OO第二次博客作业
OO第二次博客作业(PTA第四次、第五次作业及期中考试)
目录
- 作业总结
- 设计与分析
- 采坑心得
- 改进建议
- 心得体会
一、作业总结
作业四:作业四整体上难度适中,7-1和7-3难度较小,7-1重点考察同学审题的能力和对正则表达式的熟练度,7-3考察基本的设计类的能力,这两道题的通过率也很高,后面不做赘述。本次作业的难点集中在7-2凸四边形的计算上,本题也是“多边形系列”的题,不仅考察同学关于四边形相关问题的思考能力,还检验同学是否真正理解了面向对象设计的思想,想要做好这道题,需要将 之前的三角形类设计好并且没有bug,而本题的四边形类也要设计的便于使用,因为作业五也需要用到,所以下面会重点介绍如何设计好类。
作业五:本次作业作为“多边形系列”的最终篇,可以说也是坑很多,非常考验同学对类的设计能力,如果之前的三角形类和四边形类没有设计好的话,做起来可以说很困难,所以想要“舒服”地搞定这道题,还是要稳扎稳打,从点到线到三角形到四边形,每一个类都要设计的很有逻辑。
期中考试:本次考试相较于之前折磨同学很久的“多边形系列”,可以说难度下降了不知道多少个档次,基本没有需要动脑子思考的部分,只考验同学明不明白“多态”的基本使用即可,只要对多态部分的知识学的比较扎实的话,相信对于同学们来说难度很低,后续也简单介绍一下多态的基本知识。
二、设计与分析
7-2 点线形系列4-凸四边形的计算:

用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与四边形有关的计算。 以下四边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。 选项包括: 1:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是四边形、平行四边形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 2:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是菱形、矩形、正方形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral" 3:输入四个点坐标,判断是凹四边形(false)还是凸四边形(true),输出四边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral" 4:输入六个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后四个点构成一个四边形或三角形,输出直线与四边形(也可能是三角形)相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出四边形(或三角形)被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与四边形或三角形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形的输入,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。 后四个点构成三角形的情况:假设三角形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s: 1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。 2) 不符合要求的输入:z 不与xy都相邻,如z x y s、x z s y、x s z y 5:输入五个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后四个点所构成的四边形(限定为凸四边形,不考虑凹四边形)或三角形(判定方法见选项4)的内部(若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle或者on the quadrilateral"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
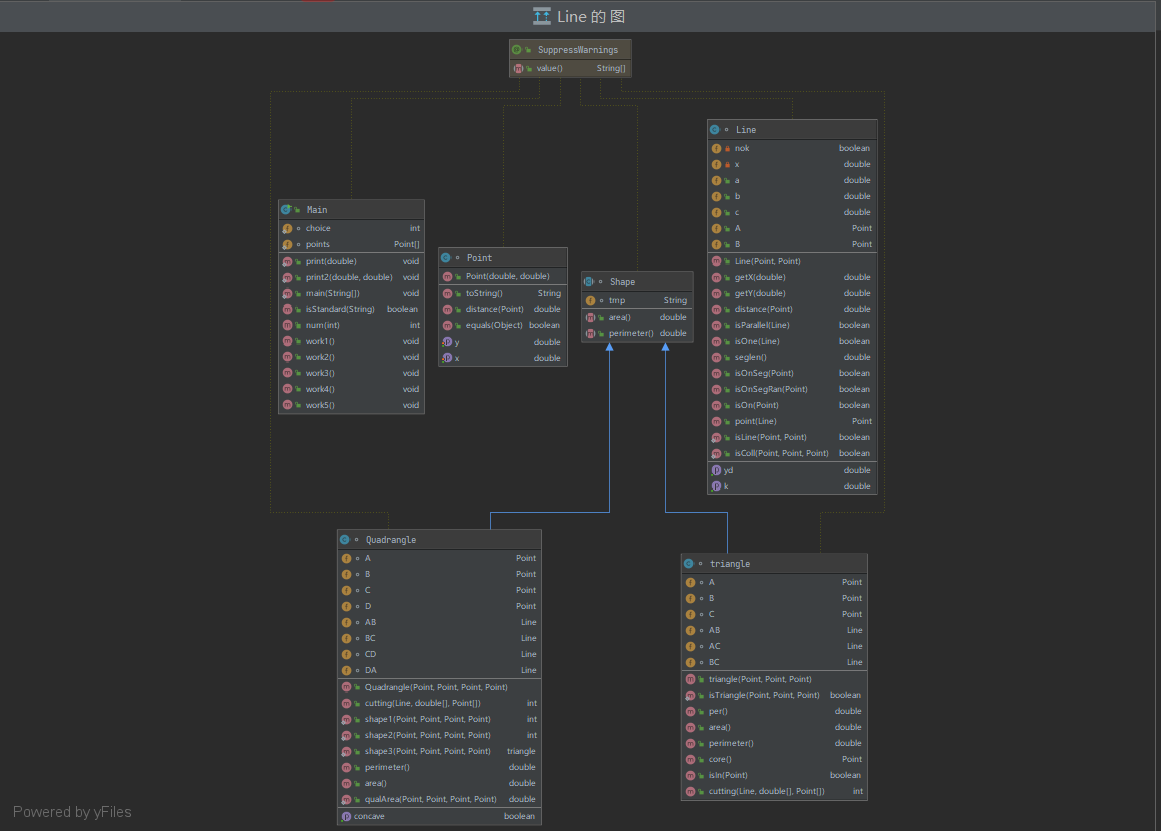
分析:“多边形系列”题目的共同点就在于要“层层递进”,从点到线到三角形,每个类都要设计的很有逻辑,才能大幅降低后续更复杂的问题,这里先贴一下我的点Point,线Line,三角形triangle类:

1 @SuppressWarnings("all") 2 class Point { 3 4 private double x; 5 private double y; 6 7 @Override 8 public String toString() { 9 /* if(x == -0.0) 10 x = 0.0; 11 if(y == -0.0) 12 y = 0.0; 13 */ 14 return x + "," + y; 15 } 16 17 public Point(double x, double y) { 18 this.x = x; 19 this.y = y; 20 } 21 22 public double getX() { 23 return x; 24 } 25 26 public void setX(double x) { 27 this.x = x; 28 } 29 30 public double getY() { 31 return y; 32 } 33 34 public void setY(double y) { 35 this.y = y; 36 } 37 38 public double distance(Point point) { 39 40 return Math.sqrt((x - point.x) * (x - point.x) + (y - point.y) * (y - point.y)); 41 } 42 43 @Override 44 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 45 Point obj1 = (Point) obj; 46 if (obj1.getX() == this.x && this.y == obj1.getY()) 47 return true; 48 else 49 return false; 50 51 } 52 }
