stringR包 字符串拼接,对字符串切分 替换 匹配提取 位置提取
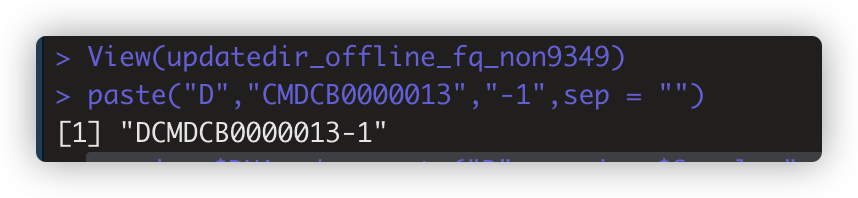
paste("D","CMDCB0000013","-1",sep = "") 拼接字符串,可以用于新增列non_json$DNAcode<-paste("D",non_json$Sample,"-1",sep="") ,当然搭配mutate用也一样
stringR 包对字符串切分 替换 匹配提取 位置提取 如下
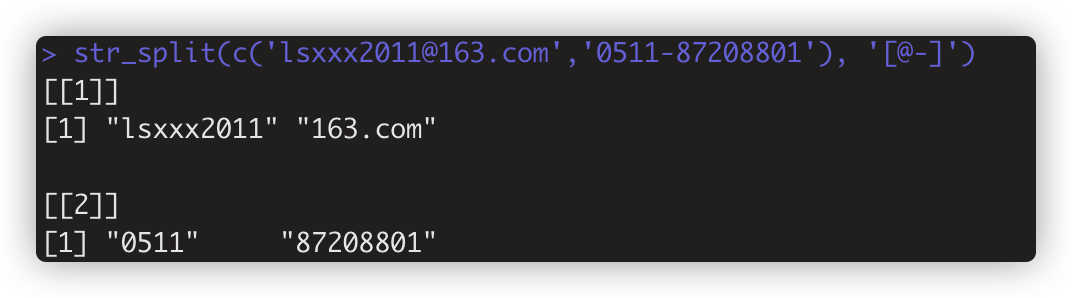
str_split(string,pattern,n=Inf,simplify=FALSE) 把字符串拆分为片 。如str_split(c('lsxxx2011@163.com','0511-87208801'), '[@-]')
string 输入字符串向量
pattern 分隔符,适用正则表达式
n 指定切成片的数量
