嵌入式开发记录-day18 设备节点简介、生成设备节点、字符设备框架
1、以模块的方式生成设备节点,不需要烧写镜像
2、生成的设备节点在ls /dev/下,可以供上层应用程序打开使用。相当于提供一个访问内核模块的一个接口。对于常见的open函数,操作一个节点设备 /dev/led0,可以按照下面这样,通过这样的方式就可以调用到模块中定义的file ops接口。
open("/dev/led0", O_RDWR); // 有点类似window下的文件路径,但是led0是一个内核模块设备
0、查看设备号:
设备分主设备号和次设备号,主设备号用于区分一大类设备,此设备号区分大类设备号下的不同设备。
cat /proc/device 查看主设备号;
cat /proc/misc 查看杂项设备的此设备号;
1、杂项设备:可以节省主设备节点(主设备节点有限255),驱动编写也相对简单,并且是必须要编译的;
2、头文件:include/linux/miscdevice.h
3、涉及到的结构体:struct miscdevice 注册的是杂项设备
struct miscdevice { int minor; // 设备号,一般随机取值,系统分配 const char *name; // 生成设备节点的名称,随便取 const struct file_operations *fops; // 设备结点文件 struct list_head list; struct device *parent; struct device *this_device; const char *nodename; mode_t mode; };
4、注册函数、卸载函数;杂项设备注册与卸载
extern int misc_register(struct miscdevice * misc); extern int misc_deregister(struct miscdevice *misc);
5、上面需要注册结构体中所包含的结构体 const struct file_operations *fops; // 设备结点文件,操作该结构体中的函数,进而读写相应的设备
对外界提供访问该设备的接口;需要自己实现函数功能;
上层应用对接该结构体的函数接口;
在头文件include/linux/miscdevice.h
const struct file_operations *i_fop; struct file_operations { struct module *owner; // 模块属于者 loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int); // 定位函数 ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); // 读操作 ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); // 写操作 ssize_t (*aio_read) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t); ssize_t (*aio_write) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t); int (*readdir) (struct file *, void *, filldir_t); unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *); ... // 包含非常多,只列举常用的
6、常用的结构体变量:
.owner = THIS_MODULE // 使用宏定义 .open .release .unlocked_ioctl() 对GPIO的操作 应用向节点串参数
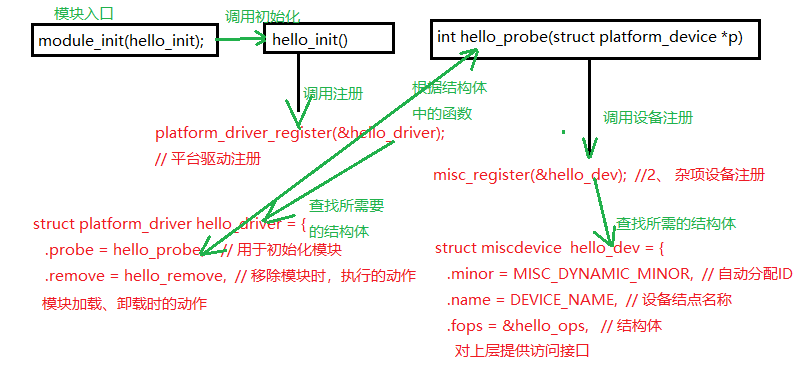
7、实验代码devicenode_linux_module.c,生成设备结点 hello_ctl123
杂项设备与platform总线结合:
1 // 驱动注册所需头文件 包含结构体,注册和卸载所需的函数 2 #include <linux/platform_device.h> 3 #include <linux/module.h> 4 #include <linux/init.h> 5 #include <linux/miscdevice.h> // 注册杂项设备头文件 6 #include <linux/fs.h> // 设备结点文件 7 8 #define DRIVER_NAME "hello_ctl" 9 #define DEVICE_NAME "hello_ctl123" 10 11 12 MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL"); 13 MODULE_AUTHOR("TOPEET"); 14 15 static int hello_open(struct inode *node, struct file *f) 16 { 17 printk(KERN_EMERG "\t func hello open\n"); 18 return 0; 19 } 20 21 static int hello_release(struct inode *node, struct file *f) 22 { 23 printk(KERN_EMERG "\t hello release\n"); 24 return 0; 25 } 26 27 static long hello_ioctl(struct file *f, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg) 28 { 29 printk(KERN_EMERG "\t hello ioctl\n"); 30 printk("hello_ioctl cmd is %d ...arg is %d\n",cmd,arg); 31 return 0; 32 } 33 34 // 文件操作,对应生成的设备结点具体如何操作 35 static struct file_operations hello_ops = { 36 .owner = THIS_MODULE, 37 .open = hello_open, 38 // int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *); 39 .release = hello_release, 40 // int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *); 41 .unlocked_ioctl = hello_ioctl, 42 // long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);long); 43 44 }; 45 46 static struct miscdevice hello_dev = { 47 .minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR, // 自动分配ID 48 .name = DEVICE_NAME, // 设备结点名称 49 .fops = &hello_ops, // 