目录:
数据分析:是把隐藏在一些看似杂乱无章的数据背后的信息提炼出来,总结出所研究对象的内在规律
数据分析三剑客:Numpy,Pandas,Matplotlib
NumPy(Numerical Python) 是 Python 语言的一个扩展程序库,支持大量的维度数组与矩阵运算,此外也针对数组运算提供大量的数学函数库。
import numpy as np
一、创建ndarray
1.1 一维数据创建:
np.array([1,2,3,4,5]) # array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
1.2 二维数组创建:
np.array([[1,2,3],['a','b',1.1]]) # array([['1', '2', '3'], ['a', 'b', '1.1']], dtype='<U11')
注意:
1. numpy默认ndarray的所有元素的类型是相同的;
2. 如果传进来的列表中包含不同的类型,则统一为同一类型,优先级:str>float>int;
1.3 使用matplotlib.pyplot获取一个numpy数组,数据来源于一张图片:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img_arr = plt.imread('./bobo.jpg')
plt.imshow(img_arr)
# <matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7635048>

plt.imshow(img_arr - 66)
# <matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x75bfd68>

注:操作该numpy数据,该操作会同步到图片中
2 使用np的routines函数创建
2.1 np.linspace(start, stop, num=50, endpoint=True, retstep=False, dtype=None) 等差数列
np.linspace(1,100,num=50)
输出:
array([ 1. , 3.02040816, 5.04081633, 7.06122449,
9.08163265, 11.10204082, 13.12244898, 15.14285714,
17.16326531, 19.18367347, 21.20408163, 23.2244898 ,
25.24489796, 27.26530612, 29.28571429, 31.30612245,
33.32653061, 35.34693878, 37.36734694, 39.3877551 ,
41.40816327, 43.42857143, 45.44897959, 47.46938776,
49.48979592, 51.51020408, 53.53061224, 55.55102041,
57.57142857, 59.59183673, 61.6122449 , 63.63265306,
65.65306122, 67.67346939, 69.69387755, 71.71428571,
73.73469388, 75.75510204, 77.7755102 , 79.79591837,
81.81632653, 83.83673469, 85.85714286, 87.87755102,
89.89795918, 91.91836735, 93.93877551, 95.95918367,
97.97959184, 100. ])
2.2 np.arange([start, ]stop, [step, ]dtype=None)
np.arange(1,100,2)
输出:
array([ 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33,
35, 37, 39, 41, 43, 45, 47, 49, 51, 53, 55, 57, 59, 61, 63, 65, 67,
69, 71, 73, 75, 77, 79, 81, 83, 85, 87, 89, 91, 93, 95, 97, 99])
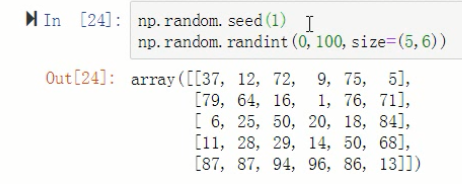
2.3 np.random.randint(low, high=None, size=None, dtype='l')
np.random.seed(1) # 保持一个因素不变,则seed(1)对应的下面的输出结果会保持不变
arr = np.random.randint(0,100,size=(5,6)) # 生成一个 5*6 的 二维数组,里面的元素都是 0到100 的随机数
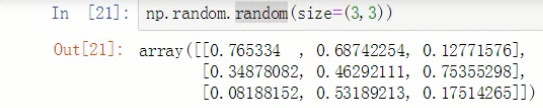
2.4 np.random.random(size=None) 生成0到1的随机数,左闭右开
np.random.seed(3)
np.random.random(size=(3,3)) # 生成一个 3*3 的 二维数组,里面的元素都是 0到1的随机数
二. ndarray的属性
4个必记参数: ndim:维度; shape:形状(各维度的长度);
size:总长度; dtype:元素类型;
1 img_arr.shape
输出:(626, 413, 3)
2 img_arr.ndim
输出:3
3 img_arr.size
输出:775614
4 img_arr.dtype
输出:dtype('uint8')
5 type(img_arr)
输出:numpy.ndarray
三. ndarray的基本操作
1. 索引
注:一维与列表完全一致 多维时同理
arr
输出:array([[ 9, 15, 64, 28, 89, 93],
[29, 8, 73, 0, 40, 36],
[16, 11, 54, 88, 62, 33],
[72, 78, 49, 51, 54, 77],
[69, 13, 25, 13, 92, 86]])
arr[[1,2]]
输出:
array([[29, 8, 73, 0, 40, 36],
[16, 11, 54, 88, 62, 33]])
2. 切片
注:一维与列表完全一致 多维时同理
arr
输出:
array([[ 9, 15, 64, 28, 89, 93],
[29, 8, 73, 0, 40, 36],
[16, 11, 54, 88, 62, 33],
[72, 78, 49, 51, 54, 77],
[69, 13, 25, 13, 92, 86]])
2.1 #获取二维数组前两行
arr[0:2]
输出:
array([[ 9, 15, 64, 28, 89, 93],
[29, 8, 73, 0, 40, 36]])
2.2 #获取二维数组前两列
arr[:,0:2] # 逗号前面是对行切片,后面是对列切片
输出:
array([[ 9, 15],
[29, 8],
[16, 11],
[72, 78],
[69, 13]])
2.3 #获取二维数组前两行和前两列数据
arr[0:2,0:2]
输出:
array([[ 9, 15],
[29, 8]])
2.4 #将数组的行倒序
arr[::-1]
输出:
array([[69, 13, 25, 13, 92, 86],
[72, 78, 49, 51, 54, 77],
[16, 11, 54, 88, 62, 33],
[29, 8, 73, 0, 40, 36],
[ 9, 15, 64, 28, 89, 93]])
2.5 #列倒序
arr[:,::-1]
输出:
array([[93, 89, 28, 64, 15, 9],
[36, 40, 0, 73, 8, 29],
[33, 62, 88, 54, 11, 16],
[77, 54, 51, 49, 78, 72],
[86, 92, 13, 25, 13, 69]])
2.6 #全部倒序
arr[::-1,::-1]
输出:
array([[86, 92, 13, 25, 13, 69],
[77, 54, 51, 49, 78, 72],
[33, 62, 88, 54, 11, 16],
[36, 40, 0, 73, 8, 29],
[93, 89, 28, 64, 15, 9]])
2.7 #将图片进行全倒置操作
plt.imshow(img_arr)