simplify 默认FALSE,返回字符向量列表,如果是TRUE,返回字符矩阵。
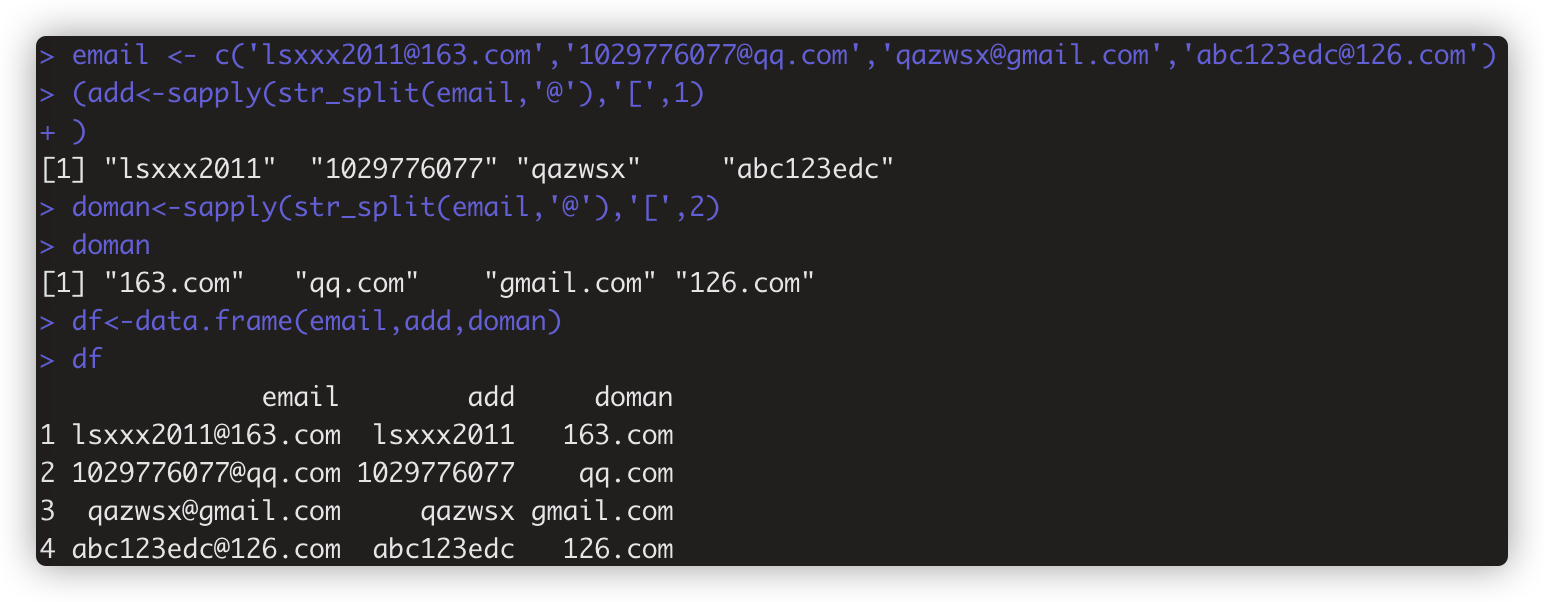
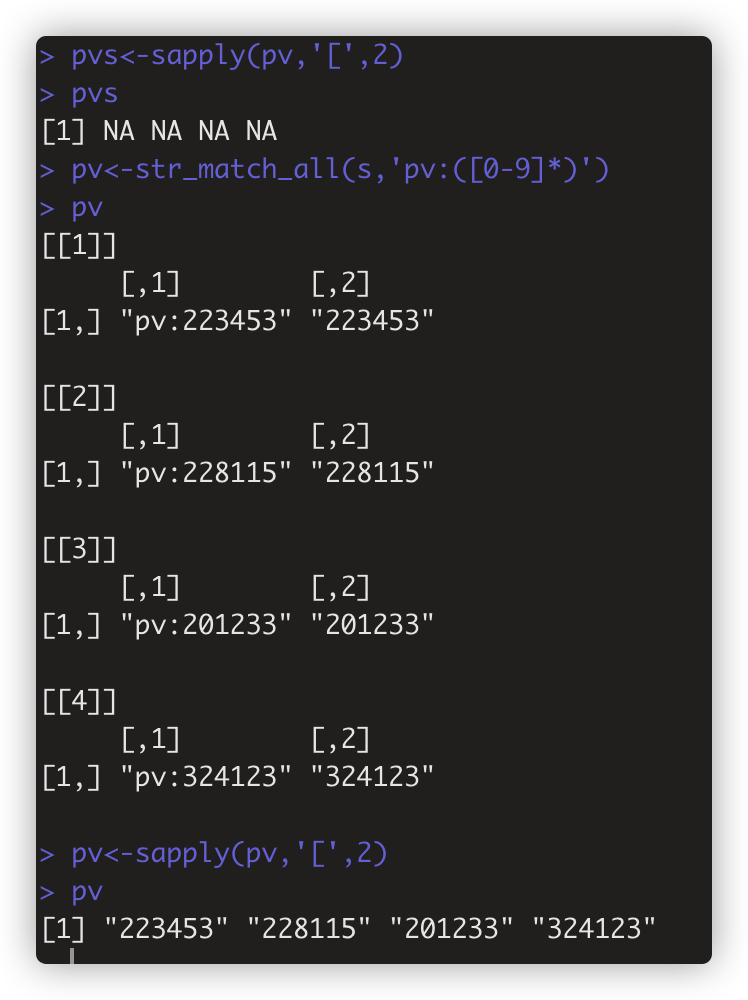
搭配sapply 使用获得向量的前/后缀 如:add<-sapply(str_split(email,'@'),'[',1)
str_replace(string,pattern,replacement) 只替换首次满足条件的子字符串
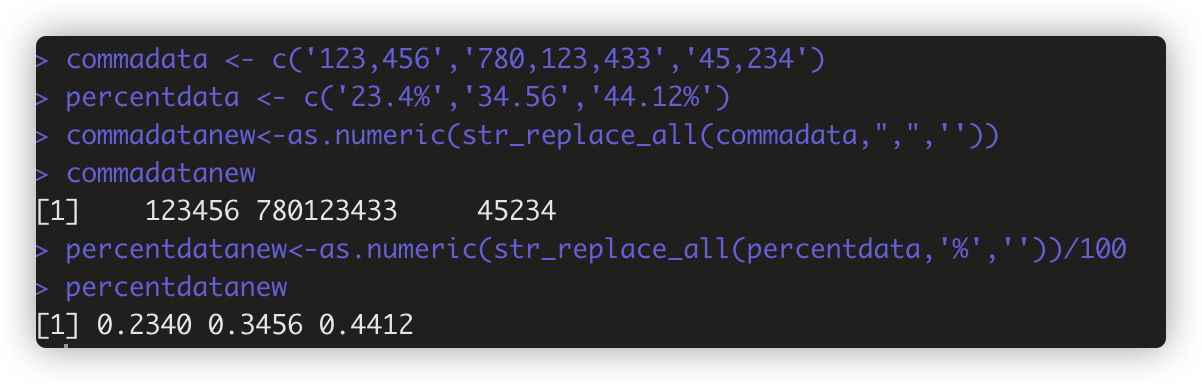
str_replace_all(string,pattern,replacement) 替换掉所有满足条件的字符串, 如 str_replace_all(commadata, ',', ''
string 字符串向量
pattern 待替换的字符串,试用正则表达式
replacement 用来替换的字符串
匹配提取字符串 str_extract(string,patterm) #只提取首次满足条件的子字符串
