分离分层的 platform驱动
一、分离分层
输入子系统、usb设备比驱动以及platform类型的驱动等都体现出分离分层机制;如下图所示,一种典型的分离分层框架:
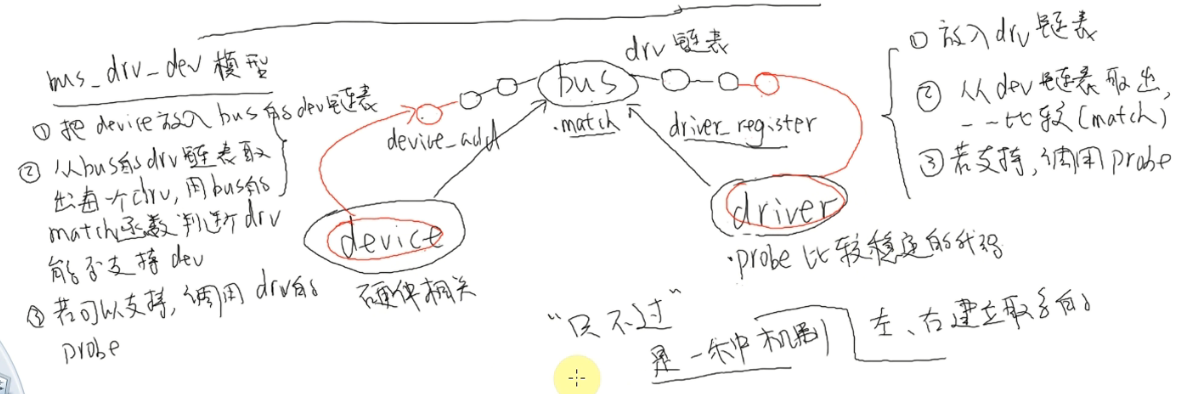
二、platform机制下的分离
分离就是在驱动层中使用platform机制把硬件相关的代码(固定的,如板子的网卡、中断地址)和驱动(会根据程序作变动,如点哪一个灯)分离开来,即要编写两个文件:dev.c和drv.c(platform设备和platform驱动)。
会在开发板/sys/bus/platform目录下出现这两个文件,并且在两个文件目录下存在命名相同的设备和驱动程序。
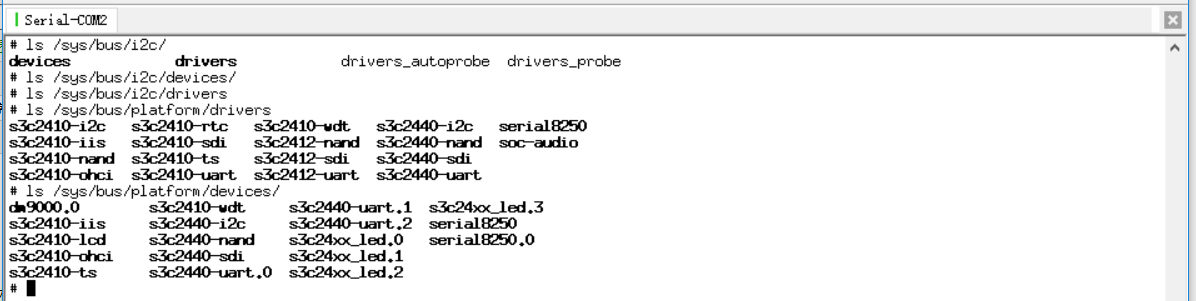
同样的,在/sys/bus/i2c等其它的总线类型目录下,也存在设备和驱动各自的目录。
platform总线:为platform_bus_type,是个全局变量,属于虚拟设备总线, 属于Linux中bus的一种:
1 struct bus_type platform_bus_type = {
2 .name = "platform",
3 .dev_attrs = platform_dev_attrs,
4 .match = platform_match,
5 .uevent = platform_uevent,
6 .suspend = platform_suspend,
7 .suspend_late = platform_suspend_late,
8 .resume_early = platform_resume_early,
9 .resume = platform_resume,
10 };
利用该设备总线,一旦一方注册就会调用.match函数进行匹配,将driver和device连接在一起,匹配成功后会调用driver程序里的.probe函数:
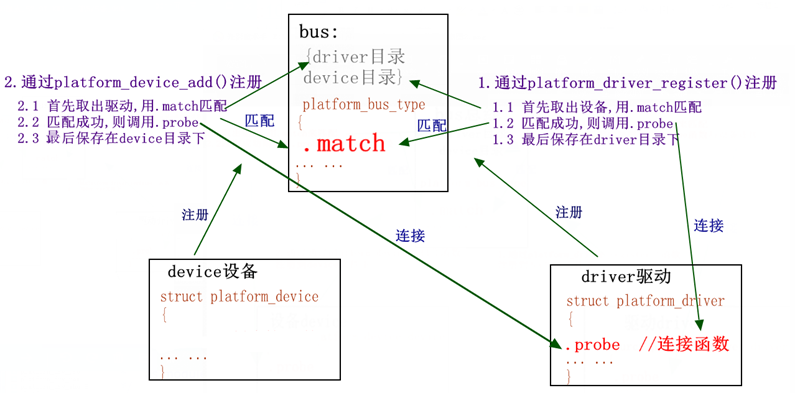
其中,device设备为挂接在platform总线下的设备, platform_device结构体类型,driver驱动为挂接在platform总线下,与某种设备相关的驱动程序, platform_driver结构体类型。
三、例程--基于platform机制,编写led设备和驱动程序
需要分别编写设备代码和驱动代码: led_dev.c 、led_drv.c。其中,
led_dev.c:指定设备硬件/寄存器资源。
led_drv.c:获取设备资源,初始化并操作led。
3.1 led_drv.c
1 /* 分配/设置/注册一个platform_driver */
3 #include <linux/module.h>
4 #include <linux/version.h>
6 #include <linux/init.h>
7 #include <linux/fs.h>
8 #include <linux/interrupt.h>
9 #include <linux/irq.h>
10 #include <linux/sched.h>
11 #include <linux/pm.h>
12 #include <linux/sysctl.h>
13 #include <linux/proc_fs.h>
14 #include <linux/delay.h>
15 #include <linux/platform_device.h>
16 #include <linux/input.h>
17 #include <linux/irq.h>
18 #include <asm/uaccess.h>
19 #include <asm/io.h>
20
21 static int major;
24 static struct class *cls;
25 static volatile unsigned long *gpio_con;
26 static volatile unsigned long *gpio_dat;
27 static int pin;
28
29 static int led_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
30 {
31 /* 配置为输出 */
32 *gpio_con &= ~(0x3<<(pin*2));
33 *gpio_con |= (0x1<<(pin*2));
34 return 0;
35 }
37 static ssize_t led_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t * ppos)
38 {
39 int val;
41 copy_from_user(&val, buf, count); // copy_to_user();
42
43 if (val == 1)
44 {
45 // 点灯
46 *gpio_dat &= ~(1<<pin);
47 }
48 else
49 {
50 // 灭灯
51 *gpio_dat |= (1<<pin);
52 }
54 return 0;
55 }
58 static struct file_operations led_fops = {
59 .owner = THIS_MODULE, /* 这是一个宏,推向编译模块时自动创建的__this_module变量 */
60 .open = led_open,
61 .write = led_write,
62 };
63
64 /* 2.1 当驱动和设备都insmod加载后,然后bus总线会匹配成功,就进入.probe函数,
