结对编程——个人项目代码分析
一、简介
本博客为姑丽加娜提同学的个人项目(中小学数学卷子自动生成程序)的代码个人分析与学习。
二、程序功能测试
运行测试
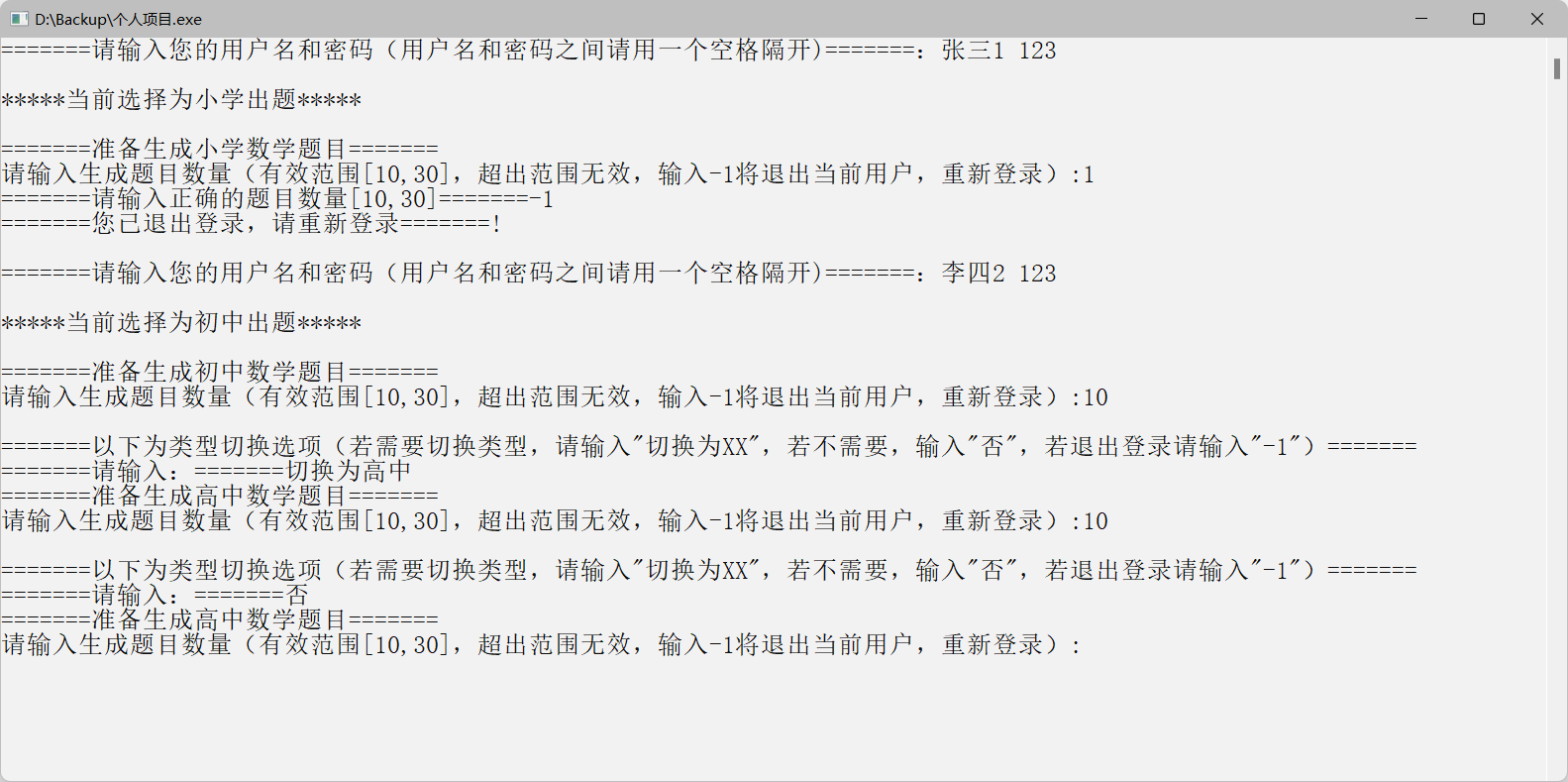
结果检查
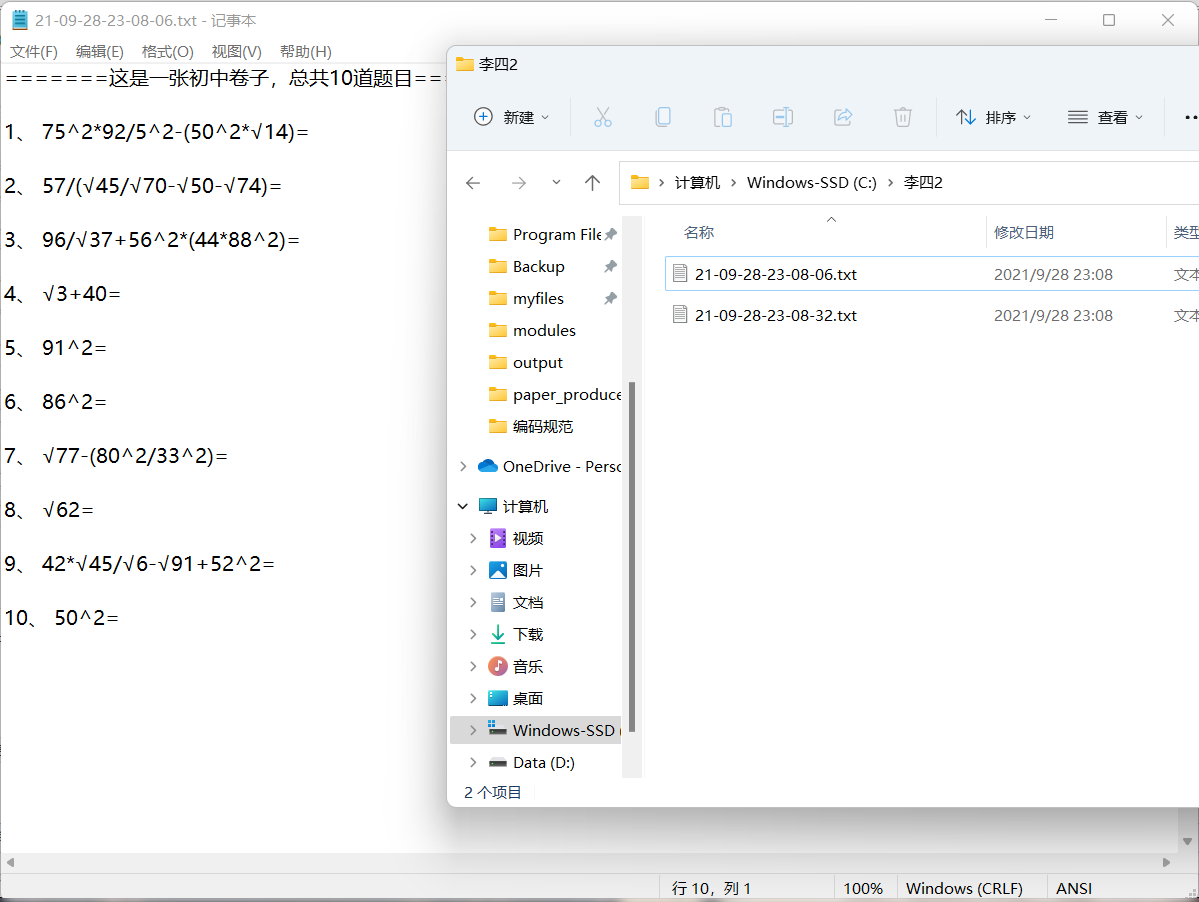
功能基本实现
三、代码结构分析
该代码中定义了一个使用者的User类,其中包括用户的一些基本属性如用户名、密码和教学年级等,同时也定义了一些成员函数用于登录和生成试卷:
class User {
private:
string Name; //用户名
string Type; //教学年级
string Passward; //用户名密码
int Num; //出题数量
string folderPath; //文件夹的路径
char FileName[100]; //当前文件路径
string Path; // txt文件夹的路径
ofstream Paper; // 以输出方式打开试卷
stringstream question; //
public:
void SignIn();
void Creat_Paper();
void Symbol(int option,int ope);
void Switch_Type();
void Name_File();
bool Check();
};具体实现如下
- void User::SignIn()
点击查看代码
void User::SignIn() { //用户登录函数
while(1) {
cout<<"=======请输入您的用户名和密码(用户名和密码之间请用一个空格隔开)=======:";
cin>>Name>>Passward;
if(Name=="张三1"||Name=="张三2"||Name=="张三3") {
if(Passward=="123") {
Type="小学";
break;
}
} else if(Name=="李四1"||Name=="李四2"||Name=="李四3") {
if(Passward=="123") {
Type="初中";
break;
}
} else if(Name=="王五1"||Name=="王五2"||Name=="王五3") {
if(Passward=="123") {
Type="高中";
break;
}
}
cout<<"=======请输入正确的用户名、密码=======:"<<endl<<endl;
}
cout<<endl<<"*****当前选择为"<<Type<<"出题*****"<<endl<<endl;
//folderPath="E:\\software_engineering\\Personal_job\\"+Name;//确定当前账号对应的文件夹的位置
folderPath=Name;//确定当前账号对应的文件夹的位置
Name_File();//文件命名
Creat_Paper();//生出符合输入的数学试卷
}- void User::Creat_Paper()
点击查看代码
void User::Creat_Paper() {
cout<<"=======准备生成"<<Type<<"数学题目======="<<endl;
cout<<"请输入生成题目数量(有效范围[10,30],超出范围无效,输入-1将退出当前用户,重新登录):";
cin>>Num;//输入生成题目数量
while(Num<10||Num>30) {
