九、方法重载、Debug调试
第一章 方法重载
1.1 概念
- 方法重载:指在同一个类中,允许存在一个以上的同名方法,只要它们的参数列表不同即可,与修饰符和返回值类型无关。
- 多个方法在同一个类中
- 多个方法具有相同的方法名
- 多个方法的参数不相同,类型不同或者数量不同
- 注意
- 参数列表:个数不同,数据类型不同,顺序不同。
- 重载方法调用:JVM通过方法的参数列表,调用不同的方法。
- 正确范例:
public class MethodDemo { public static void fn(int a) { //方法体 } public static int fn(double a) { //方法体 } } public class MethodDemo { public static float fn(int a) { //方法体 } public static int fn(int a , int b) { //方法体 } }
- 错误范例:
public class MethodDemo { public static void fn(int a) { //方法体} public static int fn(int a) { /*错误原因:重载与返回值无关*/ //方法体 } } public class MethodDemo01 { public static void fn(int a) { //方法体 } } public class MethodDemo02 { public static int fn(double a) { /*错误原因:这是两个类的两个fn方法*/ //方法体 } }
1.2 方法重载练习
- 需求1:使用方法重载的思想,设计比较两个两个数据是否相等的方法,兼容全整数类型byte,short,int,long)
- 思路:
- ①定义比较两个数字的是否相同的方法compare()方法,参数选择两个int型参数
- ②定义对应的重载方法,变更对应的参数类型,参数变更为两个long型参数
- ③定义所有的重载方法,两个byte类型与两个short类型参数
- ④完成方法的调用,测试运行结果
- 代码:
public static void main(String[] args) { //定义不同数据类型的变量 byte a = 10; byte b = 20; short c = 10; short d = 20; int e = 10; int f = 10; long g = 10; long h = 20; } // 两个byte类型的 public static boolean compare(byte a, byte b) { System.out.println("byte"); return a == b; } // 两个short类型的 public static boolean compare(short a, short b) { System.out.println("short"); return a == b; } // 两个int类型的 public static boolean compare(int a, int b) { System.out.println("int"); return a == b; } // 两个long类型的 public static boolean compare(long a, long b) { System.out.println("long"); return a == b; }
- 需求2:使用方法重载的思想,设计获取一个数字的绝对值的方法,兼容double,flfloat,int,long类型。
- 思路:
- ①定义获取一个数字的绝对值的abs()方法,参数选择一个double型参数,返回double类型型结果
- ②定义获取一个数字的绝对值的abs()方法,参数选择一个flfloat型参数,返回flfloat类型型结果
- ③定义获取一个数字的绝对值的abs()方法,参数选择一个int型参数,返回int类型型结果
- ④定义获取一个数字的绝对值的abs()方法,参数选择一个long型参数,返回long类型型结果
- ⑤完成方法的调用,测试运行结果
- 代码:
public static void main(String[] args) { //定义不同数据类型的变量 double a = -6.6; double b = 8.8; float c = -7.7F; float d = 9.9F; int e = -5; int f = 6; long g = -10L; long h = 20L; // 调用 System.out.println(abs(a)); System.out.println(abs(b)); System.out.println(abs(c)); System.out.println(abs(d)); System.out.println(abs(e)); System.out.println(abs(f)); System.out.println(abs(g)); System.out.println(abs(h)); } // 一个double类型的 public static double abs(double d) { if (d >= 0) { return d; } else { return -d; } } // 一个float类型的 public static float abs(float d) { return d >= 0 ? d : -d; } // 一个int类型的 public static int abs(int d) { return d >= 0 ? d : -d; } // 一个long类型的 public static long abs(long d) { return d >= 0 ? d : -d; }
- 需求3:使用方法重载的思想,设计获取两个数字的最大值的方法,兼容两个double,flfloat,int,long类型。
- 思路:
- ①定义获取两个数字的最大值的max()方法,参数选择两个double型参数,返回double类型型结果
- ②定义获取两个数字的最大值的max()方法,参数选择两个flfloat型参数,返回flfloat类型型结果
- ③定义获取两个数字的最大值的max()方法,参数选择两个int型参数,返回int类型型结果
- ④定义获取两个数字的最大值的max()方法,参数选择两个long型参数,返回long类型型结果
- ⑤完成方法的调用,测试运行结果
- 代码:
public static void main(String[] args) { //定义不同数据类型的变量 double a = -6.6, b = 8.8; float c = 7.7F, d = 9.9F; int e = -5, f = -6; long g = 10L, h = 20L; // 调用 System.out.println(max(a, b)); System.out.println(max(c, d)); System.out.println(max(e, f)); System.out.println(max(g, h)); } // 两个double类型的 public static double max(double a, double b) { if (a >= b) { return a; } else { return b; } } // 两个float类型的 public static float max(float a, float b) { return a > b ? a : b; } // 两个int类型的 public static int max(int a, int b) { if (a > b) return a; return b; } // 两个long类型的 public static long max(long a, long b) { long max = a;//假设a是最大的 if (max < b) { max = b; } return max; }
- 需求4:判断哪些方法是重载关系。
//3和8一样不是方法的重载,5和6一样不是方法的重载 public static void open() { } public static void open(int a) { } static void open(int a, int b) { } public static void open(double a, int b) { } public static void open(int a, double b) { } public void open(int i, double d) { } public static void OPEN() { } public static void open(int i, int j) { }
第二章 方法的参数传递
2.1 参数传递的概念
- 可以理解当我们要调用一个方法时,我们会把指定的数值,传递给方法中的参数,这样方法中的参数就拥有了这个指
定的值,可以使用该值,在方法中运算了。这种传递方式,我们称为参数传递。
- 在这里,定义方法时,参数列表中的变量,我们称为形式参数
- 调用方法时,传入给方法的数值,我们称为实际参数
2.2 基本数据类型作为方法参数