结构体 50 }; 51 52 // int (*probe)(struct platform_device *); 53 // 初始化相关动作 54 static int hello_probe(struct platform_device *p) 55 { 56 printk(KERN_EMERG "\t initialized\n"); 57 misc_register(&hello_dev); //2、 杂项设备注册 58 return 0; 59 } 60 // int (*remove)(struct platform_device *); 61 static int hello_remove(struct platform_device *p) 62 { 63 printk(KERN_EMERG "\t hello_ct123 removed\n"); 64 misc_deregister(&hello_dev); 65 return 0; 66 } 67 // int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state); 68 static int hello_suspend(struct platform_device *p, pm_message_t state) 69 { 70 return 0; 71 } 72 // int (*resume)(struct platform_device *); 73 static int hello_resume(struct platform_device *p) 74 { 75 return 0; 76 } 77 // void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *); 78 static void hello_shutdown(struct platform_device *p) 79 { 80 81 } 82 83 // 3、结构体数据初始化 84 // 注册驱动传入的结构体 85 struct platform_driver hello_driver = { 86 .probe = hello_probe, // 用于初始化模块 87 .remove = hello_remove, // 移除模块时,执行的动作 88 .suspend = hello_suspend,// 模块挂起时,执行的动作 89 .resume = hello_resume, // 挂起的模块,恢复运行执行动作 90 .shutdown = hello_shutdown, 91 .driver = { 92 .name = DRIVER_NAME, // 驱动名称 93 .owner = THIS_MODULE,// 驱动所有者,THIS_MODULE宏定义 94 }, 95 }; 96 // 2、模块初始化相关实现 97 // 模块的入口函数 加载模块执行动作 98 static int hello_init(void) 99 { 100 int DriverState; 101 printk(KERN_EMERG "HELLO WORLD enter!\n");
// 平台驱动注册 102 DriverState = platform_driver_register(&hello_driver); // 注册驱动 转而执行初始化动作 103 printk(KERN_EMERG "\tDriverState is %d\n", DriverState); // 注册驱动执行状态 104 105 return 0; 106 } 107 // 模块退出函数 卸载模块所执行 108 static void hello_exit(void) 109 { 110 printk(KERN_EMERG "HELLO WORLD exit!\n"); 111 platform_driver_unregister(&hello_driver); // 卸载驱动函数 112 } 113 114 //1、 入口函数module_nint 115 module_init(hello_init); 116 module_exit(hello_exit);
上面调用流程
8、测试结果,使用ls dev// 查看生成的设备结点
[root@iTOP-4412]# ./mnt/disk/app_hello.o [ 234.644663] func hello open [ 234.646263] hello ioctl [ 234.648756] hello_ioctl cmd is 1 ...arg is 6 [ 234.653025] hello release App open /dev/hello_ctl123 success // 执行顺兴,貌似内核优先级比较高
9、需要注意,设备、驱动注册都是嵌入到内中的,生成设备结点则是面向应用;
10、编写简单的应用,调用设备结点App_hello_ctl123
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <sys/types.h> 3 #include <sys/stat.h> 4 #include <fcntl.h> 5 #include <unistd.h> 6 #include <sys/ioctl.h> 7 8 int main(void) 9 { 10 int fd; 11 char* hello_node = "/dev/hello_ctl123"; 12 fd = open(hello_node,O_RDWR|O_NDELAY); // 非阻塞打开 13 if(fd < 0){ 14 printf("func open app %s failed\n",hello_node); 15 return -1; 16 }else{ 17 printf("App open %s success\n",hello_node); 18 ioctl(fd,1,6); // 应用程序向驱动传值 19 } 20 close(fd); 21 return 0; 22 }
11、设备结点、驱动注册、设备注册
设备结点面向上层应用程序;驱动注册和设备注册需要嵌入到linux内核中;
12、简化上面的生成设备结点代码,devicenode_Samp.c
杂项设备驱动框架:
使用结构体描述杂项设备:
struct miscdevice { int minor; const char *name; const struct file_operations *fops; struct list_head list; struct device *parent; struct device *this_device; const struct attribute_group **groups; const char *nodename; umode_t mode; }; int misc_register(struct miscdevice *misc); void misc_deregister(struct miscdevice *misc); // 通过fops成员提供向外的访问接口
简化后的实例:
