python学习笔记(一)matplotlib、numpy、Pandas
整合自网络与https://space.bilibili.com/243821484?from=search&seid=8124768530697300938
2.numpy
-
2.1 平均值
使用np.mean()函数,numpy.mean(a, axis, dtype)
假设a为[time,lat,lon]的数据,那么
·axis 不设置值,对 timelatlon 个值求均值,返回一个数
·axis = 0:压缩时间维,对每一个经纬点求均值,返回 [lat, lon] 数组(如求一个场的N年气候态)
·axis =1,2 :压经度纬度,对每个时间求平均值,返回 [time] 矩阵(如求某时间序列,或指数)
需要特别注意的是,气象数据中常有缺测,在NCL中,使用求均值函数会自动略过,而在python中,当任意一数与缺测(np.nan)计算的结果均为np.nan,比如求[1,2,3,4,np.nan]的平均值,结果为np.nan
因此,当数据存在缺测数据时,通常使用np.nanmean()函数,用法同上,此时[1,2,3,4,np.nan]的平均值为(1+2+3+4)/4 = 2.5
同样的,求某数组最大最小值时也有np.nanmax(), np.nanmin()函数来补充np.max(), np.min()的不足。
其他很多np的计算函数也可以通过在前边加‘nan’来使用。
-
2.2 增减维数
增加
在操作数组情况下,需要按照某个轴将不同数组的维度对齐,这时候需要为数组添加维度(特别是将二维数组变成高维张量的情况下)。numpy提供了expand_dims()函数来为数组增加维度:
1 import numpy as np 2 3 a = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]]) 4 a.shape 5 print(a) 6 >>> 7 """ 8 (2L, 2L) 9 [[1 2] 10 [3 4]] 11 """ 12 # 如果需要在数组上增加维度,输入需要增添维度的轴即可,注意index从零还是 13 a_add_dimension = np.expand_dims(a,axis=0) 14 a_add_dimension.shape 15 >>> (1L, 2L, 2L) 16 17 a_add_dimension2 = np.expand_dims(a,axis=-1) 18 a_add_dimension2.shape 19 >>> (2L, 2L, 1L) 20 21 22 a_add_dimension3 = np.expand_dims(a,axis=1) 23 a_add_dimension3.shape 24 >>> (2L, 1L, 2L)
squeeze函数来压缩冗余维度1 e= np.arange(10) 2 e 3 array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
1 e.reshape(1,1,10) 2 array([[[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]]])
1 e.reshape(1,1,10) 2 array([[[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]]]) 3 e.reshape(1,10,1) 4 array([[[0], 5 [1], 6 [2], 7 [3], 8 [4], 9 [5], 10 [6], 11 [7], 12 [8], 13 [9]]])
squeeze 函数:从数组的形状中删除单维度条目,即把shape中为1的维度去掉
用法:numpy.squeeze(a,axis = None)
-
a表示输入的数组;
-
axis用于指定需要删除的维度,但是指定的维度必须为单维度,否则将会报错;
-
axis的取值可为None 或 int 或 tuple of ints, 可选。若axis为空,则删除所有单维度的条目;
-
返回值:数组
-
不会修改原数组;
1 a = e.reshape(1,1,10) 2 a 3 array([[[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]]]) 4 np.squeeze(a) 5 array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
3.Pandas
如果用 python 的列表和字典来作比较, 那么可以说 Numpy 是列表形式的,没有数值标签,而 Pandas 就是字典形式
1 import pandas as pd 2 import numpy as np 3 s = pd.Series([1,3,6,np.nan,44,1]) 5 print(s)
################### 0 1.0 1 3.0 2 6.0 3 NaN 4 44.0 5 1.0 dtype: float64 ###################
Series的字符串表现形式为:索引在左边,值在右边。由于我们没有为数据指定索引。
-
3.1DataFrame
1 dates = pd.date_range('20160101',periods=6) 2 print(dates) 3 df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(6,4),index=dates,columns=['a','b','c','d']) # 行 列 5 print(df)
