RepositoryBase文件解析
public class RepositoryBase<T> : IRepository<T> where T : class
RepositoryBase 是IRepository的一个 实例,泛型的作用是为特定的模型层提供标准的增删查改操作。
protected XltAppDataContext DataContext;
一个继承了DbContext的类(数据库上下文)↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
public class XltAppDataContext : DbContext
新增一个实体
public object Add(T entity)
{
DataContext.Set<T>().Add(entity);
return entity;
}
创建一个实体
public T Create()
{
return DataContext.Set<T>().Create();
}
Create 和 Add 有什么区别呢,以下摘自MSDN?
Create:Creates a new instance of an entity for the type of this set. Note that this instance is NOT added or attached to the set. The instance returned will be a proxy if the underlying context is configured to create proxies and the entity type meets the requirements for creating a proxy.
Add:Adds the given entity to the context underlying the set in the Added state such that it will be inserted into the database when SaveChanges is called.
今天我们来 最后分析一下这个基础 方法:
public T CloneWithDynamicProxiesType(T modelObject)
这个方法说的是“克隆,连带着代理类型”,下面我们来 分析一下这个方法的语句,今天不做深入分析。

public T CloneWithDynamicProxiesType(T modelObject) { T dataModelProxy = DataContext.Set<T>().Create(); Type dynamicType = typeof(T).GetType(); var properties = dataModelProxy.GetType().GetProperties(); //TODO: consider a better way to filter out all 'virual' properties of the model class foreach (var property in properties.Where(p => !p.PropertyType.Namespace.StartsWith("HP.XLT"))) { try { //TODO: consider a better way to filter out all 'virual' properties of the model class var genArgType = property.PropertyType.GetGenericArguments().FirstOrDefault(); if (genArgType== null || !genArgType.Namespace.StartsWith("HP.XLT")) { var value = property.GetValue(modelObject, null); if (value == null) { continue; } property.SetValue(dataModelProxy, value); } } catch (Exception) { throw; } } return dataModelProxy; }
分析如下:
下面这句话的意思应该是从DataContext中的固定类型中创建 一个实例,但是 这个实例是和具体的数据库无关的,也就是没有Attach or Set 到具体的表。
T dataModelProxy = DataContext.Set<T>().Create();
这个就是从泛型类中获取动态类型。
Type dynamicType = typeof(T).GetType();
下面是有关介绍:
typeoftakes a type name (which you specify at compile time).
GetTypegets the runtime type of an instance.
相当于先得到这个类型的名字,然后再得到类型的实例,一个是编译时,一个是 运行时。
下面的一句话,相当于利用反射从Type中获取Properties(属性)。
var properties = dataModelProxy.GetType().GetProperties();
下面 是一个foreach循环,它的意思是首先过滤 掉命名 空间 不以HP.XLT开头的Property
foreach (var property in properties.Where(p => !p.PropertyType.Namespace.StartsWith("HP.XLT")))
具体的关于GetProperties的介绍请参考Stackoverflow中的这个问题。