if(Num==-1) {
cout<<"=======您已退出登录,请重新登录=======!"<<endl<<endl;
SignIn();
break;
}
cout<<"=======请输入正确的题目数量[10,30]=======";
cin>>Num;
}
Path="C:\\"+Name;
if(0!=access(Path.c_str(),0)){
mkdir(Path.c_str());
}
Path=Path+"\\"+FileName;
Paper.open(Path.c_str(),ios_base::out);
if(!Paper){
cout<<"=======打开文件夹失败======="<<endl;
}
Paper<<"=======这是一张"<<Type<<"卷子,总共"<<Num<<"道题目======="<<endl<<endl;
int n=Num;
while(n!=0) { //每道题的出题过程,循环Number次即生成Number个题目
n--;
int OperandNumber=rand()%5+1; //随机生成操作数的个数
if(OperandNumber==1&&Type=="小学") { //小学至少是两位操作数
OperandNumber=rand()%4+2; //生成2-5个操作数
}
int oNum=OperandNumber; //保存操作数的个数
int Left_Bracket=0; //左括号的位置
int Num_Bracket=0; //括号括住的操作数的个数
if(OperandNumber>2&&rand()%2==1) { //生成的题目有括号
if(OperandNumber==3) {
Left_Bracket=rand()%2+1;
Num_Bracket=2;
} else if(OperandNumber==4) {
Left_Bracket=rand()%3+1;
if(Left_Bracket==3) Num_Bracket=2; //位于最后,最多只能括住两个数
else Num_Bracket=rand()%2+2; //位于前面,可以括住2-3个数
} else {
Left_Bracket=rand()%4+1;
if(Left_Bracket==4) Num_Bracket=2; //只能括住两个的情况
else if(Left_Bracket==3) Num_Bracket=rand()%2+2; //可以括住2-3个的情况
else Num_Bracket=rand()%3+2; //可以括住2-4个的情况
}
}
bool flag=false;//确保初中的每道题目中都至少有平方或者根号,高中的每道题都至少有sin,cos或tan中的一个
while(oNum!=0) {
oNum--;
if(oNum==OperandNumber-Left_Bracket) question<<"(";
int option;
if(Type=="小学") option=0;
else if(Type=="初中") {
option=rand()%3;
if(option!=0) flag=true;//说明已经生成了平方或者根号中的一个了
if(oNum==0&&flag==false) option=rand()%2+1;
} else if(Type=="高中") {
option=rand()%6;
if(option>2) flag=true;//说明已经生成了平sin,cos或tan中的一个了