############################################################################# DatetimeIndex(['2016-01-01', '2016-01-02', '2016-01-03', '2016-01-04', '2016-01-05', '2016-01-06'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='D') a b c d 2016-01-01 -0.362729 0.025856 -0.453970 0.521317 2016-01-02 -0.694964 -0.418078 -0.034875 -0.382649 2016-01-03 -1.308891 -0.465486 -0.892237 -0.094203 2016-01-04 0.331540 0.621307 0.033407 -1.490113 2016-01-05 -1.770037 1.443139 -0.465179 -1.571931 2016-01-06 0.017418 -0.007310 1.151194 -0.043637 #############################################################################
DataFrame是一个表格型的数据结构,它包含有一组有序的列,每列可以是不同的值类型(数值,字符串,布尔值等)。DataFrame既有行索引也有列索引, 它可以被看做由Series组成的大字典。
选择显示pd其中一行
1 print(df['b'])
######################## 2016-01-01 0.743081 2016-01-02 -0.558816 2016-01-03 0.287229 2016-01-04 1.850405 2016-01-05 0.619291 2016-01-06 0.847188 Freq: D, Name: b, dtype: float64 ########################
不选择显示列索引,默认从零开始
1 df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape((3,4))) 2 print(df1)
########## 0 1 2 3 0 0 1 2 3 1 4 5 6 7 2 8 9 10 11 ##########
显示列的序号、数据的名称、所有的值
1 df2 = pd.DataFrame({'A' : 1., 2 'B' : pd.Timestamp('20130102'), 3 'C' : pd.Series(1,index=list(range(4)),dtype='float32'), 4 'D' : np.array([3] * 4,dtype='int32'), 5 'E' : pd.Categorical(["test","train","test","train"]), 6 'F' : 'foo'}) 7 8 print(df2)
""" A B C D E F 0 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 test foo 1 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 train foo 2 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 test foo 3 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 train foo """
1 print(df2.index)
"""
Int64Index([0, 1, 2, 3], dtype='int64')
"""
1 print(df2.columns)
""" Index(['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F'], dtype='object') """
1 print(df2.values)
""" array([[1.0, Timestamp('2013-01-02 00:00:00'), 1.0, 3, 'test', 'foo'], [1.0, Timestamp('2013-01-02 00:00:00'), 1.0, 3, 'train', 'foo'], [1.0, Timestamp('2013-01-02 00:00:00'), 1.0, 3, 'test', 'foo'], [1.0, Timestamp('2013-01-02 00:00:00'), 1.0, 3, 'train', 'foo']], dtype=object) """
显示行索引信息
1 print(df2.dtypes)
""" df2.dtypes A float64 B datetime64[ns] C float32 D int32 E category F object dtype: object """
数据的总结。只针对数值类型
1 df2.describe()
A C D count 4.0 4.0 4.0 mean 1.0 1.0 3.0 std 0.0 0.0 0.0 min 1.0 1.0 3.0 25% 1.0 1.0 3.0 50% 1.0 1.0 3.0 75% 1.0 1.0 3.0 max 1.0 1.0 3.0
翻转数据
1 print(df2.T)
0 1 2 \ A 1 1 1 B 2013-01-02 00:00:00 2013-01-02 00:00:00 2013-01-02 00:00:00 C 1 1 1 D 3 3 3 E test train test F foo foo foo 3 A 1 B 2013-01-02 00:00:00 C 1 D 3 E train F foo
对数据的 index 进行排序并输出
1 print(df2.sort_index(axis=0, ascending=True)) #axis=0为选择列索引,axis=1为选择行索引
