反向传播算法
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
#plt设置
plt.rcParams['font.size']=16
plt.rcParams['font.family']=['STKaiti']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False
#生成数据集
def load_dataset():
#采样点数
N_SAMPLES = 2000
#测试样本集比例
TEST_SIZE=0.3
#生成数据集
X,y = make_moons(n_samples = N_SAMPLES,noise = 0.2,random_state = 100)
#将2000个点分为训练集与测试集,比例0.3
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size = TEST_SIZE,random_state = 56)
return X,y,X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test
def make_plot(X,y,plot_name,XX=None,YY=None,preds = None,dark=False):
#绘制X为坐标,y为标签
if (dark):
plt.style.use('dark_background')
else:
sns.set_style('whitegrid')
plt.figure(figsize=(16,12))
axes = plt.gca()
axes.set(xlabel='$X_1$',ylabel = '$X_2$')
plt.title(plot_name,fontsize = 30)
plt.subplots_adjust(left = 0.2)
plt.subplots_adjust(right = 0.8)
if XX is not None and YY is not None and preds is not None:
plt.contourf(XX,YY,preds.reshape(XX.shape),25,alpha=1,cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
plt.contour(XX, YY, preds.reshape(XX.shape), levels=[.5], cmap="Greys", vmin=0, vmax=.6)
# 绘制散点图,根据标签区分颜色
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y.ravel(), s=40, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral, edgecolors='none')
plt.show()
X, y, X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = load_dataset()
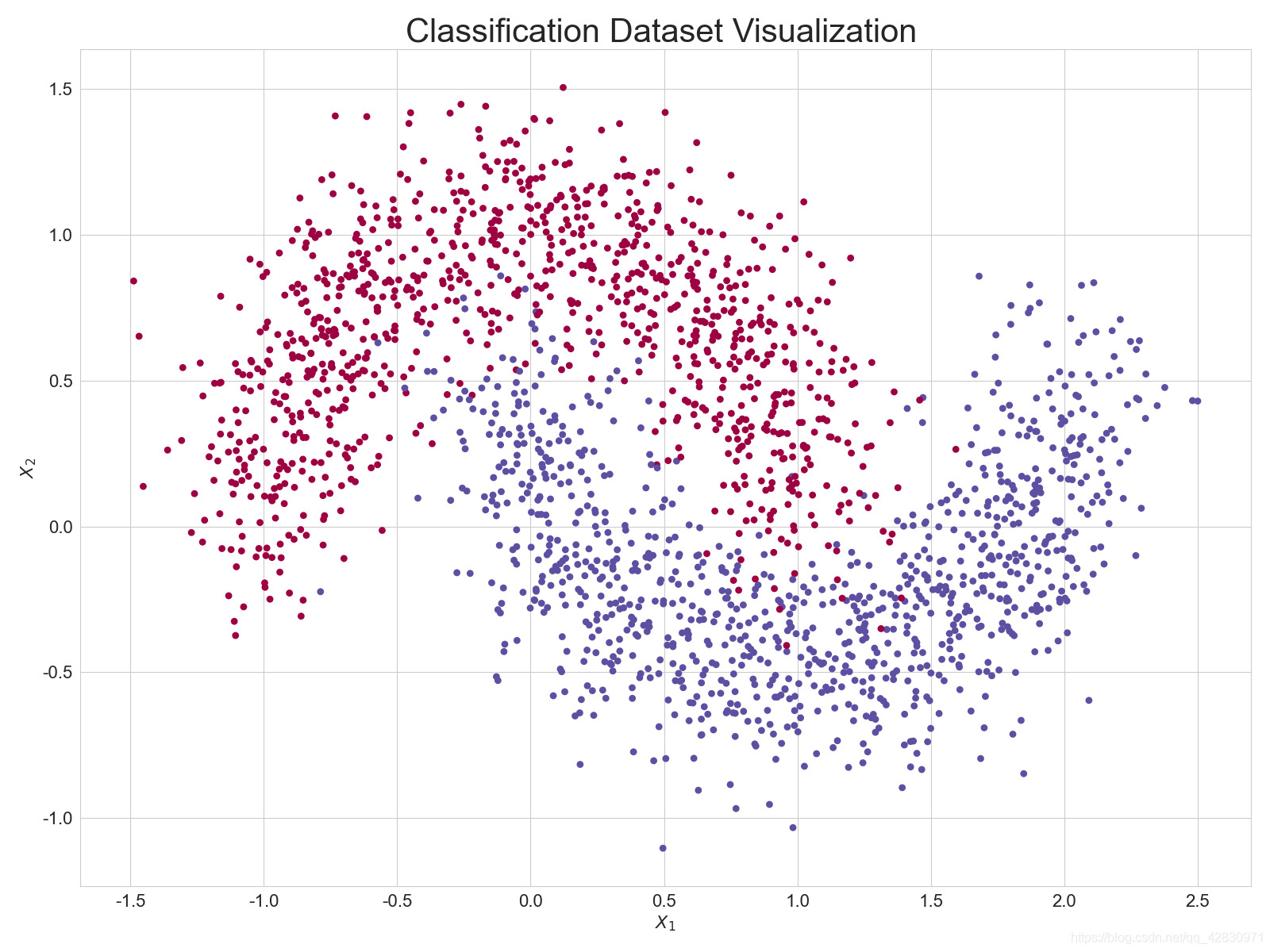
# 调用 make_plot 函数绘制数据的分布,其中 X 为 2D 坐标, y 为标签
make_plot(X, y, "Classification Dataset Visualization ")
class Layer:
def __init__(self,n_input,n_neurons,activation = None,weights = None,bias = None):
self.weights= weights if weights is not None else np.random.randn(n_input,n_neurons) * np.sqrt(1/n_neurons)
self.bias = bias if bias is not None else np.random.rand(n_neurons) * 0.1
self.activation = activation