里面存储了点的x和y两个二维坐标以及一些基本的获取与设置信息的方法和distance(Point p){求与p点的距离}方法,以及重写了祖宗类Object的tostring方法和equals方法,方便后续进行输出和比较

1 @SuppressWarnings("all") 2 class Line { 3 private double k = 0; 4 private double yd; 5 private boolean nok = false; 6 private double x; 7 public double a; 8 public double b; 9 public double c; 10 public Point A; 11 public Point B; 12 13 public double getK() { 14 15 return k; 16 } 17 18 public double getYd() { 19 return yd; 20 } 21 22 public Line(Point p1, Point p2) { 23 this.a = p1.getY() - p2.getY(); 24 this.b = p2.getX() - p1.getX(); 25 this.c = p1.getX() * p2.getY() - p2.getX() * p1.getY(); 26 if ((p1.getX() - p2.getX()) == 0) { 27 nok = true; 28 x = p1.getX(); 29 k = Double.NaN; 30 31 if (p1.getY() > p2.getY()) { 32 A = p2; 33 B = p1; 34 } else { 35 A = p1; 36 B = p2; 37 } 38 } else { 39 this.k = -(a / b); 40 this.yd = -(c / b); 41 if (p1.getX() < p2.getX()) { 42 A = p1; 43 B = p2; 44 } else { 45 A = p2; 46 B = p1; 47 48 } 49 50 } 51 } 52 53 public double getX(double y) { 54 55 56 return -((c + b * y) / a); 57 } 58 59 public double getY(double x) { 60 61 62 return -((c + a * x) / b); 63 } 64 65 public double distance(Point p) { 66 67 68 double mol = Math.abs(a * p.getX() + b * p.getY() + c); 69 double den = Math.sqrt(a * a + b * b); 70 return mol / den; 71 } 72 73 public boolean isParallel(Line line) { 74 75 if (Math.abs(a * line.b - b * line.a) < 0.000001) 76 return true; 77 else 78 return false; 79 80 } 81 82 public boolean isOne(Line line) { 83 if (!isParallel(line)) 84 return false; 85 else { 86 if (Math.abs(a * line.c - line.a * c) < 0.00001 && Math.abs(a * line.b - line.a * b) < 0.00001 && Math.abs(b * line.c - line.b * c) < 0.00001) 87 return true; 88 else 89 return false; 90 } 91 92 } 93 94 public double seglen() { 95 96 return A.distance(B); 97 } 98 99 100 public boolean isOnSeg(Point p) { 101 102 if (!isOn(p)) 103 return false; 104 105 if (!nok) { 106 107 if (p.getX() >= A.getX() && p.getX() <= B.getX()) 108 return true; 109 else return false; 110 } else { 111 112 if (p.getY() >= A.getY() && p.getY() <= B.getY()) 113 return true; 114 