1 #include <linux/platform_device.h> 2 #include <linux/module.h> 3 #include <linux/init.h> 4 #include <linux/miscdevice.h> // 注册杂项设备头文件 5 #include <linux/fs.h> // 设备结点文件 6 7 #define DEVICE_NAME "hello_ctl123" 8 9 10 MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL"); 11 MODULE_AUTHOR("TOPEET"); 12 13 static int hello_open(struct inode *node, struct file *f) 14 { 15 printk(KERN_EMERG "\t func hello open\n"); 16 return 0; 17 } 18 19 static int hello_release(struct inode *node, struct file *f) 20 { 21 printk(KERN_EMERG "\t hello release\n"); 22 return 0; 23 } 24 25 static long hello_ioctl(struct file *f, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg) 26 { 27 printk(KERN_EMERG "\t hello ioctl\n"); 28 printk("hello_ioctl cmd is %d ...arg is %d\n",cmd,arg); 29 return 0; 30 } 31 32 // 文件操作,对应生成的设备结点具体如何操作 33 static struct file_operations hello_ops = { 34 .owner = THIS_MODULE, 35 .open = hello_open, 36 // int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *); 37 .release = hello_release, 38 // int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *); 39 .unlocked_ioctl = hello_ioctl, 40 // long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);long); 41 42 }; 43 44 static struct miscdevice hello_dev = { 45 .minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR, // 自动分配ID 46 .name = DEVICE_NAME, // 设备结点名称 47 .fops = &hello_ops, // 结构体 48 }; 49 50 // 2、模块初始化相关实现 51 // 模块的入口函数 加载模块执行动作 52 static int hello_init(void) 53 { 54 int DriverState; 55 printk(KERN_EMERG "HELLO WORLD enter!\n"); 56 DriverState = misc_register(&hello_dev); 57 printk(KERN_EMERG "\tDriverState is %d\n", DriverState); // 注册驱动执行状态 58 59 return 0; 60 } 61 // 模块退出函数 卸载模块所执行 62 static void hello_exit(void) 63 { 64 printk(KERN_EMERG "HELLO WORLD exit!\n"); 65 misc_deregister(&hello_dev); 66 } 67 68 //1、 入口函数module_nint 69 module_init(hello_init); 70 module_exit(hello_exit);
平台驱动注册
二、字符设备驱动框架
内核中使用struct cdev{};来描述一个字符设备;
#include <linux/cdev.h>struct cdev { struct kobject kobj; struct module *owner; const struct file_operations *ops; struct list_head list; dev_t dev; unsigned int count; }; // 1. 分配一个字符设备 struct cdev *cdev_alloc(void); // 初始化字符设备,配置习惯的系统调用接口。 void cdev_init(struct cdev *, const struct file_operations *); // 添加字符设备到内核。 int cdev_add(struct cdev *, dev_t, unsigned); // 释放时候,删除设备 void cdev_del(struct cdev *); // 暂时用不到。 void cdev_put(struct cdev *p); void cdev_set_parent(struct cdev *p, struct kobject *kobj); int cdev_device_add(struct cdev *cdev, struct device *dev); void cdev_device_del(struct cdev *cdev, struct device *dev); void cd_forget(struct inode *);
1、注册字符设备
/** * alloc_chrdev_region() - register a range of char device numbers * @dev: output parameter for first assigned number * @baseminor: first of the requested range of minor numbers * @count: the number of minor numbers required * @name: the name of the associated device or driver * * Allocates a range of char device numbers. The major number will be * chosen dynamically, and returned (along with the first minor number) * in @dev. Returns zero or a negative error code. */ int alloc_chrdev_region(dev_t * dev, unsigned baseminor, unsigned count, const char * name); // 内核自动分配设备号 /** * register_chrdev_region() - register a range of device numbers * @from: the first in the desired range of device numbers; must include * the major number. * @count: the number of consecutive device numbers required * @name: the name of the device or driver. * * Return value is zero on success, a negative error code on failure. */ int register_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count, const char *name) // 由调用者传入设备号参数