if(oNum==0&&flag==false) option=rand()%5+1;//说明一直到最后一个操作数都没有sin,cos或tan,则最后一个必须有
}
int Operand=rand()%100+1;
Symbol(option,Operand);
if(oNum==OperandNumber-Left_Bracket-Num_Bracket+1) question<<")";
if(oNum!=0) {
int opt=rand()%4;
switch(opt) {
case 0:
question<<"+";
break;
case 1:
question<<"-";
break;
case 2:
question<<"*";
break;
case 3:
question<<"/";
break;
}
} else question<<"=";
}
question<<endl;
bool check_result=Check();//检查
if(check_result==true) {
int order=Num-n;
Paper<<order<<"、 "<<question.str()<<endl;
question.str(" ");
} else n++;
}
Paper.close();
}- void User::Symbol(int option,int ope)
点击查看代码
void User::Symbol(int option,int ope) {//对每个操作数进行处理
switch(option) {
case 0://不处理,即小学的题目
question<<ope;
break;
case 1:
question<<ope<<"^2";
break;
case 2://当处于情况0-2时,生成初中生的题目
question<<"√"<<ope;
break;
case 3:
question<<"sin"<<ope;
break;
case 4:
question<<"cos"<<ope;
break;
case 5://当处于情况0-5时,生成高中生的题目
question<<"tan"<<ope;
break;
}
}- void User::Switch_Type()
点击查看代码
void User::Switch_Type() { //切换类型选项
string TypeSwitch;
while(1) {
cout<<endl<<"=======以下为类型切换选项(若需要切换类型,请输入\"切换为XX\",若不需要,输入\"否\",若退出登录请输入\"-1\")======="<<endl;
cout<<"=======请输入:=======";
cin>>TypeSwitch;
if(TypeSwitch=="否"||TypeSwitch=="") {
Name_File();
Creat_Paper();//生出符合输入的数学试卷
continue;
} else if(TypeSwitch=="-1") break; //退出当前操作
if(TypeSwitch=="切换为小学"||TypeSwitch=="切换为初中"||TypeSwitch=="切换为高中") {
Type=TypeSwitch.erase(0,6);
Name_File();
Creat_Paper();//生出符合输入的数学试卷
continue;
} else {
while(1) {