65 2.2 在.probe函数中便使用platform_get_resource()函数获取LED的地址和引脚,然后初始化LED,并注册字符设备,和设备节点"led",
66 2.3 编写注册时的file_operations成员函数
67 */
68 static int led_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
69 {
70 struct resource *res;
71
72 /* 根据platform_device的资源进行ioremap */
73 res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0); //IORESOURCE_MEM资源中的第0个
74 gpio_con = ioremap(res->start, res->end - res->start + 1);
75 gpio_dat = gpio_con + 1; //指针加1==》相当于+4
76
77 res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_IRQ, 0); //IORESOURCE_IRQ资源中的第0个
78 pin = res->start;
79
80 /* 注册字符设备驱动程序 */
82 printk("led_probe, found led\n");
83
84 major = register_chrdev(0, "myled", &led_fops);
85
86 cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "myled");
87
88 class_device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "led"); /* /dev/led */
89
90 return 0;
91 }
93 static int led_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
94 {
95 /* 卸载字符设备驱动程序 */
96 /* iounmap */
97 printk("led_remove, remove led\n");
98
99 class_device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major, 0));
100 class_destroy(cls);
101 unregister_chrdev(major, "myled");
102 iounmap(gpio_con);
103
104 return 0;
105 }
108 struct platform_driver led_drv = {
109 .probe = led_probe,
110 .remove = led_remove,
111 .driver = {
112 .name = "myled",
113 }
114 };
115
116 /*1. 注册的led驱动*/
117 static int led_drv_init(void)
118 {
119 platform_driver_register(&led_drv);
120 return 0;
121 }
123 static void led_drv_exit(void)
124 {
125 platform_driver_unregister(&led_drv);
126 }
128 module_init(led_drv_init);
129 module_exit(led_drv_exit);
131 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
其中, platform_get_resource函数为:
struct resource * platform_get_resource(struct platform_device *dev, unsigned int type,unsigned int num); //获取设备的某个资源,获取成功,则返回一个resource资源结构体 //参数: // *dev: 指向某个platform device设备 // type: 获取的资源类型 // num: type资源下的第几个数组
platform_driver结构体:
struct platform_driver {
int (*probe)(struct platform_device *);
int (*remove)(struct platform_device *);
void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *); //断电
int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state); //休眠
int (*suspend_late)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume_early)(struct platform_device *);
int (*resume)(struct platform_device *); //唤醒
struct device_driver driver; //内嵌的driver, 主要是name成员:设备的名称
};
3.2 led_dev.c
1 #include <linux/module.h>
2 #include <linux/version.h>
3 #include <linux/init.h>
4 #include <linux/kernel.h>