今天 写到这里 ,明天继续 ------于2015/12/1日记录。
又一天开始了,哈哈,今天继续。。。。
我们 注意到了上面的GetProperties其实是得到了这个东西,也就是PropertyInfo:
public PropertyInfo[] GetProperties();
下面的语句:
var genArgType = property.PropertyType.GetGenericArguments().FirstOrDefault();
其实 本质上是得到一个Type,而这个Type是“每个”Property的Type,而GetGenericArguments()这个方法 是 得到了Type的一个数组,形如Type [].我们 可以通过如下的方法来使用,这是我写的:

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ConsoleApplicationCSharp { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("-------NonGenericType---------"); IsGenericType(typeof(NonGenericType)); Console.WriteLine("----------GenericType---------"); IsGenericType(typeof(GenericType<>)); Console.ReadLine(); } public static void IsGenericType(Type t) { if (t.IsGenericType) { // If this is a generic type, display the type arguments. // Type[] typeArguments = t.GetGenericArguments(); Console.WriteLine("\tList type arguments ({0}):", typeArguments.Length); foreach (Type tParam in typeArguments) { // If this is a type parameter, display its // position. // if (tParam.IsGenericParameter) { Console.WriteLine("\t\t{0}\t(unassigned - parameter position {1})", tParam, tParam.GenericParameterPosition); } else { Console.WriteLine("\t\t{0}", tParam); } } } } } public class NonGenericType { public string Name { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } } public class GenericType<T> where T : class { public string Name { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } public void Add(T t) { } } }
结果如下,我们 可以 看出只有使用了泛型类的,才会进方法,具体的参考上面的代码:
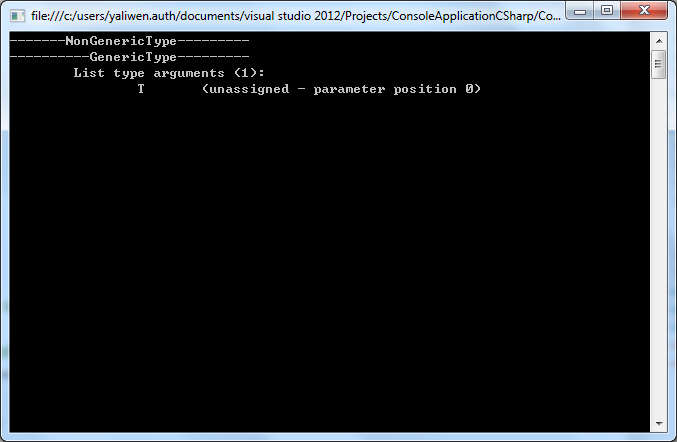
下面 这句话 的意思 是,如果 没有参数或者参数的所属的类的命名空间不以XXX开头 的 时候,那么就,其实这个项目 所有的命名 空间都是有HP.XLT的,所以这句话的意思就是“找不到”相对应的参数。
if (genArgType== null || !genArgType.Namespace.StartsWith("HP.XLT"))
下面一句话,我觉得还是MSDN上面说得最好
Returns the property value of a specified object with optional index values for indexed properties.
意思就是返回特定的属性值---对于特定的对象:
var value = property.GetValue(modelObject, null);
下面展示了如果VALUE不为空,那么就把这个值赋给dataModelProxy,而这个dataModelProxy也是我们最终要 返回的实例,因为这里是一个基础方法,所以返回T。
if (value == null)
{
continue;
}
property.SetValue(dataModelProxy, value);
下面的代码,循环添加:
public virtual IEnumerable<T> Add(IEnumerable<T> entities)
{
foreach (var entity in entities)
{
Add(entity);
}
return entities;
}
其中上面的方法 用到了单个 添加 ,代码 如下 :
public object Add(T entity)
{
DataContext.Set<T>().Add(entity);
return entity;
}
有些人可能对Add方法为什么要返回object有疑问,不能返回void吗?这里我说说我的理解 ,有2个 方面:
- 已过期 :框架要考虑的是全部,如果你 返回的是一个VOID,那么如果想用这个实体,那么必然要重新去得到这个实体,这样浪费了时间和空间,所以返回VOID在 框架层面上是不好的。
- 更新:返回VOID比 返回 OBJEECT要好,原因 很简单 ,没用到过。
