一. 初识Spring
1.1 spring
spring是一个开源的轻量级的应用开发框架,其意在降低耦合。
1.2 spring框架组成
spring IOC 控制反转
spring DI 依赖注入
spring AOP spring的面向切面
spring 事务 spring的事务管理
spring jdbc spring的数据库操作
等……
1.3 jar包(本博客以4.3.7为例)
1.3.1 手动导入jar包
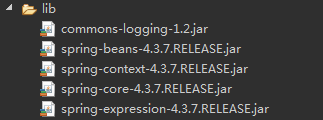
1.3.2 Maven
使用阿里镜像,以及依赖.
①修改maven文件的conf下的settings.xml文件
//添加阿里的镜像 <mirror> <id>alimaven</id> <name>aliyun maven</name> <url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url> <mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf> </mirror>
②在eclipse的Preferences中找到Maven选项--->在Installations中add maven的文件夹--->在UserSettings将Global Settings和User Settings中添加maven的conf中的settings.xml文件引入---->Local Repository是放maven中依赖dependency自动导入的jar包的地方
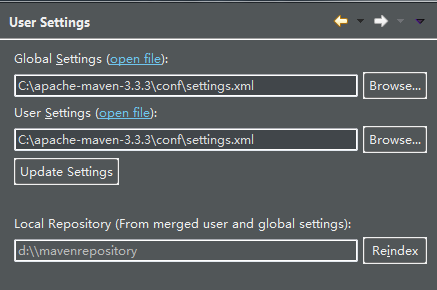
③添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>4.3.7.RELEASE</version>
<classifier>javadoc</classifier>
</dependency>
二.Spring IOC
2.1 spring IOC:Inversion of Control 控制反转。
控制反转:控制权的转,即把创建对象的权利,反转给第三方spring框架去创建(new)
2.2 简单案例(本博客以4.3.7为参考)
2.2.1创建类Hello
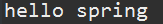
1 package com.hdu.ioc; 2 3 public class Hello { 4 public Hello() { 5 System.out.println("Hello.created"); 6 } 7 public void sayHello() { 8 System.out.println("hello spring"); 9 } 10 public void init() { 11 System.out.println("Hello.init..."); 12 } 13 public void destroy() { 14 System.out.println("Hello.destroy..."); 15 } 16 }
2.2.2 spring配置文件
以4.3.7版本的参考文档为例【注:此文件模板一定从对应版本的开发文档上获取】

将配置文件的框架复制到【.xml】中
添加bean节点
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- <bean spring框架读取到bean的时候,就知道需要创建一个对象 id: 创建完的对象名称,此名称必须唯一 class: 全路径类名(包名+类名),指定spring要实例化哪一个类的对象 底层:Object obj = Class.forName("com.hdu.ioc.Hello").newInstance(); 对象实例化完毕后把id的值作为key,把实例化完的对象作为value 存储到map集合中,以便需要时根据key来去除value 全路径类名是否正确:ctrl+鼠标 --> <bean id="hello" class="com.hdu.ioc.Hello"> </bean> </beans>
2.2.3 测试
根据参考文档:
初始化容器

使用容器

进行junit测试
1 package com.hdu.test; 2 3 import org.junit.Test; 4 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 5 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 6 7 import com.hdu.ioc.Hello; 8 9 public class TestIOC { 10 @Test 11 public void testMethod() { 12 //启动spring的容器,spring读取spring.xml文件 13 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[] {"resources/spring.xml"}); 14 //从spring容器中取出spring创建完的对象 15 Hello hello = (Hello)context.getBean("hello"); 16 hello.sayHello(); 17 } 18 }
Spring原理:
①启动spring容器,并读取和解析清单文件
②把spring.xml中的bean节点的内容解析出并存储(map)
③ 循环遍历map集合中的所有数据,取出class属性对应的值,反射实例化对象
Objectobj=Class.forName("包名.类名").newInstance();
④把所有创建完的对象存储另一个map集合,id当key,对象当value
关于getBean方法:
getBean(Class);//按照类型获取 ,必须容器中的类型对象唯一
getBean(String);//按照id获取必须强制转换到具体类型的对象
getBean(Class,Object);
getBean(String,Class);//按照id和类型,不需要强制转化
getBean(String,Object);