self.last_activation = None
self.error = None
self.delta = None
def activate(self,x):
r=np.dot(x,self.weights)+self.bias
self.last_activation = self._apply_activation(r)
return self.last_activation
def _apply_activation(self,r):
if self.activation is None:
return r # 无激活函数,直接返回
# ReLU 激活函数
elif self.activation == 'relu':
return np.maximum(r, 0)
# tanh 激活函数
elif self.activation == 'tanh':
return np.tanh(r)
# sigmoid 激活函数
elif self.activation == 'sigmoid':
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-r))
return r
def apply_activation_derivative(self, r):
# 计算激活函数的导数
# 无激活函数,导数为1
if self.activation is None:
return np.ones_like(r)
# ReLU 函数的导数实现
elif self.activation == 'relu':
grad = np.array(r, copy=True)
grad[r > 0] = 1.
grad[r <= 0] = 0.
return grad
# tanh 函数的导数实现
elif self.activation == 'tanh':
return 1 - r ** 2
# Sigmoid 函数的导数实现
elif self.activation == 'sigmoid':
return r * (1 - r)
return r
class NeuralNetwork:
def __init__(self):
self._layers =[]
def add_layer(self,layer):
self._layers.append(layer)
def feed_forward(self,X):
for layer in self._layers:
X = layer.activate(X)
return X
def backpropagation(self, X, y, learning_rate):
output = self.feed_forward(X)
for i in reversed(range(len(self._layers))): # 反向循环
layer = self._layers[i] # 得到当前层对象
# 如果是输出层
if layer == self._layers[-1]: # 对于输出层
layer.error = y - output # 计算2 分类任务的均方差的导数
# 关键步骤:计算最后一层的delta,参考输出层的梯度公式
layer.delta = layer.error * layer.apply_activation_derivative(output)
else: # 如果是隐藏层
next_layer = self._layers[i + 1] # 得到下一层对象
layer.error = np.dot(next_layer.weights, next_layer.delta)
# 关键步骤:计算隐藏层的delta,参考隐藏层的梯度公式
layer.delta = layer.error * layer.apply_activation_derivative(layer.last_activation)
# 循环更新权值
for i in range(len(self._layers)):
layer = self._layers[i]
# o_i 为上一网络层的输出
o_i = np.atleast_2d(X if i == 0 else self._layers[i - 1].last_activation)