- 另一个问题是返回object好还是T好 ,可以明确的说,返回T好,因为T是一个泛型类,指向的是一个具体的类型,而如果 返回object,我还要进行强制类型转换才能得到 具体的实体。
剩下的类似的方法如下:
public T Create()
{
return DataContext.Set<T>().Create();
}
public T Get(object id)
{
return DataContext.Set<T>().Find(id);
}
今天 写到这里 ,明天继续 ------于2015/12/2日记录。
下面 的一个方法是 从DbContext中过滤数据
public IEnumerable<T> FilterContext(System.Linq.Expressions.Expression<Func<T, bool>> predicate)
{
return DataContext.Set<T>().Local.Where(predicate.Compile());
}
上面的代码 有几个知识点:
2.Local永远不会去访问 数据库里的东西 ,它的目的是 把东西放在本地 缓存,这句话永远 用在查询 语句已经被 执行以后。
下面的方式 是关于"Filter"的一个最重要的方法

public IQueryable<T> Filter(System.Linq.Expressions.Expression<Func<T, bool>> expression, string includePath) { DbQuery<T> result = null; if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(includePath)) { var includePathArray = includePath.Split(';'); foreach (var singlePath in includePathArray) { if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(singlePath)) { result = result == null ? DataContext.Set<T>().Include(singlePath) : result.Include(singlePath.Trim()); } } } else { result = DataContext.Set<T>(); } return expression == null ? result.AsQueryable() : result.Where(expression).AsQueryable(); }
它是通过lambda表达式去进行过滤,DbQuery是一个 非泛型的Linq to Entity实例对于DbContext来说。
DbQuery<T> result = null;
上面 这句话 先 判断IncludePath是否为空,至于Include是 干啥的呢?Include当中 包含了“属性的名称”,表示包含了此属性的所有的结果集。比如
public ClassA Ainstance{get;set;} //这里面,属性的名称就是Ainstance
注意ClassA是这里的一个 导航属性,也就是不能为基本数据类型,比如int,string什么的。
下面 最后来 总结 一下 这个方法:
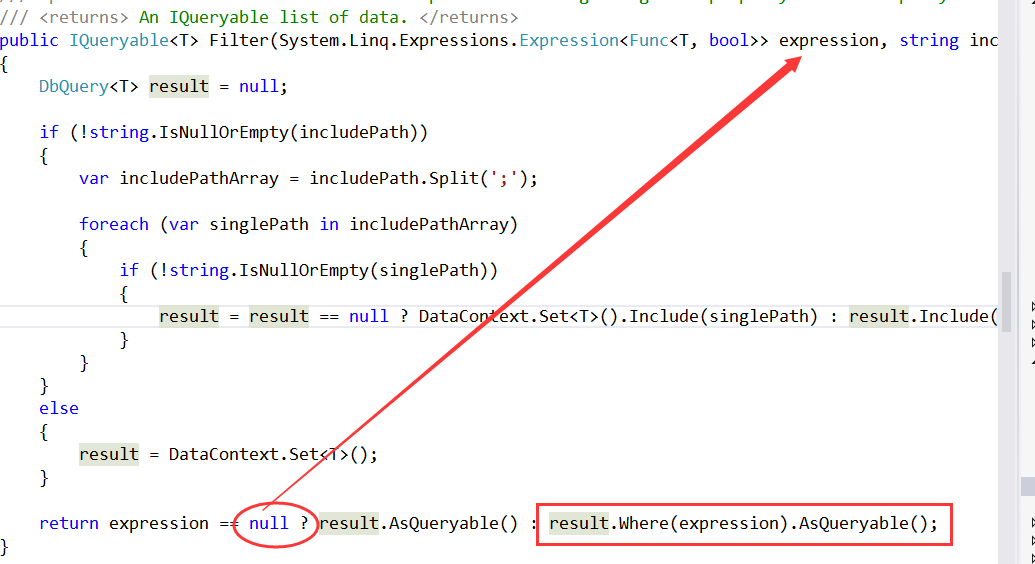
下面再来看看一个特殊的方法:
public void Update(T entity)
{
DataContext.Entry<T>(entity).State = EntityState.Modified;
}
这里的Entry,State是表示什么意思呢?下面的图可以揭开迷雾:
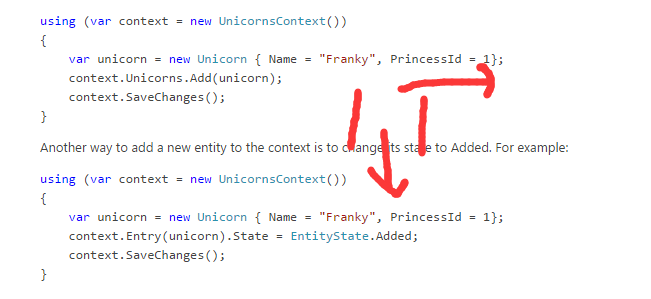
其实不同的State对应了不同的状态,可以有不同的CRUD状态,上半部分的代码 和 下半部分的代码 其实 是 一个意思。
下面介绍最后一个方法:
public void Detach(T entity)
{
try //Catch 'invalid operation exception' - most likely cause: object is not attached
{
((IObjectContextAdapter)DataContext).ObjectContext.Detach(entity);
}
catch (InvalidOperationException)
{ }
}
这么 写的目的是:不能有2个相同的KEY值在ObjectStateManager中,所以 需要把旧的实体从ORM中分离出去,这样才可以更新数据。
大家 可以按转到定义按钮,去看看DbContext,得到如下结果,这证明了Dbcontext可以和IObjectContextAdapter进行强制 类型转换:
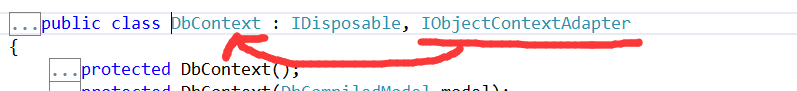
MSDN上对于 ObjectContext.Detach的介绍相对 来说 比较 简单:从objectContext中移除相应的object.
好了,这个文件讲解完毕----于2015-12-3日。
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/kmsfan
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。
欢迎大家加入KMSFan之家,以及访问我的优酷空间!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号