public static void main(String[] args) { int number = 100; System.out.println("调用change方法前:" + number); change(number); System.out.println("调用change方法后:" + number); } public static void change(int number) { number = 200; }
结论:
- 基本数据类型的参数,形式参数的改变,不影响实际参数
2.3 基本数据类型作为方法参数调用图解
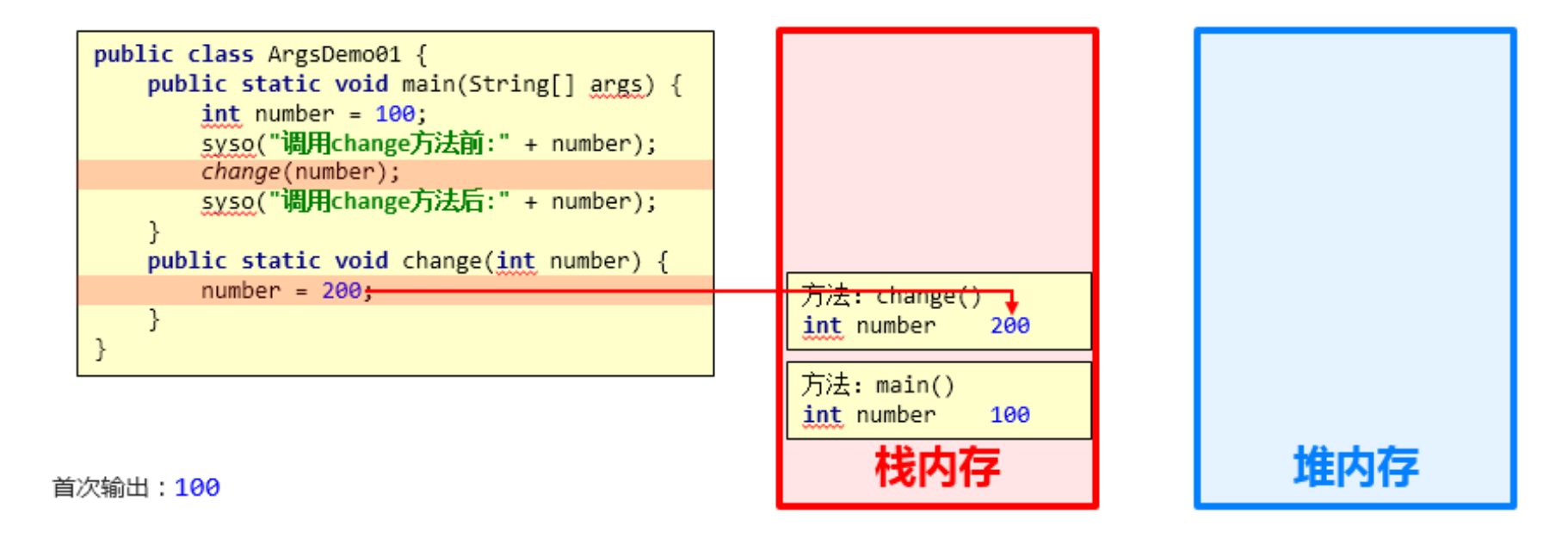
结论依据:
- 每个方法在栈内存中,都会有独立的栈空间,方法运行结束后就会弹栈消失
2.4 引用数据类型作为方法参数
public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {10, 20, 30}; System.out.println("调用change方法前:" + arr[1]); change(arr); System.out.println("调用change方法后:" + arr[1]); } public static void change(int[] arr) { arr[1] = 200; }
注意:引用类型,作为方法参数,形式参数的改变会影响实际参数
结论:
- 对于引用类型的参数,形式参数的改变,影响实际参数的值
2.5 引用数据类型作为方法参数调用图解
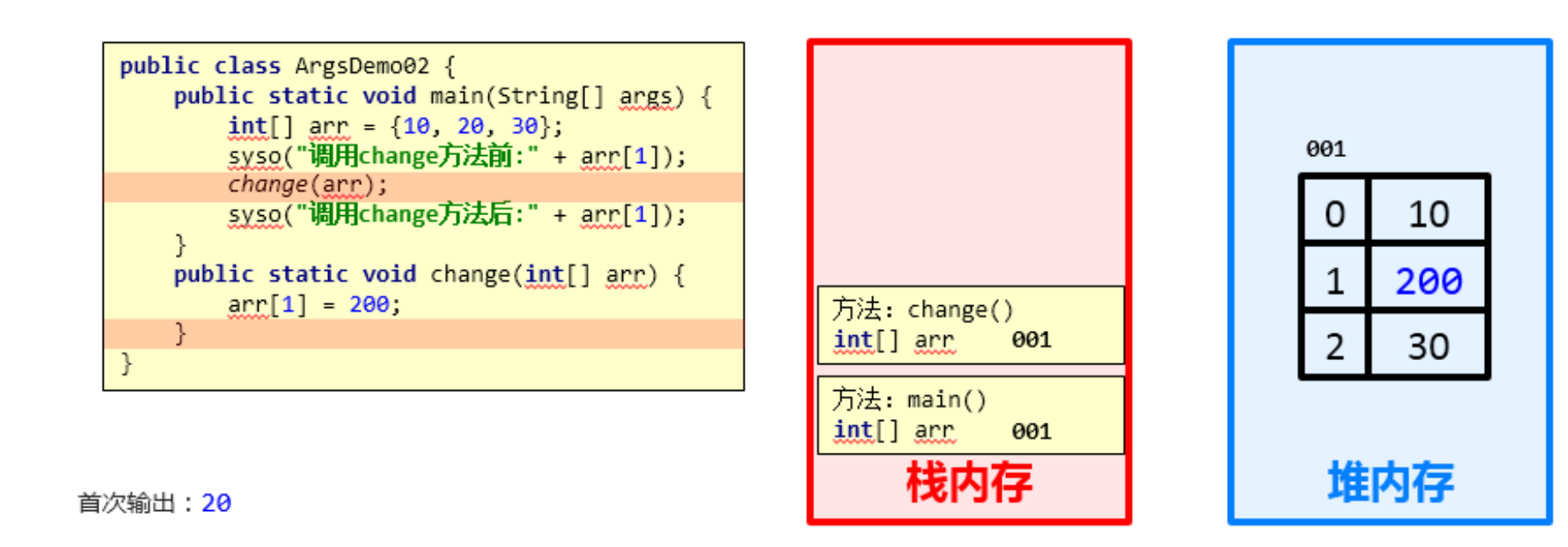
结论依据:
- 引用数据类型的传参,传入的是地址值,内存中会造成两个引用指向同一个内存的效果,所以即使方法弹栈,堆内存中的数据也已经是改变后的结果
第三章 方法的练习
3.1 练习一
- 需求1:设计一个方法用于数组遍历,要求遍历的结果是在一行上的。例如:[11, 22, 33, 44, 55]
- 思路:
- ①因为要求结果在一行上输出,所以这里需要在学习一个新的输出语句System.out.print(“内容”);
System.out.println(“内容”); 输出内容并换行System.out.print(“内容”); 输出内容不换行System.out.println(); 起到换行的作用
- ①因为要求结果在一行上输出,所以这里需要在学习一个新的输出语句System.out.print(“内容”);
-
- ②定义一个数组,用静态初始化完成数组元素初始化
- ③定义一个方法,用数组遍历通用格式对数组进行遍历
- ④用新的输出语句修改遍历操作
- ⑤调用遍历方法
- 代码:
public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {11, 22, 33, 44, 55}; printArray(arr); } //定义一个方法,用数组遍历通用格式对数组进行遍历 /* * 两个明确: * 返回值类型:void * 参数:int[] arr * * */ public static void printArray(int[] arr) { System.out.println("["); for (int x = 0; x < arr.length; x++) { if (x == arr.length - 1) { System.out.print(arr[x]); } else { System.out.print(arr[x] + ", "); } } System.out.println("]"); }
3.2 练习二
- 需求2:设计一个方法用于获取数组中元素的最大值
- 思路:
- ①定义一个数组,用静态初始化完成数组元素初始化
- ②定义一个方法,用来获取数组中的最大值,最值的认知和讲解我们在数组中已经讲解过了
- ③调用获取最大值方法,用变量接收返回结果
- ④把结果输出在控制台
- 代码:
public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {12, 45, 98, 73, 60}; int number = getMax(arr); System.out.println("number:" + number); } /** * * @param arr * @return 最大值 */ public static int getMax(int[] arr) { int max = arr[0]; for (int x = 1; x < arr.length; x++) { if (arr[x] > max) { max = arr[x]; } } return max; }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号