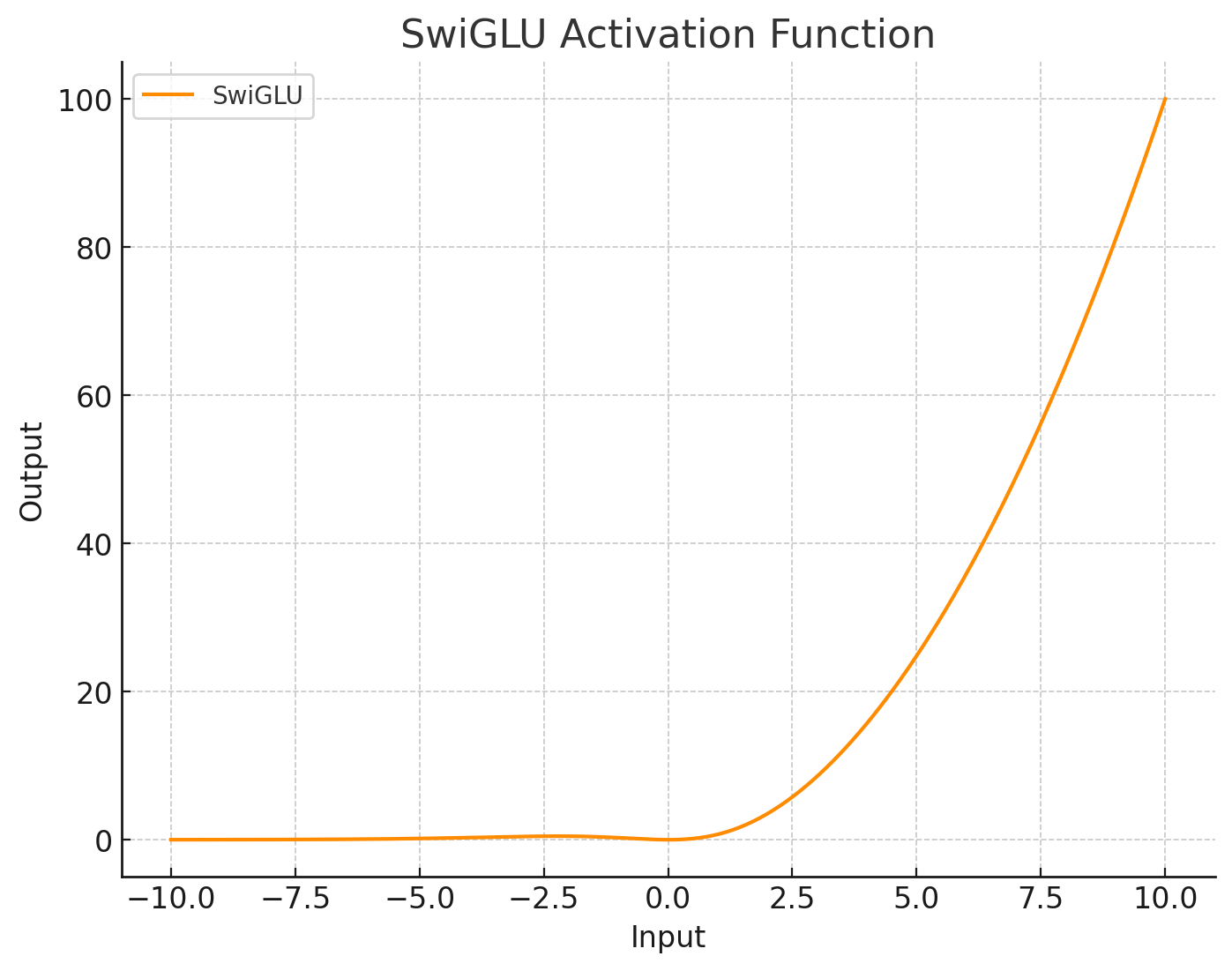
| SwiGLU |
|
|
|
|
|
comparison
| sigmoid | tanh | softmax | ReLU | ReLU6 | SwiGLU | |
| sigmoid | - |
the gradient in [0,1], output in [-1,1], mean(output)=0 used in RNN gradient in [0,0.25], output in [0, 1], mainly used in binary classification same: smooth and gradient vanishing, high computation |
gradient in [0-1], output in [0, -), used in binary classification gradient in [0,0.25], output in [0, 1], mainly used in binary classification same: smooth and gradient vanishing, high computation |
the gradient in [0, a], output in [0, -) widely used in the vision field, high efficiency, preventing gradient vanishing gradient in [0,0.25], output in [0, 1], mainly used in binary classification, low-efficiency |
gradient in [0,1], output in [0, 6], used in mobile devices, high-efficiency the gradient in [0,0.25], output in [0, 1], mainly used in binary classification, low-efficiency |
output in [0, -), high-performance gradient in [0,0.25], output in [0, 1], mainly used in binary classification |
| tanh | - |
output in [0, -), used in binary classification output in [-1,1] , mean(output)=0, used in RNN same: gradient in [0, 1] |
the gradient in [0, a], output in [0, -] widely used in the vision field, high efficiency, preventing gradient vanishing gradient in [0, 1], output in [-1,1] , mean(output)=0, used in RNN |
output in [0, 6], used in mobile devices, high efficiency output in [-1,1] , mean(output)=0, used in RNN same: gradient in [0, 1] |
output in [0, -], high performance gradient in [0, 1], output in [-1,1], mean(output)=0, used in RNN |
|
| softmax | - |
the gradient in [0, a], widely used in the vision field, high efficiency, preventing gradient vanishing gradient in [0-1], used in binary classification, gradient vanishing same: output in [0, -) |
output in [0, 6], used in mobile devices, high efficiency output in [0, 1], used in binary classification, gradient vanishing same: gradient in [0, 1] |
high performance gradient in [0, 1], gradient vanishing same: output in [0, -)
|
||
| ReLU | - |
gradient in [0,1], output in [0, 6], used in mobile device gradient in [0, a], output in [0, -) widely used in the vision field same: high efficiency |
the high performance gradient in [0, a], high efficiency, preventing gradient vanishing same: output in [0, -) |
|||
| ReLU6 | - |
output in [0, -], high performance gradient in [0,1], output in [0, 6], used in mobile devices, high efficiency |
||||
| SwiGLU | - |

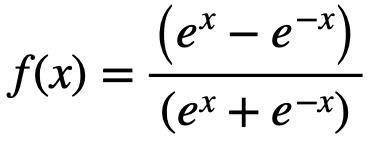


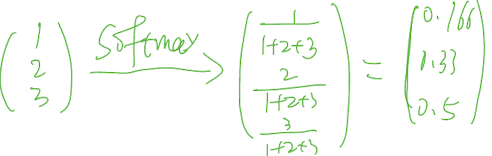
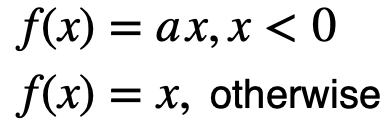


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号