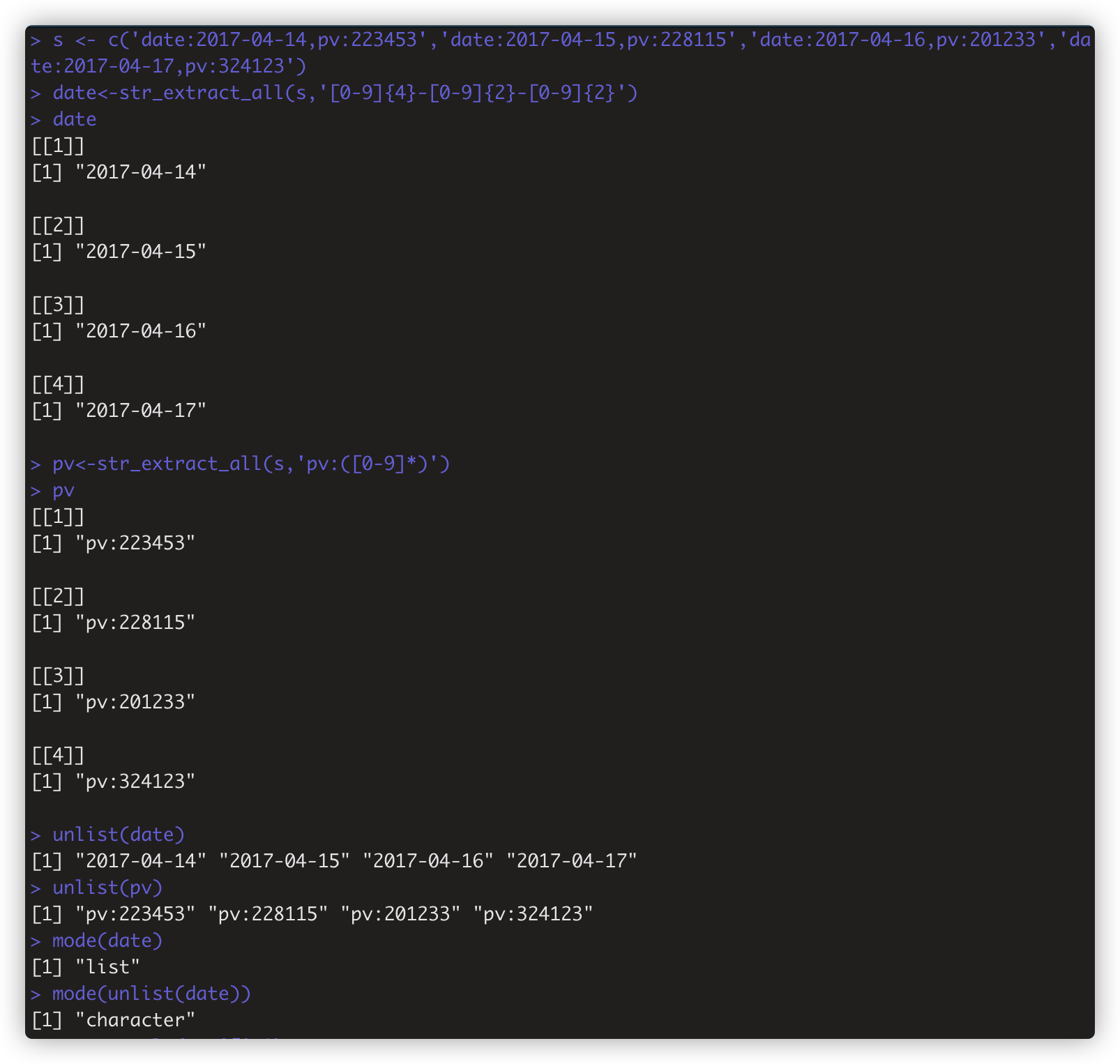
str_extract_all(string,pattern.simplify=FALSE) #提取所有满足条件的子字符串。如date<-str_extract_all(s,'[0-9]{4}-[0-9]{2}-[0-9]{2}')
参数
string 字符串向量 ;
pattern 抽取出满足条件的字符串,适用正则表达式
simplify: 默认Flase,返回列表。
str_match(string,pattern)和str_match_all(string,pattern) 类似上面两个extract函数,但返回结果不同。如pv<-str_match_all(s,'pv:([0-9]*)')
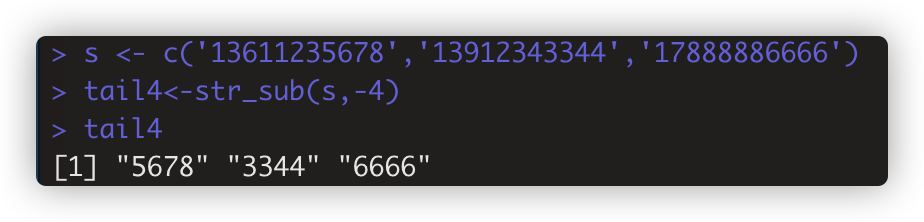
str_sub(string,start=1L,end=-1L) 按位置提取 如tail4<-str_sub(s,-4)
