今日内容:
python基础:
一 python的安装与使用
1.安装python解释器
2.安装pycharm编辑器
3.编写python代码,并输出打印hello world!
二 变量
变量,可变化的量。
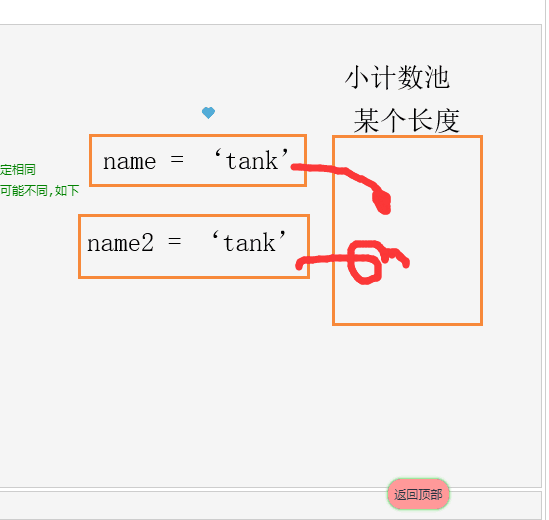
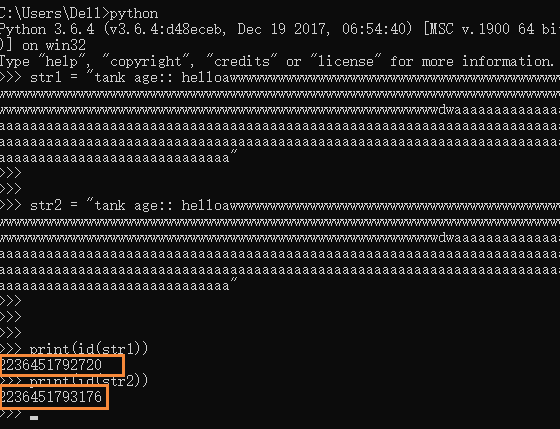
#变量值: 'tank' ,会在内存中产生-份内存地址。
#变量名:相当于一个门]牌号,用于与变量进行绑定。
# =:用来把变量值绑定给变量。
变量的命名规范:
驼峰命名法: AgeofTank
# python强烈推荐使用
下划线命名: age_of_tank
变量名定义规范:
1.要以英文字母或下划线开头命名
al #英文字母开头
_a #下划线开头
2.不能以数字开头命名
1a # 错误!!!
3.关键字不能命名:
'and', 'as', 'assert', 'break', ’class',’continue',
'def’, 'de1',’elif', 'else', 'except', 'exec' ,
'finally', 'for','from','global', 'if', 'import'
'in','is', 'lambda', 'not',or’, 'pass','print',
’raise',’return',’try', while', 'with','yield'
定义变量名不好的方式:
1.不要以中文命名
2.变量名过长
3.变量名词不达意
定义变量的三大特征
id # 用来表示变量的值在内存中唯一的一份内存地址。
type # 变量值的类型
value # 变量的值
三 常量
常量:
指的是不变的量。
常量本质上也是变量,在python不会有任何机制限制你不能修改常量。
而是python程序员人为去限制自己,凡是遇见大写的变量都不能对其进行修改。
命名规范:
变量名全大写。
SCHOOL =’合肥学院’
四 用户与程序交互
输入:
input()
输出:
print()
# 让用户输入用户名
# name = input('请输入名字:')
# 输出用户名
# print(name)
# 在python3中,input内输入的任何数据类型都是字符串
# print(type(name))
五 格式化输出
尊敬的用户,你好!您本月的话费扣除99元,还剩0元。
# 通过某种占位符,用于替换字符串中某个位置的字符。
占位符:
%s: 可以替换任意类型
%d: 可以替换数字类型
示例:
尊敬的用户,你好!您本月的话费扣除%s元,还剩%d元。
'''
字符串格式化输出
%s
%d
'''
# 把100替换给了%s
# str1 = '尊敬的用户,你好!您本月的话费扣除%s元,还剩0元。' % 100
# 把一百替换给了%s, 把50替换给了%d
# str1 = '尊敬的用户,你好!您本月的话费扣除%s元,还剩%d元。' % ('一百', 50)
# print(str1)
# 报错
# str1 = '尊敬的用户,你好!您本月的话费扣除%s元,还剩%d元。' % ('一百', '50')
# print(str1)
六 注释
单行注释: #
快捷键: ctrl + /
多行注释:三引号 ''' """
快捷键:
''' + 回车键
""" + 回车键
六 基本数据类型
1.数字类型:
整型: int
浮点型: float
# int
# age = int(18)
# print (age)
# print(type(age))
# age2 = 19
# print(age2)
# print (type(age2))
# float
# sal = 1.01
# print(sal)
# print(type(sal))
2.字符串类型
作用:名字,性别,国籍,地址等描述信息
定义:在单引号\双引号\三引号内,由一串字符组成
name='tank'
优先掌握的操作:
1、按索引取值(正向取+反向取) :只能取
# 正向取
str1 = 'hello tank!'
