集合(三) HashMap
三、Map
先来讲一下Map,Map和Collection完全不是一个系列的,按理说讲完Collection的List,应该接着讲Collection的Set,但是因为Set中很多实现是基于Map来实现的,所以将Map提前。Map是一个接口,存储内容是键值对key-value,键不可重复。
1.HashMap
AbstractMap是实现Map接口的抽象类,HashMap继承于AbstractMap。
Map的API:(JDK1.8版本新增较多,为25个详见 https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/index.html)
abstract void clear() abstract boolean containsKey(Object key) abstract boolean containsValue(Object value) abstract Set<Entry<K, V>> entrySet() abstract boolean equals(Object object) abstract V get(Object key) abstract int hashCode() abstract boolean isEmpty() abstract Set<K> keySet() abstract V put(K key, V value) abstract void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map) abstract V remove(Object key) abstract int size() abstract Collection<V> values()
AbstractMap的API只比Map新增了两个方法:
String toString() Object clone()
Map.Entry是Map类的静态接口,其API为 :
abstract boolean equals(Object object) abstract K getKey() abstract V getValue() abstract int hashCode() abstract V setValue(V object)
HashMap是线程不安全的,其key和value都可以是null。此外,HashMap不是有序的映射(什么是有序? 2019.1.1补:遍历的顺序和插入的顺序无直接关系)。
(1)HashMap成员域
HashMap基本成员域有:
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
transient int size;
transient int modCount;
int threshold;
final float loadFactor;
table即为实现hashmap的核心,数组的每个元素是Node类型,本质上是一个链表,用于存储键值对。JDK7以下的table可以用下图来表示原理:
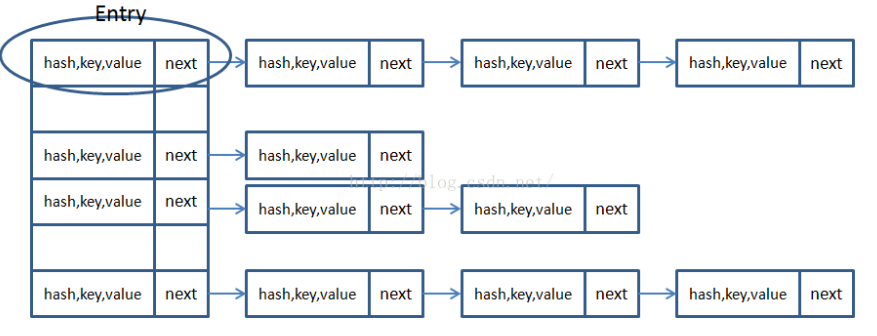
size是存储键值对的个数,loadfactor称为装载因子,默认为0.75,threshold=capacity*loadfactor,如果size大于阈值threshold就要进行扩容,而容量一般是2的幂数。因此loadfactor作用是为了使哈希中的存储更加均匀,减小冲突。显而易见的是,如果想节省存储空间,那么loadfactor应该设置的大一点(记住减少扩容就很好理解了),若想提高查询效率,loadfactor应该设置的大一点。
Note:桶的数量即为capacity。
(2)HashMap的构造函数
HashMap共有四种构造函数:
public HashMap()
public HashMap(int initialCapacity)
public HashMap(int initialCapacity,float loadFactor)
public HashMap(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m)
HashMap默认设置容量capacity为16,而装载因子loadfactor为0.75,也可以按照上面构造函数自定义。
详细的构造函数如下面的代码:

/** * Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial * capacity and load factor. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity * @param loadFactor the load factor * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative * or the load factor is nonpositive */ public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity); if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); this.loadFactor = loadFactor; this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity); } /** * Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial * capacity and the default load factor (0.75). * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative. */ public HashMap(int initialCapacity) { this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR); } /** * Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the default initial capacity * (16) and the default load factor (0.75). */ public HashMap() { this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted } /** * Constructs a new <tt>HashMap</tt> with the same mappings as the * specified <tt>Map</tt>. The <tt>HashMap</tt> is created with * default load factor (0.75) and an initial capacity sufficient to * hold the mappings in the specified <tt>Map</tt>. * * @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map * @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null */ public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; putMapEntries(m, false); }
(3)“拉链法"
众所周知,哈希冲突的时候最经典的处理方法有再哈希和拉链法,HashMap采用的正是后者。这次我们来详细探讨以下拉链法相关的内容。
Node的数据结构

static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; V value; Node<K,V> next; Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { this.hash = hash; this.key = key; this.value = value; this.next = next; } public final K getKey() { return key; } public final V getValue() { return value; } public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; } public final int hashCode() { return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value); } public final V setValue(V newValue) { V oldValue = value; value = newValue; return oldValue; } public final boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) return true; if (o instanceof Map.Entry) { Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o; if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) && Objects.equals(value, e.getValue())) return true; } return false; } }
可以看出Node不过是一个单链表,值得注意的是该链表的数据域中有一个hash的整型变量,代表该节点的哈希值。还有一个hashCode()方法,我决定和插入一起讲解可能效果会好一些。
(4)HashMap的插入put()方法
来看put()方法的源码:
public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); }
接着来看hash()方法和putVal的源码:
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length; if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else { Node<K,V> e; K k; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p; else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); else { for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; }
static final int hash(Object key) { int h; return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); }
上面代码量极少,效率极高,令人咂舌。
(h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16)这行代码代表计算出key的hashCode()之后把高16位和低16位进行异或操作(相同结果为0,不同结果为1)得到新元素(姑且将一个键值对称为一个元素)的hash值
![]() 高低16位的异或操作,图片来源见图水印
高低16位的异或操作,图片来源见图水印
然后开始执行putVal()方法,一定详细来看,首先是第一个if语句
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length;