5 #include <linux/types.h>
6 /* 分配/设置/注册一个platform_device */
7 #include <linux/interrupt.h>
8 #include <linux/list.h>
9 #include <linux/timer.h>
10 #include <linux/init.h>
11 #include <linux/serial_core.h>
12 #include <linux/platform_device.h>
13
14 static struct resource led_resource[] = {
15 [0] = {
16 .start = 0x56000050, //寄存器的起始物理地址 GPFCON 0x56000050
17 .end = 0x56000050 + 8 - 1,
18 .flags = IORESOURCE_MEM, //哪一类资源
19 },
20 [1] = {
21 .start = 5, //哪(位)个引脚
22 .end = 5,
23 .flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ,
24 }
25
26 };
27
28 static void led_release(struct device * dev)
29 {
30 }
32 static struct platform_device led_dev = {
33 .name = "myled",
34 .id = -1, //表示只有一个设备
35 .num_resources = ARRAY_SIZE(led_resource),//资源数量,ARRAY_SIZE()函数:获取数量
36 .resource = led_resource,
37 .dev = {
38 .release = led_release,
39 },
40 };
41
42 static int led_dev_init(void)
43 {
44 platform_device_register(&led_dev);
45 return 0;
46 }
47
48 static void led_dev_exit(void)
49 {
50 platform_device_unregister(&led_dev);
51 }
52 module_init(led_dev_init);
53 module_exit(led_dev_exit);
54 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
其中,platform_driver结构体:
struct platform_device {
const char * name; //设备名称,要与platform_driver的name一样,这样总线才能匹配成功
u32 id; //id号,插入总线下相同name的设备编号(一个驱动可以有多个设备),如果只有一个设备填-1
struct device dev; //内嵌的具体的device结构体,其中成员platform_data,是个void *类型,可以给平台driver提供各种数据(比如:GPIO引脚等等)
u32 num_resources; //资源数量,
struct resource * resource; //资源结构体,保存设备的信息
};
struct resource {
resource_size_t start; //起始资源,如果是地址的话,必须是物理地址
resource_size_t end; //结束资源,如果是地址的话,必须是物理地址
const char *name; //资源名
unsigned long flags; //资源的标志
//比如IORESOURCE_MEM,表示地址资源, IORESOURCE_IRQ表示中断引脚... ...
struct resource *parent, *sibling, *child; //资源拓扑指针父、兄、子,可以构成链表
};
3.3 测试程序
1 #include <sys/types.h>
2 #include <sys/stat.h>
3 #include <fcntl.h>
4 #include <stdio.h>
5
6 /* led_test on
7 * led_test off
8 */
9 int main(int argc, char **argv)
10 {
11 int fd;
12 int val = 1;
13 fd = open("/dev/led", O_RDWR);
14 if (fd < 0)
15 {
16 printf("can't open!\n");
17 }
18 if (argc != 2)
19 {
20 printf("Usage :\n");
21 printf("%s <on|off>\n", argv[0]);
22 return 0;
23 }
24
25 if (strcmp(argv[1], "on") == 0)
26 {
27 val = 1;
28 }
29 else
30 {
31 val = 0;
32 }
34 write(fd, &val, 4);
35 return 0;
36 }
1)将led_dev和led_drv编译为模块,加载。会在sys/bus/platform/devices目录下分别生成一个"myled"。
2)最后,编译应用程序,并在开发板运行可执行程序,控制led:
# led_test on
# led_test off




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号