print(str1[0]) # h
print(str1[9]) # k
# 反向取
print(str1[-2]) # k
2、切片(顾头不顾尾,步长)
str1 = 'hello tank!'
# 0 -- (5 - 1)
print(str1[0:5]) # hello
# 步长
print(str1[0:11]) # hello tank!
print(str1[0:11:2]) # hlotn!
3、长度len
print(len(str1)) # 11
4、成员运算in和not in
print('h' in str1) # True
print('h' not in str1) # False
5、移除空白strip
# 会移除字符串中左右两边的空格
str1 = ' hello tank!'
print(str1)
str1 = ' hello tank! '
print(str1)
print(str1.strip())
# 去除指定字符串
str2 = '!tank!'
print(str2.strip('!'))
6、切分split
str1 = 'hello tank!'
# 根据str1内的空格进行切分
# 切分出来的值会存放在[]列表中。
print(str1.split(' ')) # ['hello','tank!']
7、循环
# 对str1字符串进行遍历,打印每一个字符
for line in str1:
print(line)
需要掌握的:
1、strip,lstrip,rstrip
# 1、strip,lstrip,rstrip
# str1 = ' hello wuyuefeng '
# print(str1)
# # 去掉两边空格
# print(str1.strip())
# # 去掉左边空格
# print(str1.lstrip())
# # 去掉右边空格
# print(str1.rstrip())
2、lower,upper
# 2、lower,upper
# str1 = 'hello WuYueFeng'
# # 转换成小写
# print(str1.lower())
# # 转换成大写
# print(str1.upper())
3、startswith,endswith
# 3、startswith,endswith
# str1 = 'hello WuYueFeng'
# # # 判断str1字符开头是否等于hello
# print(str1.startswith('hello')) # True
# # # 判断str1字符末尾是否等于WuYueFeng
# print(str1.endswith('WuYueFeng')) # True
4、format的三种玩法
# # 4、format(格式化输出)的三种玩法
# # str1 = 'my name is %s, my age %s!' % ('tank', 18)
# # print(str1)
#
# # 方式一: 根据位置顺序格式化
# print('my name is {}, my age {}!'.format('tank', 18))
#
# # 方式二: 根据索引格式化
# print('my name is {0}, my age {1}!'.format('tank', 18))
#
# # 方式三: 指名道姓地格式化
# print('my name is {name}, my age {age}!'.format(age=18, name='tank'))
5、split,rsplit
# 5、split 切分# strl = 'hello tank!'
# 根据strl内的空格进行切分
# 切分出来的值会存放在[]列表中。
# print(strl.split(' ')) # ['hello', 'tank!']
6、join
# 6、join 字符串拼接
# 报错,只允许字符串拼接
# print(' '.join(['tank', 18]))
# # 根据空格,把列表中的每一个字符串进行拼接
# print(' '.join(['tank', '18', 'from GZ']))
# # 根据_,把列表中的每一个字符串进行拼接
# print('_'.join(['tank', '18', 'from GZ']))
7、replace
# 7、replace:字符串替换
# str1 = 'my name is WangWei, my age 73!'
# print(str1)
# str2 = str1.replace('WangWei', 'sb')
# print(str2)
8、isdigit
# 8、isdigit:判断字符串是否是数字
# choice = input('请选择功能[0, 1, 2]: ')
# 判断用户输入的选择是否是数字
# print(choice.isdigit())



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号