string 字符串向量
start 指定字符串的起始位置
end 指定字符串的终止位置
注:start 或end 为负数时,从字符串的最后一个字符串向前查找
str_wrap(x,width=0.9*getOption("width"),indent=0,exdent=0,prefix="",simplify=TRUE,initial=prefix) 把输入的字符串按widhth,indent,exdent分行,生成段落
width 指定每一行的宽度
indent 指定段首行的缩进
exdent 指定除首行外的行缩进
prefix 输入字符串作为首行外,其他行的前缀
simplify: 为TRUE时,返回结果是单行的字符向量;为FALSE时,返回list,list每个元素是单行文本的字符向量
例子
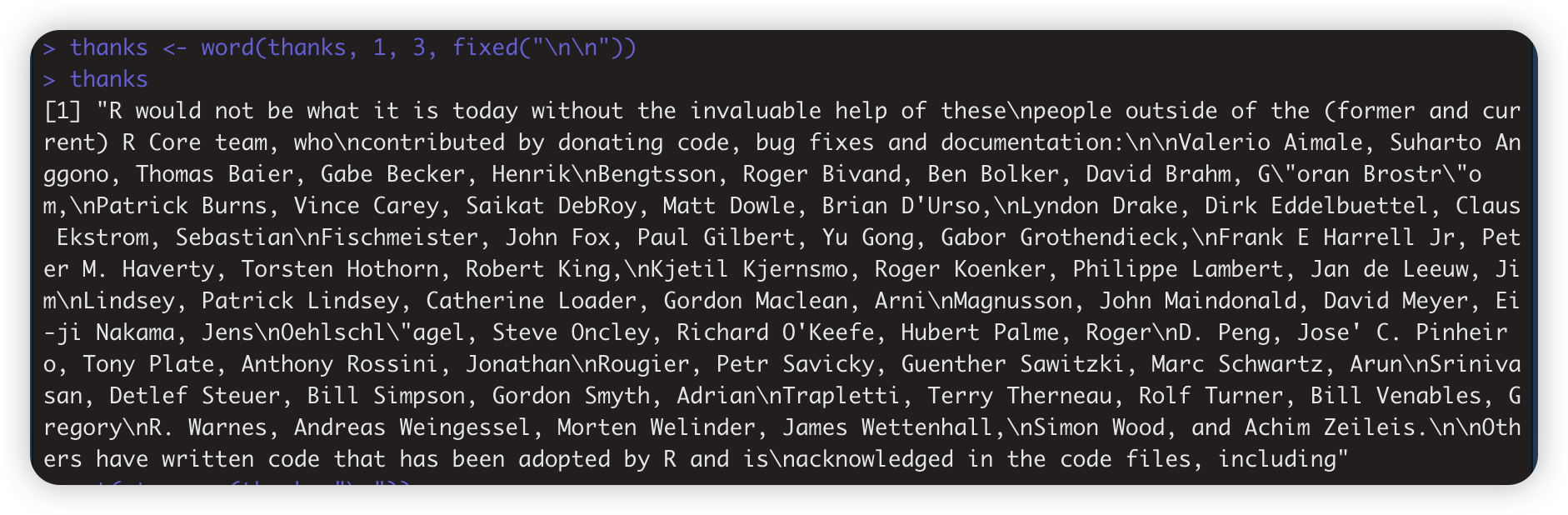
thanks_path <- file.path(R.home("doc"), "THANKS")