final Node<K,V>[] resize() { Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table; int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length; int oldThr = threshold; int newCap, newThr = 0; if (oldCap > 0) { if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return oldTab; } else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold } else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold newCap = oldThr; else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); } if (newThr == 0) { float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor; newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); } threshold = newThr; @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap]; table = newTab; if (oldTab != null) { for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) { Node<K,V> e; if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) { oldTab[j] = null; if (e.next == null) newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e; else if (e instanceof TreeNode) ((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap); else { // preserve order Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null; Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null; Node<K,V> next; do { next = e.next; if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) { if (loTail == null) loHead = e; else loTail.next = e; loTail = e; } else { if (hiTail == null) hiHead = e; else hiTail.next = e; hiTail = e; } } while ((e = next) != null); if (loTail != null) { loTail.next = null; newTab[j] = loHead; } if (hiTail != null) { hiTail.next = null; newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead; } } } } } return newTab; }
(tab=table) == null是什么概念?经过简单的实验可以知道,这句代码将table赋值给tab,然后判断这个值是否等于null?然后返回相应的boolean值,也就是说如果现有table是null或者tab的长度为0时,(注意!是先执行或语句前面的部分给tab赋值,之后或语句后面才有意义)则执行resize()操作扩容,也意味着HashMap中没有任何元素,虽然暂时不清楚两个条件有什么区别?
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
有了前面图中的基础之后,可以知道,(n-1) & hash找出将要插入的下标并赋值给i,这个桶中如果没有任何元素,或者说这个地方链表还没形成,那么直接new一个新的节点放在这个位置,而且没有后续节点,如下是newNode()方法的代码:
Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { return new Node<>(hash, key, value, next); }
接着来:
else { Node<K,V> e; K k; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p;
否则判断这个元素的key是否已经存在,如果是将首元素赋值给e.
else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
判断p是否是树节点,如果是将e申请一个新的树节点,这也是HashMap1.8的主要改变,即如果链表过长时,就会从链表转换为红黑树(之后新开详细讲解)。
else { for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; }
若p不是树节点,意味着仍是链表存储,此时需要遍历链表,查看新增节点后是否超过TREEIFY_THRESHOLD,也即树化的阈值,默认为8.如果超过,就调用treeifyBin进行树化,将链表转为红黑树的形式存储,提高查找效率。
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } }
这段怎么看着有点熟悉,没错,这里是遍历链表时发现有和新元素key重复的情况,跳出循环,而最后的p = e其实困惑了我一段时间,实际上这里是为了遍历的一部分,类似于p = p.next使链表向前推进。
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } }
这里代表已经存在key的映射,将新的value值赋给此节点。
++modCount; if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; }
modCount的含义一两句话解释不清楚,大致可以理解为集合被修改的次数,而如果插入后新的size已经大于阈值,那么扩容。
(4)HashMap的使用
插入、覆盖现象以及使用iterator进行遍历。
public static void main(String [] args) { HashMap hm=new HashMap (); hm.put("20142480135","武一鸣"); hm.put("20142480136","张三"); hm.put("20142480135","李四"); Iterator it= hm.entrySet().iterator(); while(it.hasNext()) { java.util.Map.Entry entry= (java.util.Map.Entry)it.next(); String key=(String) entry.getKey(); String value=(String) entry.getValue(); System.out.println("the key is "+key+" and the value is "+value); } }

直接打印、键值对个数、删除以及keySet()和values()方法
System.out.println("Map:"+hm);
System.out.println("the size is "+hm.size());
hm.remove("20142480135");
hm.put("20142480137","王五");
Iterator it1= hm.keySet().iterator(); //keySet()返回Set对象
while(it1.hasNext())
{
String key=(String)it1.next();
System.out.println("the key is "+key);
}
Iterator it2= hm.values().iterator(); //values()返回Collection对象
while(it2.hasNext())
{
String values=(String)it2.next();
System.out.println("the value is "+values);
}

此外,clear()、isEmpty()方法不言而喻。分别是清空和判断是否为空。
get(Object key)返回对应的value值,如果没有这个key返回null。
containsKey(Object key)和containsValue(Object value)均返回boolean值,判断是否包含该键或该值。


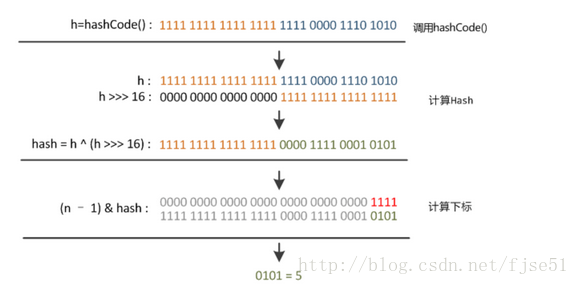 高低16位的异或操作,图片来源见图水印
高低16位的异或操作,图片来源见图水印
 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号