2、卸载字符设备
/** * unregister_chrdev_region() - unregister a range of device numbers * @from: the first in the range of numbers to unregister * @count: the number of device numbers to unregister * * This function will unregister a range of @count device numbers, * starting with @from. The caller should normally be the one who * allocated those numbers in the first place... */ void unregister_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count)
3、生成设备节点:
此时还没有生成设备节点,应用程序还无法操作设备;需要使用命令mknod在指定的路径下创建设备节点;
mknod demo_dev c 245 0 // 在当前路径创建设备节点demo_dev
#include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #include <linux/cdev.h> static dev_t devNum=0; static struct cdev* mydev; static int myopen (struct inode *node, struct file *file) { return 0; } static struct file_operations fileops={ .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = myopen, }; static int __init mdev_init(void) { int ret=0; printk("Hello cdev\n"); ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devNum, 0, 1, "dev_demo"); if(ret != 0){ printk("chr dev region err\n"); return ret; } printk("dev major:%d.\n", MAJOR(devNum)); printk("dev manor:%d.\n", MINOR(devNum)); mydev = cdev_alloc(); if(mydev == NULL){ printk("alloc cdev error\n"); } cdev_init(mydev, &fileops); ret = cdev_add(mydev, devNum, 1); if(ret < 0 ){ printk("dev add error\n"); } return 0; } static void __exit mdev_exit(void) { printk("Good bye\n"); unregister_chrdev(MAJOR(devNum), "dev_demo"); cdev_del(mydev); } module_init(mdev_init); module_exit(mdev_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
4、基于udev的文件系统(应用层的接口)创建设备节点
#include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #include <linux/cdev.h> #include <linux/device.h> #include <linux/err.h> #define COUNT 3 #define DEV_NAME "devDemo" static dev_t devNum=0; static struct cdev* mydev=NULL; static struct class * dev_cls=NULL; static struct device* devp=NULL; static int ma=240; static int myopen (struct inode *node, struct file *file) { printk("--%s--%s--%d----\n", __FILE__,__func__, __LINE__); return 0; } static struct file_operations fileops={ .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = myopen, }; static int __init mdev_init(void) { int ret=0,i; printk("Hello cdev\n"); //ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devNum, 0, 1, "dev_demo"); devNum = MKDEV(ma,0); printk("dev major:%d.\n", MAJOR(devNum)); printk("dev manor:%d.\n", MINOR(devNum)); ret = register_chrdev_region(devNum, COUNT, DEV_NAME); if(ret != 0){ printk("chr dev region err\n"); goto err0; } // 1. 为cdev分配空间. mydev = cdev_alloc(); if(mydev == NULL){ printk(KERN_ERR "alloc cdev error\n"); goto err1; } // 2. cdev初始化. cdev_init(mydev, &fileops); // 3. 添加cdev ret = cdev_add(mydev, devNum, COUNT); if(ret < 0 ){ printk(KERN_ERR "dev add error\n"); goto err1; } // 4. 