Java7/8 中的 HashMap 和 ConcurrentHashMap 全解析
Java7 HashMap
HashMap不支持并发操作
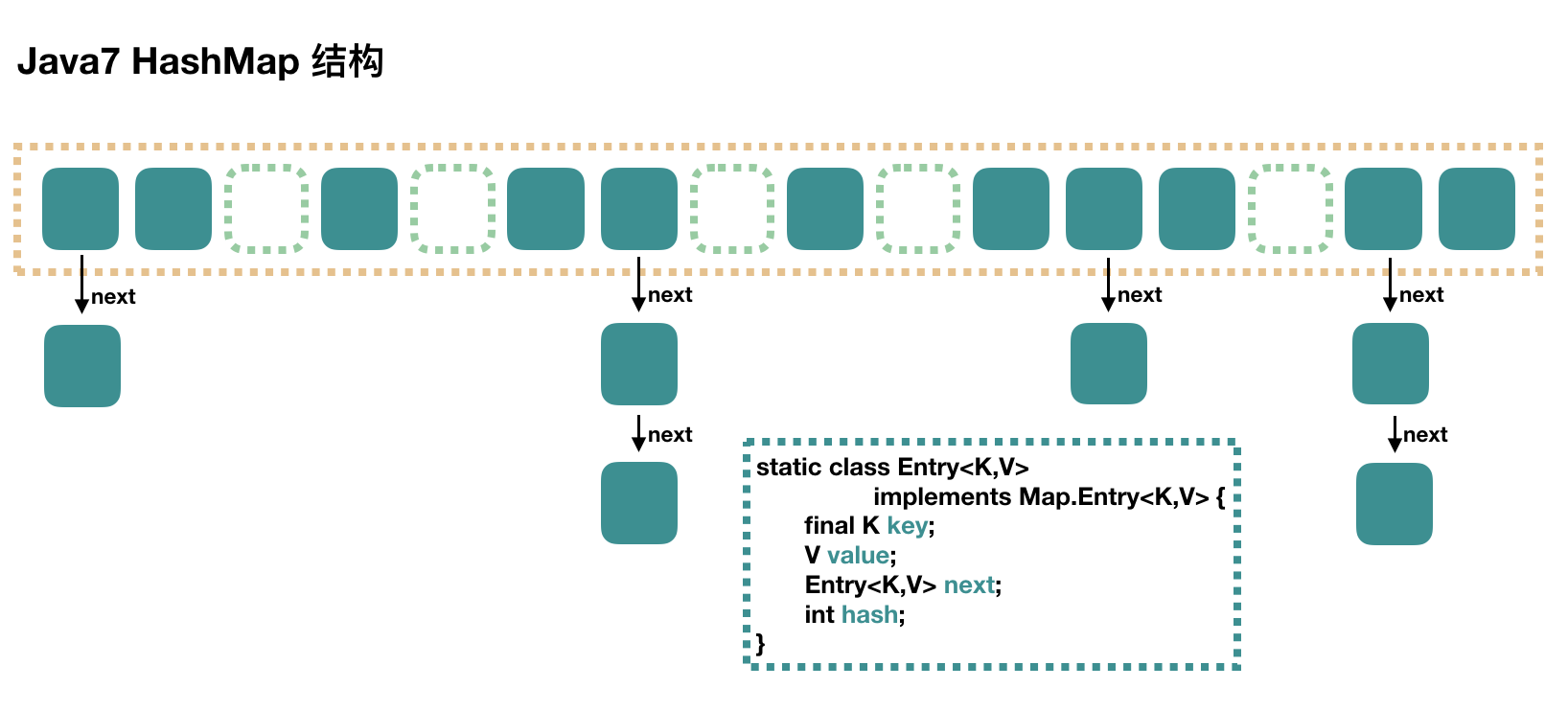
大方向上,HashMap里面是一个数组,然后数组中每个元素都是一个单向链表。
上图中,每个绿色的实体都是嵌套类Entry的实例,Entry包含四个属性:key,value,hash值和用于单向链表的next。
capacity:当前数组容量,始终保持2^n,可以扩容,扩容后数组大小为当前的两倍。
loadFactor:负载因子,默认为0.75.