else return false; 115 116 } 117 118 } 119 120 public boolean isOnSegRan(Point p) { 121 if (!nok) { 122 123 if (p.getX() >= A.getX() && p.getX() <= B.getX()) 124 return true; 125 else return false; 126 } else { 127 128 if (p.getY() >= A.getY() && p.getY() <= B.getY()) 129 return true; 130 else return false; 131 132 } 133 134 } 135 136 public boolean isOn(Point p) { 137 138 if (nok) { 139 if (p.getX() == this.x) 140 return true; 141 else 142 return false; 143 } 144 double t = getY(p.getX()); 145 if (Math.abs(t - p.getY()) < 0.000001) 146 return true; 147 else 148 return false; 149 150 } 151 152 public Point point(Line line) { 153 154 double x, y; 155 x = (c * line.b - line.c * b) / (line.a * b - a * line.b); 156 y = (a * line.c - line.a * c) / (line.a * b - a * line.b); 157 158 159 return new Point(x, y); 160 161 } 162 163 164 public static boolean isLine(Point a, Point b) { 165 166 if (a.getX() == b.getX() && a.getY() == b.getY()) 167 return false; 168 else 169 return true; 170 } 171 172 public static boolean isColl(Point p1, Point p2, Point p3) { 173 if (p1.equals(p2)) { 174 return true; 175 } else { 176 Line line = new Line(p1, p2); 177 if (line.isOn(p3)) { 178 return true; 179 } else 180 return false; 181 182 } 183 184 } 185 }
线类的构造方法需要两个点(两点组成一条线),前提是两点不能重复,所以需要在创建Line对象时进行判断两点是否相同,如若相同就不可以创建对象;线的属性有组成该线的两个点A和B(该线类不仅可以表达直线,也可以表示一条线段),组成一条直线的各个参数(这里推荐使用直线的一般式ax+by+c=0来表示直线,可以避免很多情况的讨论)a,b,c,由于我一开始使用的是y=kx+b来表示,需要对x=k这一斜率不存在的直线单独考虑,出现了很多错误,后续更改为一般式的时候,也没有完全作废掉原来的,所以我的Line类有些冗余,里面还保留了k(斜率),nok(表示斜率是否存在),x(就是斜率不存在时,x=k里面的k),特此提醒;线的方法可以很丰富,甚至在后续三角形、四边形等类中为了方便其设计,还要在Line类里面添加新的方法,所以,方法这一块可以很多,这里只列举几个常用的方法getX(double y)和getY(double x),给定x(或者y),来求直线上改点对应的y(或者x), distance(Point p)求直线到p点的距离,isParallel(Line line)该直线是否与line直线平行,isOne(Line line)该直线是否与line直线是同一条直线,seglen()返回该线段的长度,isOnSeg(Point p)p点是否处于该线段上,isOn(Point p)p点是否处于该直线上,Point point(Line line)求两直线交点。

1 @SuppressWarnings("all") 2 class triangle extends Shape { 3 4 Point A, B, C; 5 Line AB, AC, BC; 6 7 public triangle(Point a, Point b, Point c) { 8 if (!triangle.isTriangle(a, b, c)) 9 return; 10 A = a; 11 B = b; 12 C = c; 13 AB = new Line(a, b); 14 AC = new Line(a, c); 15 BC = new Line(b, c); 16 } 17 18 public static boolean isTriangle(Point a, Point b, Point c) { 19 20 if (!Line.isLine(a, b)) { 21 22 return false; 23 } 24 25 Line line = new Line(a, b); 26 if (line.isOn(c)) { 27 28 return false; 29 } else 30 return true; 31 32 } 33 34 public double per() { 35 36 return