Redis学习小结
在7月中旬,我成功入职实习,通过进入公司,认识到了个人与企业巨大的差距,首先就是对于中间件的使用,ElasticSearch、Redis、Kafka等等,都是听过却从未使用过的,然而在任务下达之后,激励了学习动力,首先就是Redis。
网站
Redis官网:https://redis.io/
Redis的中文文档网站:http://www.redis.cn/
Redis是什么(转):https://www.cnblogs.com/powertoolsteam/p/redis.html
Redis的全部命令:http://www.redis.cn/commands.html
关于Redis
Redis(Remote Dictionary Server ):远程字典服务,C语言编写,属于NoSQL,key-value数据库,支持分布式(重点),常用作缓存。
安装:前往官网下载,注意对应系统,具体内容详见:https://www.runoob.com/redis/redis-install.html
Redis数据结构
Redis支持以下5种数据结构
1)字符串(strings)
2)字符串列表(lists)
3)字符串集合(sets)
4)有序字符串集合(sorted sets)
5)哈希(hashes)
不过在文档中查找命令时可以发现分的非常细致
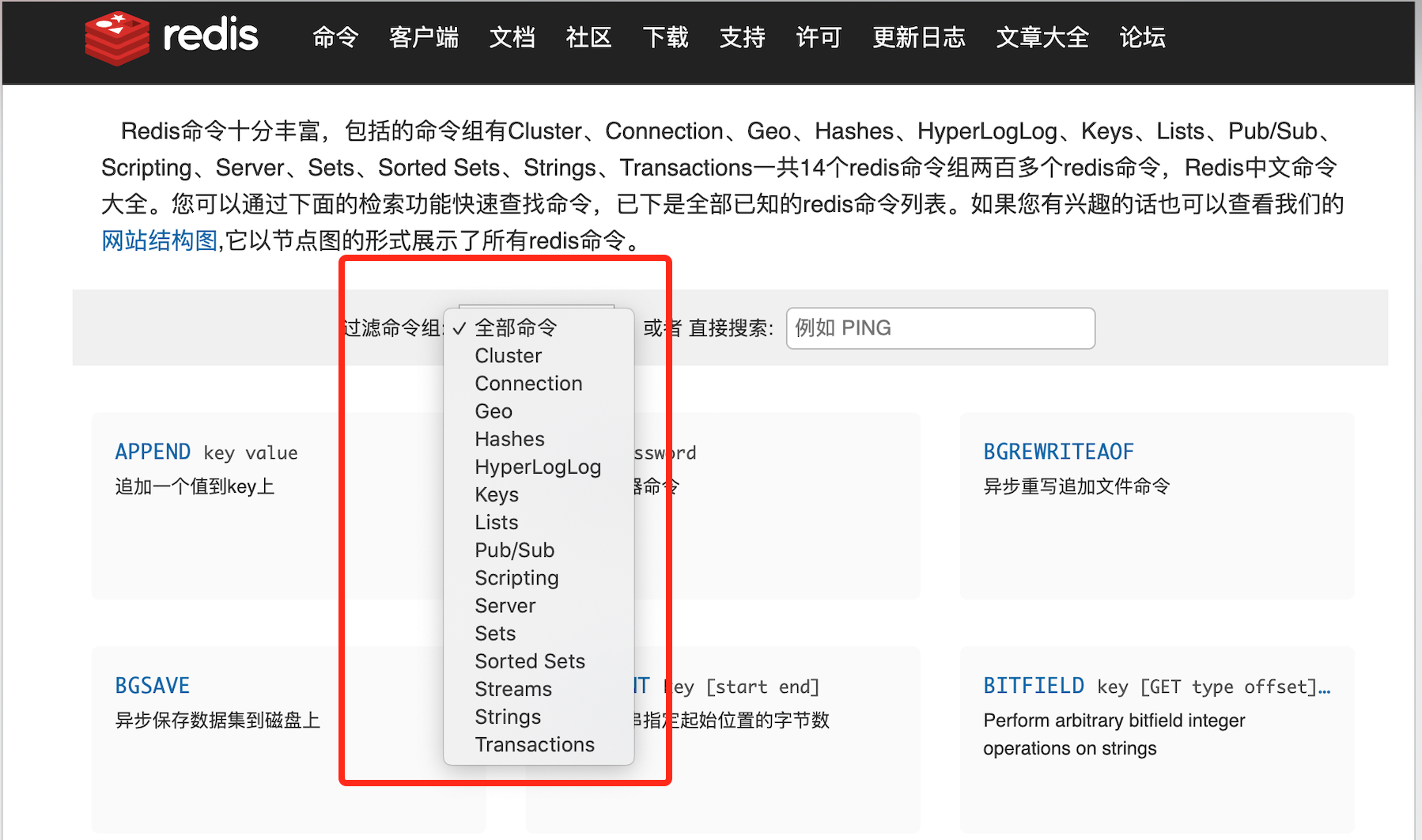
所以当需要查找命令的时候不妨分类查找或是快速搜索
字符串类型是Redis用的最多的地方,是所有存储系统最基础的类型,因此入门就必须掌握它。
以下是String中的命令(参考视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1S54y1R7SB)
1)get、set、EXISTS、APPEND、STRLEN

