NSThread方式创建线程/线程安全/线程间的通信
2015-07-29 15:23 另十 阅读(287) 评论(0) 收藏 举报
一个NSThread对象就代表一条线程
创建、启动线程
(1) NSThread *thread = [[NSThread alloc] initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(run) object:nil];
[thread start];
// 线程一启动,就会在线程thread中执行self的run方法
主线程相关用法
+ (NSThread *)mainThread; // 获得主线程
- (BOOL)isMainThread; // 是否为主线程
+ (BOOL)isMainThread; // 是否为主线程
其他用法
获得当前线程
NSThread *current = [NSThread currentThread];
线程的调度优先级:调度优先级的取值范围是0.0 ~ 1.0,默认0.5,值越大,优先级越高
+ (double)threadPriority;
+ (BOOL)setThreadPriority:(double)p;
设置线程的名字
- (void)setName:(NSString *)n;
- (NSString *)name;
其他创建线程的方式
(2)创建线程后自动启动线程 [NSThread detachNewThreadSelector:@selector(run) toTarget:self withObject:nil];
(3)隐式创建并启动线程 [self performSelectorInBackground:@selector(run) withObject:nil];
上述2种创建线程方式的优缺点
优点:简单快捷
缺点:无法对线程进行更详细的设置
二、代码示例
1.使用古老的方式创建
10 #import "YYViewController.h"
11 #import <pthread.h>
12
13
14 @interface YYViewController ()
15 - (IBAction)btnClick;
16 @end
17
18
19 @implementation YYViewController
20
21
22 - (void)viewDidLoad
23 {
24 [super viewDidLoad];
25 }
26
27
28 //按钮的点击事件
29 - (IBAction)btnClick {
30 //1.获取当前线程
31 NSThread *current=[NSThread currentThread];
32 //主线程
33 NSLog(@"btnClick----%@",current);
34
35 //2.使用for循环执行一些耗时操作
36 pthread_t thread;
37 pthread_create(&thread, NULL, run, NULL);
38 }
39
40
41 //c语言函数
42 void *run(void *data)
43 {
44 //获取当前线程,是新创建出来的线程
45 NSThread *current=[NSThread currentThread];
46
47
48 for (int i=0; i<10000; i++) {
49 NSLog(@"btnClick---%d---%@",i,current);
50 }
51 return NULL;
52 }
53
54 //多个线程,点击按钮执行按钮调用方法的时候,主线程没有被阻塞
55
56 @end
57
58
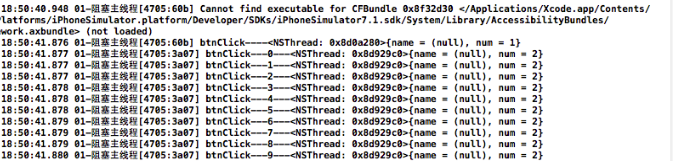
实现效果:

打印结果:
2.使用NSThread创建线程
9 #import "YYViewController.h"
10 #import <pthread.h>
11
12
13 @interface YYViewController ()
14 - (IBAction)btnClick;
15 @end
16
17
18 @implementation YYViewController
19
20 - (void)viewDidLoad
21 {
22 [super viewDidLoad];
23 }
24
25
26 //按钮的点击事件
27 - (IBAction)btnClick {
28 //1.获取当前线程
29 NSThread *current=[NSThread currentThread];
30 //主线程
31 NSLog(@"btnClick----%@",current);
32
33 //获取主线程的另外一种方式
34 NSThread *main=[NSThread mainThread];
35 NSLog(@"主线程-------%@",main);
36
37 //2.执行一些耗时操作
38 [self creatNSThread];
39 // [self creatNSThread2];
40 // [self creatNSThread3];
41 }
42
43
44 /**
45 * NSThread创建线程方式1
46 * 1> 先创建初始化线程
47 * 2> start开启线程
48 */
49 -(void)creatNSThread
50 {
51 NSThread *thread=[[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(run:) object:@"线程A"];
52 //为线程设置一个名称
53 thread.name=@"线程A";
54 //开启线程
55 [thread start];
56
57
58 NSThread *thread2=[[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(run:) object:@"线程B"];
59 //为线程设置一个名称
60 thread2.name=@"线程B";
61 //开启线程
62 [thread2 start];
63 }
64
65
66 /**
67 * NSThread创建线程方式2
68 *创建完线程直接(自动)启动
69 */
70
71 -(void)creatNSThread2
72 {
73 // NSThread *thread=[NSThread detachNewThreadSelector:@selector(run:) toTarget:self withObject:@"创建完线程直接(自动)启动"];
74
75 [NSThread detachNewThreadSelector:@selector(run:) toTarget:self withObject:@"创建完线程直接(自动)启动"];
76 }
77
78
79 /**
80 * NSThread创建线程方式3
81 * 隐式创建线程, 并且直接(自动)启动
82 */
83
84 -(void)creatNSThread3
85 {
86 //在后台线程中执行===在子线程中执行
87 [self performSelectorInBackground:@selector(run:) withObject:@"隐式创建"];
88 }
89
90
91
92 -(void)run:(NSString *)str
93 {
94 //获取当前线程
95 NSThread *current=[NSThread currentThread];
96 //打印输出
97 for (int i=0; i<10; i++) {
98 NSLog(@"run---%@---%@",current,str);
99 }
100 }
101 @end
调用线程1,打印结果为:
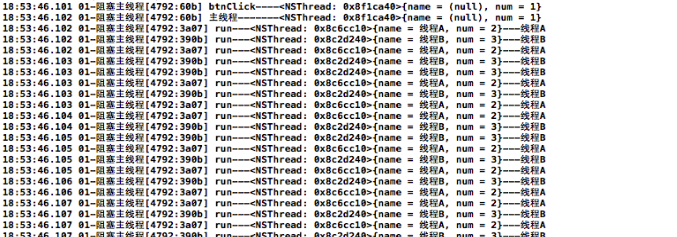
调用线程2

调用线程3
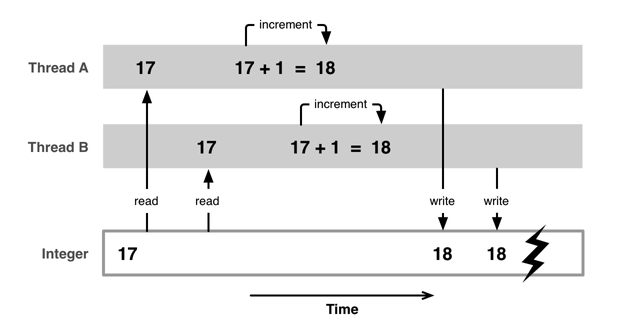
一、多线程的安全隐患
资源共享
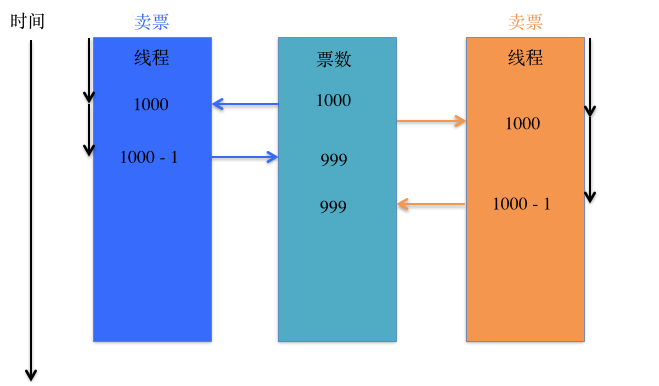
1块资源可能会被多个线程共享,也就是多个线程可能会访问同一块资源
比如多个线程访问同一个对象、同一个变量、同一个文件
当多个线程访问同一块资源时,很容易引发数据错乱和数据安全问题
示例一:

示例二:
问题代码:
10 #import "YYViewController.h"
11
12 @interface YYViewController ()
13 //剩余票数
14
15 @property(nonatomic,assign) int leftTicketsCount;
16 @property(nonatomic,strong)NSThread *thread1;
17 @property(nonatomic,strong)NSThread *thread2;
18 @property(nonatomic,strong)NSThread *thread3;
19
20
21 @end
22
23
24 @implementation YYViewController
25
26
27 - (void)viewDidLoad
28 {
29 [super viewDidLoad];
30
31 //默认有20张票
32
33 self.leftTicketsCount=10;
34
35 //开启多个线程,模拟售票员售票
36
37 self.thread1=[[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(sellTickets) object:nil];
38
39 self.thread1.name=@"售票员A";
40
41 self.thread2=[[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(sellTickets) object:nil];
42
43 self.thread2.name=@"售票员B";
44
45 self.thread3=[[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(sellTickets) object:nil];
46 self.thread3.name=@"售票员C";
47 }
48
49
50 -(void)sellTickets
51 {
52 while (1) {
53 //1.先检查票数
54 int count=self.leftTicketsCount;
55 if (count>0) {
56 //暂停一段时间
57 [NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:0.002];
58
59 //2.票数-1
60 self.leftTicketsCount= count-1;
61
62 //获取当前线程
63 NSThread *current=[NSThread currentThread];
64 NSLog(@"%@--卖了一张票,还剩余%d张票",current,self.leftTicketsCount);
65 }else
66 {
67 //退出线程
68 [NSThread exit];
69 }
70 }
71 }
72
73
74 -(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
75 {
76 //开启线程
77
78 [self.thread1 start];
79 [self.thread2 start];
80 [self.thread3 start];
81
82 }
83
84 @end
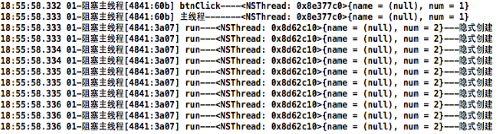
打印结果:

二、安全隐患分析

三、如何解决
互斥锁使用格式
@synchronized(锁对象) { // 需要锁定的代码 }
注意:锁定1份代码只用1把锁,用多把锁是无效的
代码示例:
9 #import "YYViewController.h"
10
11 @interface YYViewController ()
12
13 //剩余票数
14 @property(nonatomic,assign) int leftTicketsCount;
15 @property(nonatomic,strong)NSThread *thread1;
16 @property(nonatomic,strong)NSThread *thread2;
17 @property(nonatomic,strong)NSThread *thread3;
18 @end
19
20 @implementation YYViewController
21
22 - (void)viewDidLoad
23 {
24 [super viewDidLoad];
25 //默认有20张票
26 self.leftTicketsCount=10;
27 //开启多个线程,模拟售票员售票
28
29 self.thread1=[[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(sellTickets) object:nil];
30
31 self.thread1.name=@"售票员A";
32
33 self.thread2=[[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(sellTickets) object:nil];
34
35 self.thread2.name=@"售票员B";
36
37 self.thread3=[[NSThread alloc]initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(sellTickets) object:nil];
38
39 self.thread3.name=@"售票员C";
40 }
41
42
43 -(void)sellTickets
44 {
45 while (1) {
46 @synchronized(self){//只能加一把锁
47 //1.先检查票数
48
49 int count=self.leftTicketsCount;
50 if (count>0) {
51 //暂停一段时间
52 [NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:0.002];
53 //2.票数-1
54
55 self.leftTicketsCount= count-1;
56 //获取当前线程
57 NSThread *current=[NSThread currentThread];
58 NSLog(@"%@--卖了一张票,还剩余%d张票",current,self.leftTicketsCount);
59
60 }else
61 {
62 //退出线程
63 [NSThread exit];
64 }
65 }
66 }
67 }
68
69
70 -(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
71 {
72
73 //开启线程
74 [self.thread1 start];
75 [self.thread2 start];
76 [self.thread3 start];
77 }
78
79 @end
执行效果图