在sys/class下创建目录 dev_cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, DEV_NAME); if(IS_ERR(dev_cls)){ printk(KERN_ERR "class create failed:%ld\n", PTR_ERR(dev_cls)); ret = PTR_ERR(dev_cls); goto err2; } // 5、创建设备结点,在dev目录下,创建名称为DEV_NAME+i的设备结点; for(i=0;i<3;i++){ devp = device_create(dev_cls, NULL, MKDEV(ma,i), NULL, "%s%d", DEV_NAME,i); if(IS_ERR(devp)){ printk(KERN_ERR "device create failed: %ld\n", PTR_ERR(devp)); ret = PTR_ERR(devp); goto err3; } } printk(KERN_INFO "--%s--%s--%d----\n", __FILE__,__func__, __LINE__); return 0; err3: for(--i;i>=0;i--){ device_destroy(dev_cls,MKDEV(ma,i)); } class_destroy(dev_cls); err2: cdev_del(mydev); err1: unregister_chrdev_region(devNum, COUNT); err0: return 0; } static void __exit mdev_exit(void) { int i=0; printk("Good bye\n"); for(i=0;i<3;i++){ device_destroy(dev_cls,MKDEV(ma,i)); } class_destroy(dev_cls); cdev_del(mydev); unregister_chrdev_region(devNum, COUNT); } module_init(mdev_init); module_exit(mdev_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
1. 默认在/dev下根据device_create的名字创建设备节点;
hadlee@lbx-machine:~/mycode/mdriver$ ls /dev/devDemo* -l crw------- 1 root root 240, 0 4月 30 15:10 /dev/devDemo0 crw------- 1 root root 240, 1 4月 30 15:10 /dev/devDemo1 crw------- 1 root root 240, 2 4月 30 15:10 /dev/devDemo2
5、USER和KERNEL空间数据交换cop_to_user、copy_from_user
#include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #include <linux/cdev.h> #include <linux/device.h> #include <linux/err.h> #include <asm/uaccess.h> // 适用于x86平台。 #include <asm-generic/uaccess.h> // 使用ARM平台。 #define COUNT 3 #define DEV_NAME "devDemo" static dev_t devNum=0; static struct cdev* mydev=NULL; static struct class * dev_cls=NULL; static struct device* devp=NULL; static char kbuf[128]={'\0'}; static int kbufcount=0; static int ma=240; static int myopen (struct inode *node, struct file *filp) { printk(KERN_INFO "--%s--%s--%d----\n", __FILE__,__func__, __LINE__); return 0; } static ssize_t myread (struct file *filp, char __user *ubuf, size_t size, loff_t *off) { printk(KERN_INFO "--%s--%s--%d----\n", __FILE__,__func__, __LINE__); //printk(KERN_INFO "buf addr:0x%x, szie:%d\n", ubuf, size); if(size > kbufcount) size = kbufcount; if(copy_to_user(ubuf, kbuf,13)){ printk(KERN_INFO "copy to user failed\n"); return -EAGAIN; } kbufcount =0; return 0; } static ssize_t mywrite (struct file *filp, const char __user * ubuf, size_t size, loff_t *off) { //printk(KERN_INFO "buf addr:0x%x, szie:%d\n", ubuf, size); if(size > 128){ size = 128; } if(copy_from_user(kbuf, ubuf, size)){ printk(KERN_ERR "copy from user failed\n"); return -EAGAIN; // 拷贝失败应用层程序再尝试一次; } kbufcount = size; printk(KERN_INFO "write buf:%s\n", kbuf); printk(KERN_INFO "--%s--%s--%d----\n", __FILE__,__func__, __LINE__); return kbufcount; } static int myrelaese (struct inode *nod, struct file *file) { printk(KERN_INFO "--%s--%s--%d----\n", __FILE__,__func__, __LINE__); return 0; } static struct file_operations fileops={ .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = myopen, .release = myrelaese, .read = myread, .write = mywrite, }; static int __init mdev_init(void) { int ret=0,i; printk("Hello cdev\n"); //ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devNum, 0, 1, "dev_demo"); devNum = MKDEV(ma,0); printk("dev major:%d.\n", MAJOR(devNum)); printk("dev manor:%d.