cout<<"请输入小学、初中和高中三个选项中的一个:";
cin>>TypeSwitch;
if(TypeSwitch=="小学"||TypeSwitch=="初中"||TypeSwitch=="高中") {
Type=TypeSwitch;
Name_File();
Creat_Paper();//生成试卷
break;
} else if(TypeSwitch=="-1") break;
}
}
if(TypeSwitch=="-1") break;
}
cout<<"您已退出本次登录!"<<endl;
}- void User::Name_File()
点击查看代码
void User::Name_File() {//给文件命名的函数
struct tm *ptr;
time_t It=time(NULL);
ptr=localtime(&It);
strftime(FileName,30,"%y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S.txt",ptr);//以年月日时分秒对输出文件命名
}- bool User::Check()
点击查看代码
bool User::Check() {//查重
string CheckPath=folderPath+"\\Check.txt";//每个账号中都有一个check文档,该文档保存该账号生成的所有题目
fstream CheckFile;
CheckFile.open(CheckPath.c_str(),ios::in|ios::app);
string temp;
while(getline(CheckFile,temp)) {
stringstream stemp(temp);
if(stemp==question) {
return false;
}
}
CheckFile<<question.str();
CheckFile.close();
return true;
}四、优缺点分析
- 优点
- 题目生成较为灵活,且可以在一次登陆下多次生成题目
- 提示比较详细,便于用户使用
- 注释较多,便于阅读
- 缺点
- 应尽量避免直接引入整个命名空间,如“using namespace std;”
- 程序提示文字过多,可适当加入清屏的指令增加可读性。
- 所有函数和类的定义均写在一个.cpp文件中,建议拆分为多个.h和.cpp文件来实现。
- 程序运行中没有对存储路径的提示,需要阅读代码得知,不利于用户使用。
- 登录判断直接在登录函数中将账号密码与字符串常量进行比较,拓展性较差
点击查看代码
if(Name=="张三1"||Name=="张三2"||Name=="张三3") {
if(Passward=="123") {
Type="小学";
break;
}
} else if(Name=="李四1"||Name=="李四2"||Name=="李四3") {
if(Passward=="123") {
Type="初中";
break;
}
} else if(Name=="王五1"||Name=="王五2"||Name=="王五3") {
if(Passward=="123") {
Type="高中";
break;
}
}总结
通过本次代码分析,可以看出姑丽加娜提同学的程序出题部分处理的更灵活,值得我学习。封装和代码复用的部分可以再充分些,同时应注意代码的可拓展、可维护性。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号