threshold:扩容的阈值,等于capacity * loadFactor
public V put(K key, V value) {
//当插入第一个元素的时候,需要初始化数组大小
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
//如果 key 为 null, 最终这个entry放到table[0]中
if (key == null) {
return putForNullKey(value);
}
// 1. 求 key 的 hash 值
int hash = hash(key);
// 2. 找到对应的数组下标
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
// 3. 遍历一下对应下标处的链表,看是否有重复的 key 已经存在
// 如果有,直接覆盖,put方法返回旧值就结束了
for (Entry<K, V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
// 4. 不存在重复的 key,将此 entry添加到链表中
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
数组初始化
在第一个元素插入HashMap的时候做一次数组的初始化,就是先确定初始数组大小,并计算数组扩容的阈值。
private void inflateTable(int toSize) {
// 保证数组大小一定是 2 的 n 次方
// 比如这样初始化:new HashMap(20), 那么处理成初始数组大小是32
int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize);
// 计算扩容阈值:capacity * loadFactor
threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
//初始化数组
table = new Entry[capacity];
initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity);
}
计算具体数组位置
使用key的hash值对数组长度取模
static int indexFor(int hash, int length) {
// assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : " length must be a non-zero oiwer of 2";
return hash & (length - 1);
}
取hash值的低 n 位,如数组长度为 32 的时候,取的就是 key 的 hash 值的低 5 位,作为它在数组中的下标位置。
添加节点到链表中
找到数组下标后,会先进行 key 判重,如果没有重复,就准备将新值放入到链表的表头。
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucktIndex) {
// 如果当前 HashMap 大小已经达到了阈值,并且新值要插入的数组位置已经有元素了,那么要扩容
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
//扩容
resize(2 * table.length);
// 扩容以后,重新计算 hash 值
hash = (null != key) ?hash(key) : 0;
// 重新计算扩容后的新的下标
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
//
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
// 将新值放到链表的表头,然后 size++
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K, V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