1 package com.hdu.test; 2 3 import org.junit.Test; 4 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 5 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 6 7 import com.hdu.ioc.Hello; 8 9 public class TestIOC { 10 @Test 11 public void testMethod() { 12 //启动spring的容器,spring读取spring.xml文件 13 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[] {"resources/spring.xml"}); 14 //从spring容器中取出spring创建完的对象 15 //根据id,从spring容器中获取对象 16 //Hello hello = (Hello)context.getBean("hello"); 17 //根据类型,从spring容器找那个获取对象,类型的对象必须唯一 18 //Hello hello = context.getBean(Hello.class); 19 //根据id和类型来取对象 20 Hello hello = context.getBean("hello", Hello.class); 21 hello.sayHello(); 22 } 23 }
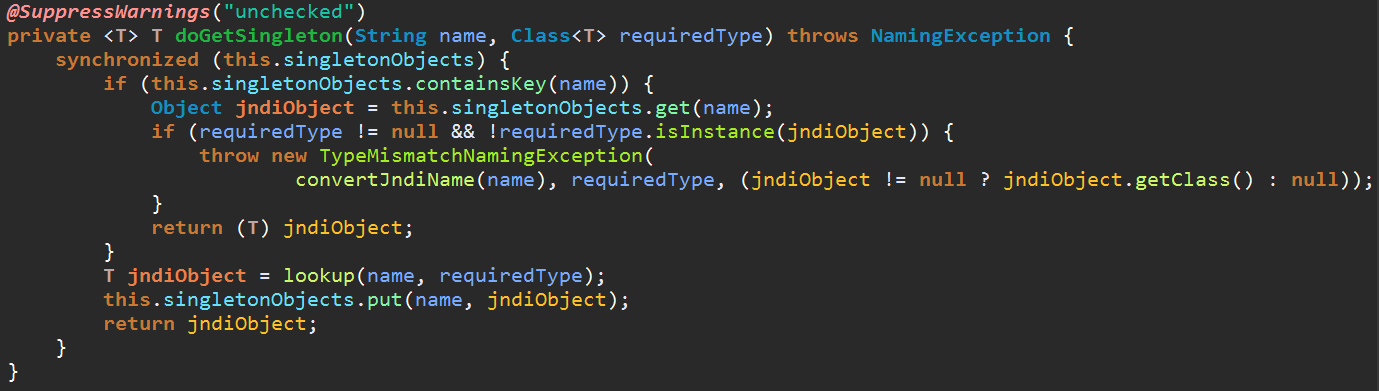
其中getBean源码
从spring容器中取出对象Hello hello = context.getBean("hello", Hello.class);
hello作为key去spring容器map集合中找对应的对象 。
三.spring容器实例化对象的四种方式
3.1 默认构造:通过无参构造的方式实例化对象(类中必须存在无参构造)
1 package com.hdu.ioc; 2 3 public class Hello { 4 public Hello() { 5 System.out.println("Hello.created"); 6 } 7 public void sayHello() { 8 System.out.println("hello spring"); 9 } 10 }
<!-- 默认构造 --> <bean id="hello" class="com.hdu.ioc.Hello"> </bean>
1 package com.hdu.test; 2 3 import org.junit.Test; 4 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 5 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 6 7 import com.hdu.ioc.Hello; 8 9 public class TestIOC { 10 @Test 11 public void testMethod() { 12 //启动spring的容器,spring读取spring.xml文件 13 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[] {"resources/spring_factory.xml"}); 14 //从spring容器中取出spring创建完的对象 15 //根据id和类型来取对象 16 Hello hello = context.getBean("hello", Hello.class); 17 hello.sayHello(); 18 } 19 }
3.2 静态工厂
有些类不能直接实例化,就不能直接通过new关键字来创建,类似这样的对象我们要通过静态工厂模式来创建对象。没有静态方法就无法直接调用。
以java.util.Calendar为例