互斥锁的优缺点
优点:能有效防止因多线程抢夺资源造成的数据安全问题
缺点:需要消耗大量的CPU资源
互斥锁的使用前提:多条线程抢夺同一块资源
相关专业术语:线程同步,多条线程按顺序地执行任务
互斥锁,就是使用了线程同步技术
四:原子和非原子属性
OC在定义属性时有nonatomic和atomic两种选择
atomic:原子属性,为setter方法加锁(默认就是atomic)
nonatomic:非原子属性,不会为setter方法加锁
atomic加锁原理
1 @property (assign, atomic) int age;
2
3 - (void)setAge:(int)age
4 {
5
6 @synchronized(self) {
7 _age = age;
8 }
9 }
原子和非原子属性的选择
nonatomic和atomic对比
atomic:线程安全,需要消耗大量的资源
nonatomic:非线程安全,适合内存小的移动设备
iOS开发的建议
所有属性都声明为nonatomic
尽量避免多线程抢夺同一块资源
尽量将加锁、资源抢夺的业务逻辑交给服务器端处理,减小移动客户端的压力
—线程间的通信
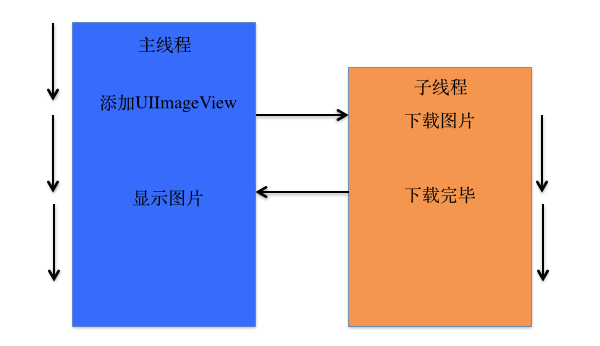
一、简单说明
线程间通信:在1个进程中,线程往往不是孤立存在的,多个线程之间需要经常进行通信
线程间通信的体现
1个线程传递数据给另1个线程
在1个线程中执行完特定任务后,转到另1个线程继续执行任务
线程间通信常用方法
- (void)performSelectorOnMainThread:(SEL)aSelector withObject:(id)arg waitUntilDone:(BOOL)wait;
- (void)performSelector:(SEL)aSelector onThread:(NSThread *)thr withObject:(id)arg waitUntilDone:(BOOL)wait;
线程间通信示例 – 图片下载
代码1:
9 #import "YYViewController.h"
10 @interface YYViewController ()
11 @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIImageView *iconView;
12 @end
13
14 @implementation YYViewController
15
16 - (void)viewDidLoad
17 {
18 [super viewDidLoad];
19 }
20
21 -(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
22 {
23
24 // 在子线程中调用download方法下载图片
25 [self performSelectorInBackground:@selector(download) withObject:nil];
26 }
27
28
29
30 -(void)download
31 {
32 //1.根据URL下载图片
33 //从网络中下载图片
34 NSURL *urlstr=[NSURL URLWithString:@"fdsf"];
35
36 //把图片转换为二进制的数据
37 NSData *data=[NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:urlstr];//这一行操作会比较耗时
38
39 //把数据转换成图片
40 UIImage *image=[UIImage imageWithData:data];
41
42 //2.回到主线程中设置图片
43 [self performSelectorOnMainThread:@selector(settingImage:) withObject:image waitUntilDone:NO];
44 }
45
46
47
48 //设置显示图片
49 -(void)settingImage:(UIImage *)image
50 {
51 self.iconView.image=image;
52 }
53
54 @end
代码2:
9 #import "YYViewController.h"
10 #import <NSData.h>
11
12 @interface YYViewController ()
13 @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIImageView *iconView;
14 @end
15
16 @implementation YYViewController
17
18 - (void)viewDidLoad
19 {
20 [super viewDidLoad];
21 }
22
23
24 -(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
25 {
26 // 在子线程中调用download方法下载图片
27
28 [self performSelectorInBackground:@selector(download) withObject:nil];
29 }
30
31
32 -(void)download
33 {
34
35 //1.根据URL下载图片
36 //从网络中下载图片
37 NSURL *urlstr=[NSURL URLWithString:@"fdsf"];
38
39 //把图片转换为二进制的数据
40 NSData *data=[NSData dataWithContentsOfURL:urlstr];//这一行操作会比较耗时
41
42 //把数据转换成图片
43 UIImage *image=[UIImage imageWithData:data];
44
45 //2.回到主线程中设置图片
46 //第一种方式
47 // [self performSelectorOnMainThread:@selector(settingImage:) withObject:image waitUntilDone:NO];
48
49 //第二种方式
50 // [self.imageView performSelector:@selector(setImage:) onThread:[NSThread mainThread] withObject:image waitUntilDone:NO];
51
52 //第三种方式
53 [self.iconView performSelectorOnMainThread:@selector(setImage:) withObject:image waitUntilDone:NO];
54 }
55
56
57 //设置显示图片
58 //-(void)settingImage:(UIImage *)image
59 //{
60 // self.iconView.image=image;
61 //}
62
63 @end




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号