2 print(df2.sort_index(axis=1, ascending=False)) #ascending=True为正序,False为倒序
A B C D E F 0 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 test foo 1 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 train foo 2 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 test foo 3 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 train foo F E D C B A 0 foo test 3 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 1 foo train 3 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 2 foo test 3 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 foo train 3 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0
对数据 值 某一列 排序输出:
1 print(df2.sort_values(by='E'))
A B C D E F 0 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 test foo 2 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 test foo 1 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 train foo 3 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 train foo
-
3.2 选择数据
1 dates = pd.date_range('20130101', periods=6) 2 df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(24).reshape((6,4)),index=dates, columns=['A','B','C','D']) 3 df
""" A B C D 2013-01-01 0 1 2 3 2013-01-02 4 5 6 7 2013-01-03 8 9 10 11 2013-01-04 12 13 14 15 2013-01-05 16 17 18 19 2013-01-06 20 21 22 23 """
选择某一列
1 print(df['A']) 2 或者 3 print(df.A)
"""
2013-01-01 0
2013-01-02 4
2013-01-03 8
2013-01-04 12
2013-01-05 16
2013-01-06 20
"""
选择跨越多行或多列
1 print(df[0:3])
""" A B C D 2013-01-01 0 1 2 3 2013-01-02 4 5 6 7 2013-01-03 8 9 10 11 """
1 print(df[0:3]["A"])
"""
2013-01-01 0 2013-01-02 4 2013-01-03 8
"""
1 print(df['20130102':'20130104'])
""" A B C D 2013-01-02 4 5 6 7 2013-01-03 8 9 10 11 2013-01-04 12 13 14 15 """
loc 使用标签来选择数据
1 print(df.loc['20130102'])
""" A 4 B 5 C 6 D 7 Name: 2013-01-02 00:00:00, dtype: int64 """
1 print(df.loc[:,['A','B']])
1 """ 2 A B 3 2013-01-01 0 1 4 2013-01-02 4 5 5 2013-01-03 8 9 6 2013-01-04 12 13 7 2013-01-05 16 17 8 2013-01-06 20 21 9 """
1 print(df.loc['20130102',['A','B']])
""" A 4 B 5 Name: 2013-01-02 00:00:00, dtype: int64 """
iloc 根据序列来选择数据
1 print(df)
2 print(df.iloc[3,1]) #第4行第2列
''' A B C D 2013-01-01 0 1 2 3 2013-01-02 4 5 6 7 2013-01-03 8 9 10 11 2013-01-04 12 13 14 15 2013-01-05 16 17 18 19 2013-01-06 20 21 22 23 13 '''
1 print(df.iloc[3:5,1:3]) # 第三行到第五行,第一列到第三列
""" B C 2013-01-04 13 14 2013-01-05 17 18 """
1 print(df.iloc[[1,3,5],1:3])
""" B C 2013-01-02 5 6 2013-01-04 13 14 2013-01-06 21 22 """
通过判断的筛选
1 print(df[df.A>8])
""" A B C D 2013-01-04 12 13 14 15 2013-01-05 16 17 18 19 2013-01-06 20 21 22 23 """
当有条件筛选时,如下图筛选出所有C列PM2.5在I列1006A处的值:
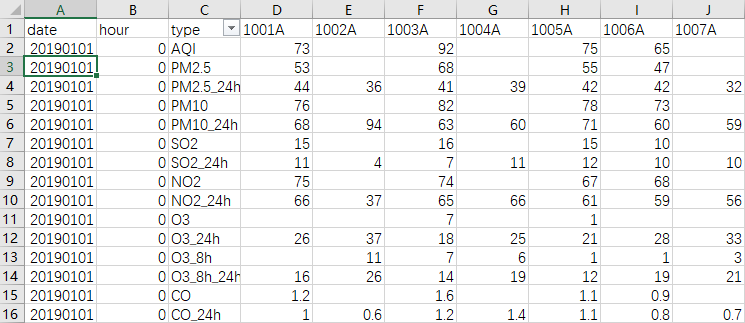