这个方法的主要逻辑就是先判断是否需要扩容,需要的话先扩容,然后再将这个新的数据插入到扩容后的数组的相应位置处的链表的表头。
数组扩容
前面我们看到,在插入新值的时候,如果当前 size 已经到了阈值,并且要插入的数组位置上已经有元素,那么就会触发扩容,扩容后,数组大小为原来的 2 倍。
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAOACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
// 新的数组
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
// 将原来的数组中的值迁移到新的更大的数组中
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}
扩容就是用一个新的大数组替换原来的小数组,并将原来数组中的值迁移到新的数组中。
由于是双倍扩容,迁移过程中,会将原来 table[i] 中的链表的所有节点,分拆到新的数组的newTable[i]和newTable[i + oldLength]位置上。如原来数组长度是16,那么扩容后,原来table[0]处的链表中的所有元素会被分配到新数组中newTable[0]和newTable[16]这两个位置。
get过程分析
相对于put过程,get过程是非常简单的
1. 根据 key 计算 hash 值
2. 找到相应的数组下标 : hash & (length - 1).
3. 遍历该数组位置处的链表,直到找到相等(== 或 equals)的 key。
public V get(object key) {
// key 为 null 的话,会被放到 table[0],所以只要遍历 table[0] 处的链表就可以了
if (key == null) {
return getForNullKey();
}
Entry<K, V> entry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
getEntry(key):
final Entry<K, V> getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
// 确定数组下标,然后从头开始遍历链表,直到找到为止
for (Entry<K, V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
return e;
}
}
return null;
}
Java7 ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentHashMap和HashMap思路差不多,但是因为它支持并发操作,所以要复杂一些。
整个 ConcurrentHashMap 由一个个 Segment 组成,Segment代表 “部分” 或 “一段” 的意思,所以很多地方都会将其描述为分段锁。
ConcurrentHashMap 是一个 Segment 数组,Segment 通过继承 ReentrantLock 来进行加锁,所以每次需要加锁的操作锁住的是一个 segment, 这样只要保证每个 Segment是线程安全的,也就实现了全局的线程安全。
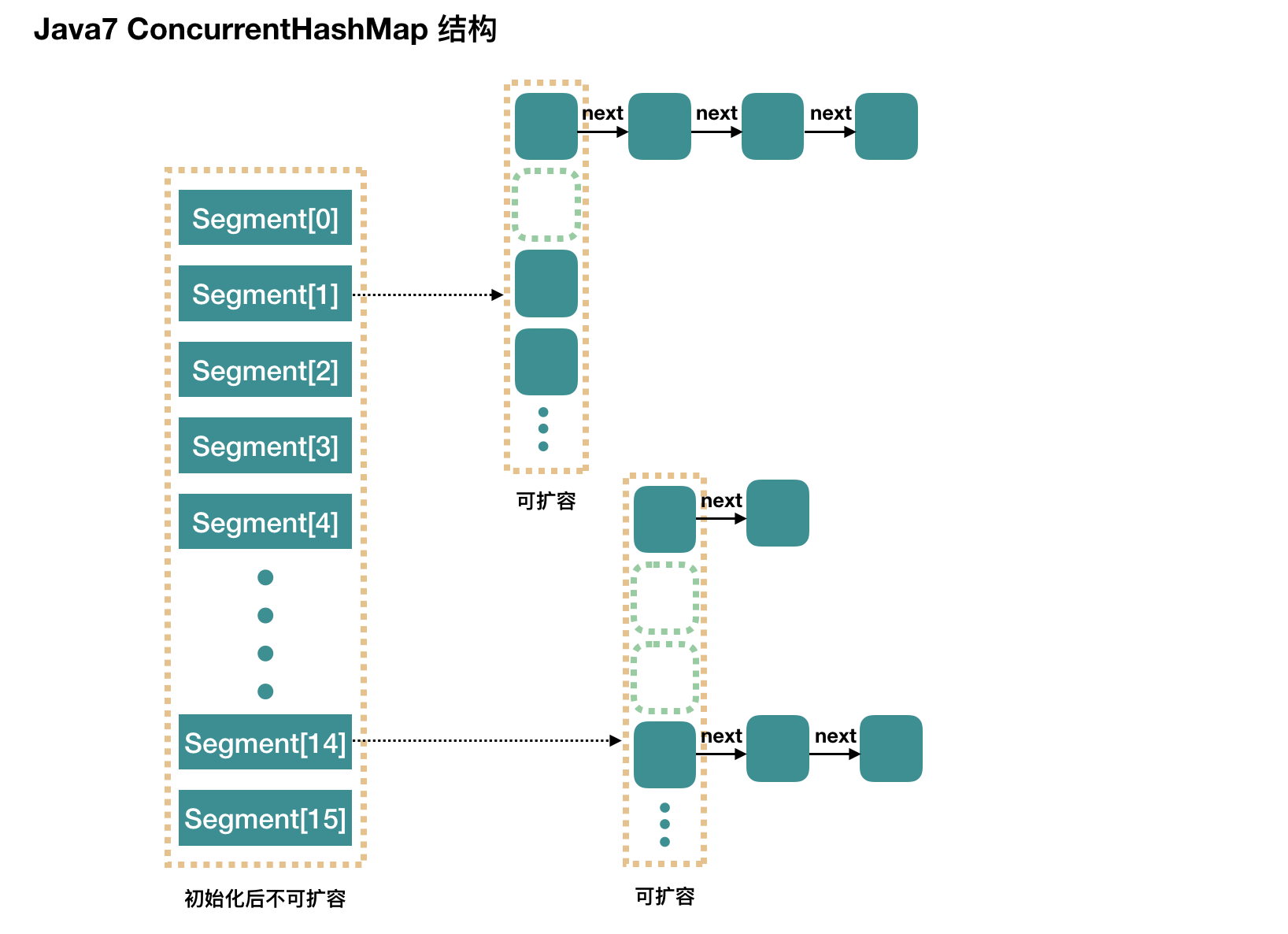
concurrencyLevel:并发级别、并发数、Segment数,默认是16,也就是说ConcurrentHashMap有16个Segments,所以理论上,这个时候最多可以同时支持16个线程并发写,只要它们的操作分别分布在不同的Segment上,这个值可以再初始化的时候设置为其他值,但是一旦初始化以后,它是不可以扩容的。
再具体到每个Segment内部,其实每个Segment很想之前介绍的 HashMap,只要它要保证线程安全,所以处理起来要麻烦些。
初始化
initlCapacity:初始容量,这个值指的是整个ConcurrentHashMap的初始容量,实际操作的时候需要平均分给每个Segment。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号