thanks <- str_c(readLines(thanks_path), collapse = "\n")
thanks

thanks <- word(thanks, 1, 3, fixed("\n\n"))
thanks
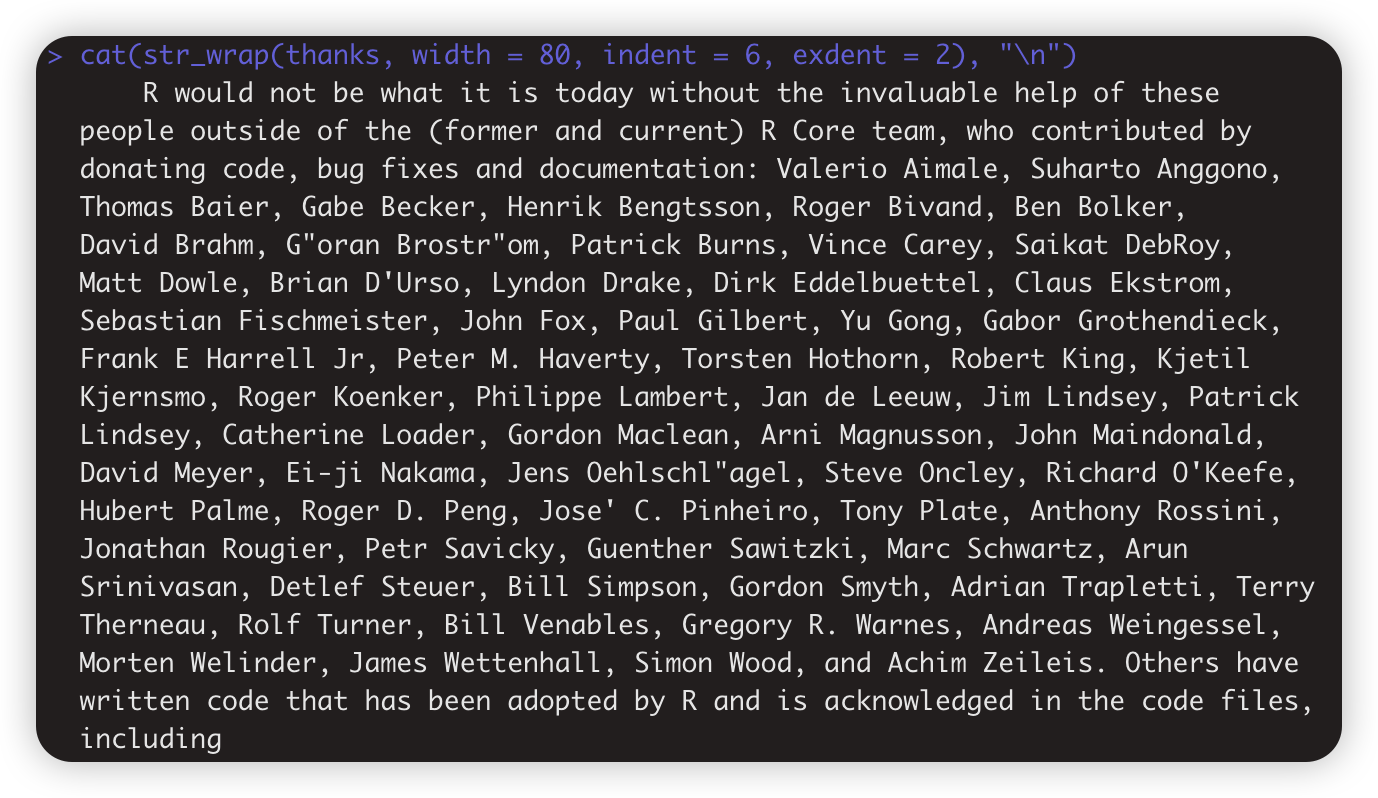
cat(str_wrap(thanks, width = 80, indent = 6, exdent = 2), "\n")
本文来自博客园,作者:BioinformaticsMaster,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/koujiaodahan/p/15821418.html
posted on 2022-01-19 11:00 BioinformaticsMaster 阅读(296) 评论(0) 收藏 举报



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号