\n", MINOR(devNum)); ret = register_chrdev_region(devNum, COUNT, DEV_NAME); if(ret != 0){ printk("chr dev region err\n"); goto err0; } // 1. 为cdev分配空间. mydev = cdev_alloc(); if(mydev == NULL){ printk(KERN_ERR "alloc cdev error\n"); goto err1; } // 2. cdev初始化. cdev_init(mydev, &fileops); // 3. 添加cdev ret = cdev_add(mydev, devNum, COUNT); if(ret < 0 ){ printk(KERN_ERR "dev add error\n"); goto err1; } // 4. 在sys/class下创建目录 dev_cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, DEV_NAME); if(IS_ERR(dev_cls)){ printk(KERN_ERR "class create failed:%ld\n", PTR_ERR(dev_cls)); ret = PTR_ERR(dev_cls); goto err2; } // 5、创建设备结点,在dev目录下,创建名称为DEV_NAME+i的设备结点; for(i=0;i<3;i++){ devp = device_create(dev_cls, NULL, MKDEV(ma,i), NULL, "%s%d", DEV_NAME,i); if(IS_ERR(devp)){ printk(KERN_ERR "device create failed: %ld\n", PTR_ERR(devp)); ret = PTR_ERR(devp); goto err3; } } printk(KERN_INFO "--%s--%s--%d----\n", __FILE__,__func__, __LINE__); return 0; err3: for(--i;i>=0;i--){ device_destroy(dev_cls,MKDEV(ma,i)); } class_destroy(dev_cls); err2: cdev_del(mydev); err1: unregister_chrdev_region(devNum, COUNT); err0: return 0; } static void __exit mdev_exit(void) { int i=0; printk("Good bye\n"); for(i=0;i<3;i++){ device_destroy(dev_cls,MKDEV(ma,i)); } class_destroy(dev_cls); cdev_del(mydev); unregister_chrdev_region(devNum, COUNT); } module_init(mdev_init); module_exit(mdev_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
参考应用:

#include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #include <linux/cdev.h> #include <linux/device.h> #include <linux/slab.h> #include <asm/uaccess.h> MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); #define CDD_MAJOR 200//cat /proc/devices找一个尚未使用的 #define CDD_MINOR 0 #define CDD_COUNT 10 dev_t dev = 0; u32 cdd_major = 0; u32 cdd_minor = 0; struct class *dev_class = NULL; #define BUF_SIZE 100 struct cdd_cdev{ struct cdev cdev; struct device *dev_device; u8 led; char kbuf[BUF_SIZE]; }; struct cdd_cdev *cdd_cdevp = NULL; int cdd_open(struct inode* inode, struct file *filp) { struct cdd_cdev *pcdevp = NULL; printk("enter cdd_open!\n"); pcdevp = container_of(inode->i_cdev, struct cdd_cdev, cdev); printk("led = %d\n", pcdevp->led); filp->private_data = pcdevp; return 0; } int cdd_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *offset) { int ret = 0; struct cdd_cdev *cdevp = filp->private_data; printk("enter cdd_read!\n"); ret = copy_to_user(buf, cdevp->kbuf, count); printk("kernel kbuf content:%s\n", cdevp->kbuf); return ret; } int cdd_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *offset) { int ret = 0; struct cdd_cdev *cdevp = filp->private_data; printk("enter cdd_write!\n"); ret = copy_from_user(cdevp->kbuf, buf, count); return ret; } int cdd_ioctl(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long data) { printk("enter cdd_ioctl!\n"); return 0; } int cdd_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) { printk("enter cdd_release!\n"); return 0; } struct file_operations cdd_fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = cdd_open, .read = cdd_read, .write = cdd_write, .ioctl = cdd_ioctl, .release = cdd_release, }; int __init cdd_init(void) { int ret = 0; int i = 0; if(cdd_major){ dev = MKDEV(CDD_MAJOR, CDD_MINOR);//生成设备号 //注册设备号;1、要注册的起始设备号2、连续注册的设备号个数3、名字 ret = register_chrdev_region(dev, CDD_COUNT, "cdd_demo"); }else{ // 动态分配设备号 ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&dev, cdd_minor, CDD_COUNT, "cdd_demo02"); } if(ret < 0){ printk("register_chrdev_region failed!