# 梯度下降算法,delta 是公式中的负数,故这里用加号
layer.weights += layer.delta * o_i.T * learning_rate
def train(self, X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test, learning_rate, max_epochs):
# 网络训练函数
# one-hot 编码
y_onehot = np.zeros((y_train.shape[0], 2))
y_onehot[np.arange(y_train.shape[0]), y_train] = 1
# 将One-hot 编码后的真实标签与网络的输出计算均方误差,并调用反向传播函数更新网络参数,循环迭代训练集1000 遍即可
mses = []
accuracys = []
for i in range(max_epochs + 1): # 训练1000 个epoch
for j in range(len(X_train)): # 一次训练一个样本
self.backpropagation(X_train[j], y_onehot[j], learning_rate)
if i % 10 == 0:
# 打印出MSE Loss
mse = np.mean(np.square(y_onehot - self.feed_forward(X_train)))
mses.append(mse)
accuracy = self.accuracy(self.predict(X_test), y_test.flatten())
accuracys.append(accuracy)
print('Epoch: #%s, MSE: %f' % (i, float(mse)))
# 统计并打印准确率
print('Accuracy: %.2f%%' % (accuracy * 100))
return mses, accuracys
def predict(self, X):
return self.feed_forward(X)
def accuracy(self, X, y):
return np.sum(np.equal(np.argmax(X, axis=1), y)) / y.shape[0]
nn = NeuralNetwork() # 实例化网络类
nn.add_layer(Layer(2, 25, 'sigmoid')) # 隐藏层 1, 2=>25
nn.add_layer(Layer(25, 50, 'sigmoid')) # 隐藏层 2, 25=>50
nn.add_layer(Layer(50, 25, 'sigmoid')) # 隐藏层 3, 50=>25
nn.add_layer(Layer(25, 2, 'sigmoid')) # 输出层, 25=>2
mses, accuracys = nn.train(X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test, 0.01, 1000)
x = [i for i in range(0, 101, 10)]
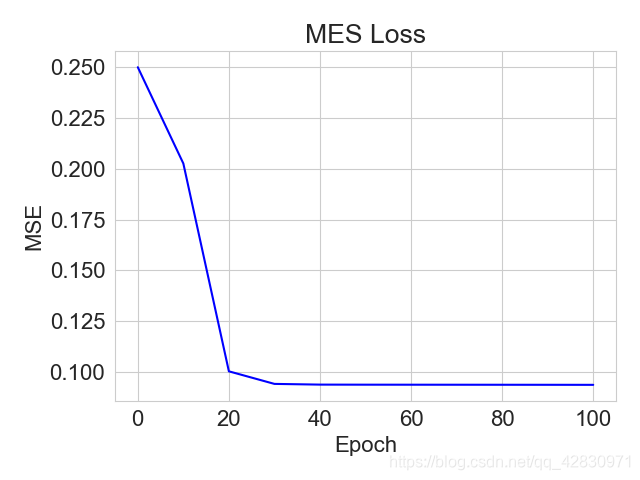
# 绘制MES曲线
plt.title("MES Loss")
plt.plot(x, mses[:11], color='blue')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('MSE')
plt.show()
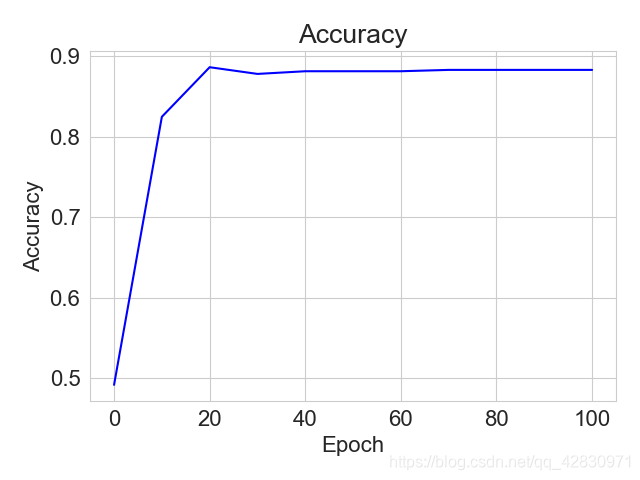
# 绘制Accuracy曲线
plt.title("Accuracy")
plt.plot(x, accuracys[:11], color='blue')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.show()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号