<!-- 静态工厂 因为getInstance这个方法是静态方法,Calendar是抽象类,不能无参构造 --> <bean id="cal" class="java.util.Calendar" factory-method="getInstance" > </bean>
1 package com.hdu.test; 2 3 import java.util.Calendar; 4 5 import org.junit.Test; 6 7 public class TestIOC { 8 @Test 9 public void testMethod1() { 10 Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance(); 11 System.out.println(cal.getTime()); 12 13 } 14 }
3.3 实例工厂
静态工厂设计模式不会创建类对象,直接调用静态方法。而工厂方法设计模式会创建类,然后通过xml中配置去访问其方法。
<!-- 实例工厂 可以由程序员自己控制调用指定的方法获取对象 但对象还不是spring创建,在别的渠道创建完交给spring容器管理 --> <bean id="if" class="com.hdu.factory.InstanceFactory"></bean> <bean id = "cal1" factory-bean="if" factory-method="getCalendar" > </bean>
1 package com.hdu.factory; 2 3 import java.util.Calendar; 4 5 public class InstanceFactory { 6 public Calendar getCalendar() { 7 return Calendar.getInstance(); 8 } 9 }
1 package com.hdu.test; 2 3 import java.util.Calendar; 4 import org.junit.Test; 5 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 6 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 7 8 public class TestIOC { 9 @Test 10 public void testMethod2() { 11 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[] {"resources/spring_factory.xml"}); 12 Calendar cal = context.getBean("cal1",Calendar.class); 13 System.out.println(cal.getTime()); 14 } 15 }
3.4 Spring工厂
这是spring框架自身提供的,它需要实现FactoryBean接口,实现代码就必须写在getObject()方法中。spring工厂的优点在于,只要实现一个接口即可,简单方便。
<!-- spring工厂 --> <bean id="hello" class="com.hdu.factory.SpringFactory"></bean>
1 package com.hdu.factory; 2 3 import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean; 4 5 import com.hdu.ioc.Hello; 6 7 public class SpringFactory implements FactoryBean<Hello>{ 8 9 @Override 10 public Hello getObject() throws Exception { 11 return new Hello(); 12 } 13 14 @Override 15 public Class<?> getObjectType() { 16 return Hello.class; 17 } 18 19 @Override 20 public boolean isSingleton() { 21 return false; 22 } 23 24 }
1 package com.hdu.test; 2 3 4 import org.junit.Test; 5 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 6 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 7 8 import com.hdu.ioc.Hello; 9 10 public class TestIOC { 11 @Test 12 public void testMethod3() { 13 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[] {"resources/spring_factory.xml"}); 14 Hello hello = context.getBean("hello",Hello.class); 15 hello.sayHello(); 16 } 17 }
四. spring对象
4.1单例
当 scope="singleton" 时,结果为 true。不写scope属性时,结果仍为true,证明默认对象是以单例创建的。
<!-- scope:范围,如果bean节点中使用的scope属性,就是要指定当前对象的范围 scope="singleton" 单例,默认,不写也是单例 scope="prototype" 多例,什么时候用,什么时候实例化对象 --> <bean id="hello" class="com.hdu.ioc.Hello" scope="singleton"> </bean>
1 package com.hdu.test; 2 3 import org.junit.Test; 4 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 5 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 6 7 import com.hdu.ioc.Hello; 8 9 public class TestIOC { 10 /** 11 * 测试单例和多例 12 */ 13 @Test 14 public void testMethod() { 15 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[] {"resources/spring.xml"}); 16 Hello hello = context.getBean("hello",Hello.class); 17 Hello hello2 = context.getBean("hello",Hello.class); 18 System.out.println(hello == hello2); 19 } 20 }
4.2多例
当 scope="prototype" 时,以上测试,结果为false。
<!-- scope:范围,如果bean节点中使用的scope属性,就是要指定当前对象的范围 scope="singleton" 单例,默认,不写也是单例 scope="prototype" 多例,什么时候用,什么时候实例化对象 --> <bean id="hello" class="com.hdu.ioc.Hello" scope="prototype"> </bean>
4.3懒加载
多例对象都是懒加载。
<!-- lazy-init="true" ,什么时候用,什么时候实例化 --> <bean id="hello" class="com.hdu.ioc.Hello" scope="singleton" lazy-init="true"> </bean>
4.4小结
|
Lazy-init |
Scope |
对象的创建结果 |
|
True |
singleton |
单例对象创建懒加载 |
|
True |
prototype |
多例对象创建懒加载 |
|
Default/false |
singleton |
单例对象创建立即加载 |
|
Default/false |
prototype |
多例对象创建懒加载 |
五.init-method destroy-method

1 package com.hdu.ioc; 2 3 public class Hello { 4 public Hello() { 5 System.out.println("Hello.created"); 6 } 7 public void sayHello() { 8 System.out.println("hello spring"); 9 } 10 public void init() { 11 System.out.println("Hello.init..."); 12 } 13 public void destroy() { 14 System.out.println("Hello.destroy..."); 15 } 16 }
<bean id="hello" class="com.hdu.ioc.Hello" scope="singleton" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy" lazy-init="true"> </bean>
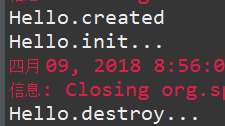
1 package com.hdu.test; 2 3 import org.junit.Test; 4 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 5 import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext; 6 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 7 8 import com.hdu.ioc.Hello; 9 10 public class TestIOC { 11 @Test 12 public void testMethod() { 13 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[] {"resources/spring.xml"}); 14 Hello hello = context.getBean("hello",Hello.class); 15 ((AbstractApplicationContext) context).close(); 16 } 17 }





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号