plt.imshow(img_arr[:,::-1,:])

plt.imshow(img_arr[::-1,::-1,::-1])

3. 变形
使用arr.reshape()函数,注意参数是一个tuple!
3.1 将一维数组变形成多维数组
arr_1.reshape((-1,15)) # 15表示15列,-1表示行会根据元素个数和列数自动运算出来
输出:
array([[ 9, 15, 64, 28, 89, 93, 29, 8, 73, 0, 40, 36, 16, 11, 54],
[88, 62, 33, 72, 78, 49, 51, 54, 77, 69, 13, 25, 13, 92, 86]])
3.2 将多维数组变形成一维数组
arr_1 = arr.reshape((30,)) # 30表示一行的元素个数
4. 级联
np.concatenate()
级联需要注意的点:
1、级联的参数是列表:一定要加中括号或小括号
2、维度必须相同
3、形状相符:在维度保持一致的前提下,如果进行横向(axis=1)级联,必须保证进行级联的数组行数保持一致。如果进行纵向(axis=0)级联,必须保证进行级联的数组列数保持一致。
4、可通过axis参数改变级联的方向
arr
输出:
array([[ 9, 15, 64, 28, 89, 93],
[29, 8, 73, 0, 40, 36],
[16, 11, 54, 88, 62, 33],
[72, 78, 49, 51, 54, 77],
[69, 13, 25, 13, 92, 86]])
4.1 一维,二维,多维数组的级联,实际操作中级联多为二维数组
np.concatenate((arr,arr),axis=1) # axis=1 列级联; axis=0则为行级联; 三维时才能有axis=2的选项
输出:
array([[ 9, 15, 64, 28, 89, 93, 9, 15, 64, 28, 89, 93],
[29, 8, 73, 0, 40, 36, 29, 8, 73, 0, 40, 36],
[16, 11, 54, 88, 62, 33, 16, 11, 54, 88, 62, 33],
[72, 78, 49, 51, 54, 77, 72, 78, 49, 51, 54, 77],
[69, 13, 25, 13, 92, 86, 69, 13, 25, 13, 92, 86]])
4.2 合并两张照片
img_3 = np.concatenate((img_arr,img_arr,img_arr),axis=1)
imgs = np.concatenate((img_3,img_3,img_3),axis=0)
plt.imshow(imgs)

4.3 np.hstack与np.vstack
5. 切割
plt.imshow(img_arr)

5.1 plt.imshow(img_arr[50:390,85:340])

5.2 plt.imshow(np.split(img_arr,[400],axis=0)[0])

四. ndarray的聚合操作
1. 求和 np.sum
arr.sum(axis=0) # axis=0表示求每一列的和,若不指定axis则表示求所有元素的和
输出:
array([195, 125, 265, 180, 337, 325])
2. 最大最小值:np.max/ np.min
同理
3. 平均值:np.mean()
4. 其他聚合操作
Function Name NaN-safe Version Description
np.sum np.nansum Compute sum of elements
np.prod np.nanprod Compute product of elements
np.mean np.nanmean Compute mean of elements
np.std np.nanstd Compute standard deviation
np.var np.nanvar Compute variance
np.min np.nanmin Find minimum value
np.max np.nanmax Find maximum value
np.argmin np.nanargmin Find index of minimum value
np.argmax np.nanargmax Find index of maximum value
np.median np.nanmedian Compute median of elements
np.percentile np.nanpercentile Compute rank-based statistics of elements
np.any N/A Evaluate whether any elements are true
np.all N/A Evaluate whether all elements are true
np.power 幂运算五. ndarray的排序
快速排序
np.sort()与ndarray.sort()都可以,但有区别:
1、np.sort()不改变输入;
2、ndarray.sort()本地处理,不占用空间,但改变输入。
1. np.sort(arr,axis=0) # axis=0表示每一列都从小到大排序; 注:原来的arr未被改变
输出:
array([[ 9, 8, 25, 0, 40, 33],
[16, 11, 49, 13, 54, 36],
[29, 13, 54, 28, 62, 77],
[69, 15, 64, 51, 89, 86],
[72, 78, 73, 88, 92, 93]])
2. arr.sort(axis=0) # 注:原来的arr被改变了
arr
输出:
array([[ 9, 8, 25, 0, 40, 33],
[16, 11, 49, 13, 54, 36],
[29, 13, 54, 28, 62, 77],
[69, 15, 64, 51, 89, 86],
[72, 78, 73, 88, 92, 93]])


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号