1 path = 'D:\python\站点_20190101-20191231\china_sites_20190101.csv' 2 csv_data = pd.read_csv(path) 3 aa=csv_data[csv_data['type'] == 'PM2.5'][['type', '1006A']] 4 aa
###### 1006A 1 47.0 16 44.0 31 43.0 46 40.0 61 42.0 76 46.0 91 47.0 106 49.0 121 47.0 136 53.0 151 46.0 166 34.0 。。。。。。 #######
3.2 编辑、写入值
1 # 创建数据 2 dates = pd.date_range('20130101', periods=6) 3 df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(24).reshape((6,4)),index=dates, columns=['A','B','C','D'])
""" A B C D 2013-01-01 0 1 2 3 2013-01-02 4 5 6 7 2013-01-03 8 9 10 11 2013-01-04 12 13 14 15 2013-01-05 16 17 18 19 2013-01-06 20 21 22 23 """
根据位置用loc 和 iloc设置
1 df.iloc[2,2] = 1111 2 df.loc['20130101','B'] = 2222
""" A B C D 2013-01-01 0 2222 2 3 2013-01-02 4 5 6 7 2013-01-03 8 9 1111 11 2013-01-04 12 13 14 15 2013-01-05 16 17 18 19 2013-01-06 20 21 22 23 """
根据条件设置
1 df.B[df.A>4] = 0 #A列>4时,B列数据等于0
""" A B C D 2013-01-01 0 2222 2 3 2013-01-02 4 5 6 7 2013-01-03 8 0 1111 11 2013-01-04 12 0 14 15 2013-01-05 16 0 18 19 2013-01-06 20 0 22 23 """
按行或列设置
1 df['F'] = np.nan
""" A B C D F 2013-01-01 0 2222 2 3 NaN 2013-01-02 4 5 6 7 NaN 2013-01-03 8 0 1111 11 NaN 2013-01-04 12 0 14 15 NaN 2013-01-05 16 0 18 19 NaN 2013-01-06 20 0 22 23 NaN """
生成日期
1 date_l=[datetime.strftime(x,'%Y%m%d') for x in list(pd.date_range(start="20190101", end="20190131"))]
#'%Y%m%d'可以改变生成日期格式,如%Y-%m-%d,
['20190101', '20190102', '20190103', '20190104', '20190105', '20190106', '20190107', '20190108', '20190109', '20190110', '20190111', '20190112', '20190113', '20190114', '20190115', '20190116', '20190117', '20190118', '20190119', '20190120', '20190121', '20190122', '20190123', '20190124', '20190125', '20190126', '20190127', '20190128', '20190129', '20190130', '20190131']
处理nan
1.直接删除,将含有NaN的列(columns)去掉:
1 import pandas as pd 2 3 df = pd.DataFrame({'a':[None,1,2,3],'b':[4,None,None,6],'c':[1,2,1,2],'d':[7,7,9,2]}) 4 print (df) 5 6 print (df.isnull().sum()) 7 #查找有多少nan
a b c d 0 NaN 4.0 1 7 1 1.0 NaN 2 7 2 2.0 NaN 1 9 3 3.0 6.0 2 2 a 1 b 2 c 0 d 0 dtype: int64
1 data_without_NaN =df.dropna(axis=1) 2 print (data_without_NaN)
c d
0 1 7
1 2 7
2 1 9
3 2 2
2.遗失值插补法
以均值填补
1 from sklearn.preprocessing import Imputer 2 # 或者from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer 3 my_imputer = Imputer() 4 data_imputed = my_imputer.fit_transform(df) 5 print (type(data_imputed)) 6 # array转换成df 7 df_data_imputed = pd.DataFrame(data_imputed,columns=df.columns) 8 print (df_data_imputed)
a b c d
0 2.0 4.0 1.0 7.0
1 1.0 5.0 2.0 7.0
2 2.0 5.0 1.0 9.0
3 3.0 6.0 2.0 2.0


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号