2)incr、decr、INCRBY、DECRBY
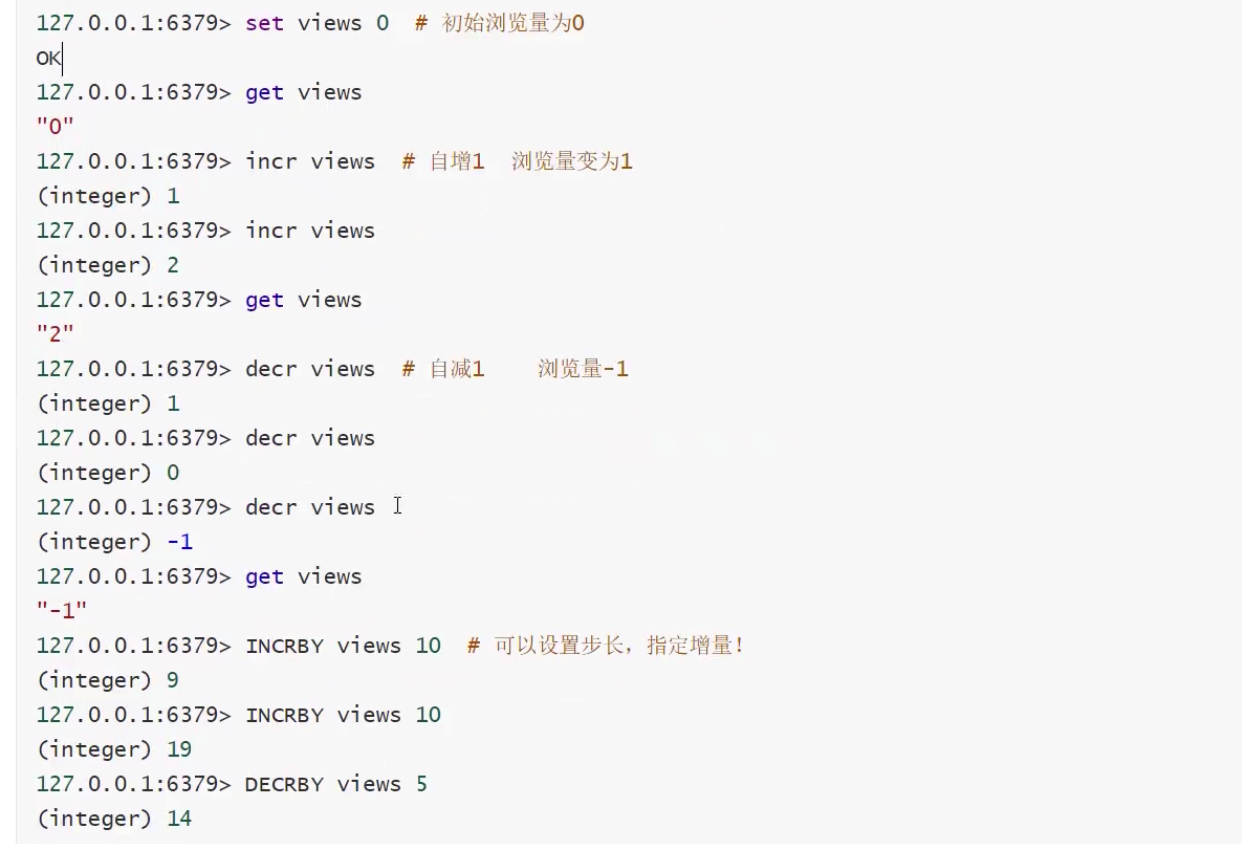
3)GETRANGE、SETRANGE

4)setex、setnx

5)mset(可以设置对象)、mget、getset
mset

mget

getset

List

其他还有很多类型,就不一一列举了,详情参考文档--命令
Springboot配置Redis
Springboot作为目前Java开发主流框架,自然可以支持Redis。
首先在 pom.xml 中引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> <version>${redis-version}</version> </dependency>
然后就是配置文件,这里我使用的是 properties文件
# Redis数据库索引(默认为0)
spring.redis.database=0
# Redis服务器地址
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1
# Redis服务器连接端口
spring.redis.port=6379
# Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空)
spring.redis.password=
# 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制)
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=20
# 连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制)
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait=-1
# 连接池中的最大空闲连接
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=10
# 连接池中的最小空闲连接
spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle=0
# 连接超时时间(毫秒)
spring.redis.timeout=1000
配置就OK了,简单使用
创建jdisCluster
package com.zs.springboot.config.redis; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import redis.clients.jedis.HostAndPort; import redis.clients.jedis.JedisCluster; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; @Configuration public class RedisConfig { private RedisProperties redisProperties; public RedisConfig(RedisProperties redisProperties) { this.redisProperties = redisProperties; } @Bean public JedisCluster jedisCluster() { Integer[] ports = redisProperties.getPorts(); String host = redisProperties.getIp(); Set<HostAndPort> hostAndPortSet = new HashSet<>(); for (Integer port : ports) { hostAndPortSet.add(new HostAndPort(host, port)); } return new JedisCluster(hostAndPortSet, redisProperties.getMaxActive(), redisProperties.getMaxWait()); } }
增、删测试
@Service public class RedisService { @Autowired private JedisCluster jedisCluster; public Map<String, Object> set(String key, Object value) { Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); String result = jedisCluster.set(key, JsonUtil.toJsonString(value)); System.out.println(result);return map; } public String get(String key) { String jsonString = jedisCluster.get(key); if (jsonString==null || jsonString.equals("")) { return null; } return jsonString; } public Map<String, Object> del(String key) { Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); Long del = jedisCluster.del(key); if (del>0) { map.put("code", 200); } else { map.put("code", 404); } return map; } //设置失效时间 public Long expire(String key,Integer seconds) { return jedisCluster.expire(key, seconds); } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号