\n"); goto failure_register_chrdev; } //获取主设备号 cdd_major = MAJOR(dev); printk("cdd_major = %d\n", cdd_major); cdd_cdevp = kzalloc(sizeof(struct cdd_cdev)*CDD_COUNT, GFP_KERNEL); if(IS_ERR(cdd_cdevp)){ printk("kzalloc failed!\n"); goto failure_kzalloc; } /*创建设备类*/ dev_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "cdd_class"); if(IS_ERR(dev_class)){ printk("class_create failed!\n"); goto failure_dev_class; } for(i=0; i<CDD_COUNT; i++){ /*初始化cdev*/ cdev_init(&(cdd_cdevp[i].cdev), &cdd_fops); /*添加cdev到内核*/ cdev_add(&(cdd_cdevp[i].cdev), dev+i, 1); /* “/dev/xxx” */ device_create(dev_class, NULL, dev+i, NULL, "cdd%d", i); cdd_cdevp[i].led = i; } return 0; failure_dev_class: kfree(cdd_cdevp); failure_kzalloc: unregister_chrdev_region(dev, CDD_COUNT); failure_register_chrdev: return ret; } void __exit cdd_exit(void) { /*逆序消除*/ int i = 0; for(; i < CDD_COUNT; i++){ device_destroy(dev_class, dev+i); cdev_del(&(cdd_cdevp[i].cdev)); //cdev_del(&((cdd_cdevp+i)->cdev)); } class_destroy(dev_class); kfree(cdd_cdevp); unregister_chrdev_region(dev, CDD_COUNT); } module_init(cdd_init); module_exit(cdd_exit);
6、ioctl接口传参数:
内核中有两个ioctl接口,具体使用那个和内核版本有关系吧,不确定;
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
应用层:
int ioctl(int d, int request, ...);
@fd: 文件描述符;
@request: 命令码;
第三个参数一般用于,传递数据结构的地址,根据地址配合copy_from_user将结构中的数据内容拷贝过来;完成数据传输;
// 自定义传输的数据结构 struct KData{ int id; char buf[64]; }; static struct KData myData={0}; // 声明变量 // 一般User通过结构体的形式,将结构体的地址传过来args_addr,然后再copy_form_user将数据拷贝过来; static long myioctl (struct file *filp, unsigned int req_code, unsigned long args_addr) { switch(req_code){ case 11: printk(KERN_INFO "----------case11------------\n"); if(copy_from_user((void*)&myData, (void*)args_addr, sizeof(struct KData))){ printk(KERN_INFO "copy data failed\n"); return -EAGAIN; } printk(KERN_INFO "id:%d..buf:%s\n", myData.id,myData.buf); break; case 22: printk(KERN_INFO "----------case22------------\n"); if(copy_from_user((void*)&myData, (void*)args_addr, sizeof(struct KData))){ printk(KERN_INFO "copy data failed\n"); return -EAGAIN; } printk(KERN_INFO "id:%d..buf:%s\n", myData.id,myData.buf); break; default: break; } printk(KERN_INFO "--%s--%s--%d----\n", __FILE__,__func__, __LINE__); return 0; }
在ioctl接口中:命令码cmd一般充分使用所有bits
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long);
对于cmd中的参数,充分使用所有bit,使用命令码生成参数,内核提供了相应的bit操作:
_IOC(dir,type,nr,size): 32bits由dir(读写)、type(数据类型)、nr(序号)、size(大小)组成;
#define _IO(type,nr) _IOC(_IOC_NONE,(type),(nr),0)
#define _IOR(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_READ,(type),(nr),sizeof(size))
#define _IOW(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_WRITE,(type),(nr),sizeof(size))
#define _IOWR(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_READ|_IOC_WRITE,(type),(nr),sizeof(size))
比如:
cmd1 = _IO('A',1);
取出响应的bit:
_IOC_DIR(nr)
_IOC_TYPE(nr)
_IOC_NR(nr)
_IOC_SIZE(nr)





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号