A.distance(B) + B.distance(C) + A.distance(C); 37 } 38 39 public double area() { 40 41 double h = AB.distance(C); 42 return h * A.distance(B) / 2; 43 44 } 45 46 @Override 47 public double perimeter() { 48 return AB.seglen() + AC.seglen() + BC.seglen(); 49 } 50 51 public Point core() { 52 53 double x = (A.getX() + B.getX() + C.getX()) / 3; 54 double y = (A.getY() + B.getY() + C.getY()) / 3; 55 return new Point(x, y); 56 } 57 58 public boolean isIn(Point p) { 59 60 double d1 = (AB.seglen() * AB.distance(p)) / 2; 61 double d2 = (AC.seglen() * AC.distance(p)) / 2; 62 double d3 = (BC.seglen() * BC.distance(p)) / 2; 63 64 65 if (Math.abs(d1 + d2 + d3 - this.area()) < 0.00001) { 66 return true; 67 } else { 68 return false; 69 } 70 } 71 72 public int cutting(Line line, double[] ds, Point[] ps) { 73 if (this.AB.isOne(line) || this.BC.isOne(line) || this.AC.isOne(line)) { 74 75 return -1; 76 } 77 Point p1 = null, p2 = null, p3 = null, tool = null; 78 79 if (this.AB.isParallel(line)) { 80 p1 = null; 81 } else { 82 tool = this.AB.point(line); 83 if (this.AB.isOnSeg(tool)) { 84 p1 = tool; 85 } else 86 p1 = null; 87 } 88 if (this.BC.isParallel(line)) { 89 p2 = null; 90 } else { 91 tool = this.BC.point(line); 92 if (this.BC.isOnSeg(tool)) { 93 p2 = tool; 94 } else 95 p2 = null; 96 } 97 if (this.AC.isParallel(line)) { 98 p3 = null; 99 } else { 100 tool = this.AC.point(line); 101 if (this.AC.isOnSeg(tool)) { 102 p3 = tool; 103 } else 104 p3 = null; 105 } 106 107 if (p1 == null && p2 == null && p3 == null) { 108 return 0; 109 } 110 if (p1 == null) { 111 if (p2.equals(p3)) { 112 return 1; 113 } else { 114 115 double d1 = new triangle(p2, p3, this.C).area(); 116 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 117 ps[0] = this.C; 118 ps[1] = null; 119 ds[0] = d1; 120 ds[1] = d2; 121 return 2; 122 } 123 } 124 if (p2 == null) { 125 if (p1.equals(p3)) { 126 return 1; 127 } else { 128 129 double d1 = new triangle(p1, p3, this.A).area(); 130 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 131 ps[0] = this.A; 132 ps[1] = null; 133 ds[0] = d1; 134 ds[1] = d2; 135 return 2; 136 } 137 } 138 if (p3 == null) { 139 if (p1.equals(p2)) { 140 return 1; 141 } else { 142 143 double d1 = new triangle(p1, p2, this.B).area(); 144 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 145 ps[0] = this.B; 146 ps[1] = null; 147 ds[0] = d1; 148 ds[1] = d2; 149 return 2; 150 } 151 } 152 153 154 if (p1.equals(p2)) { 155 156 double d1 = new triangle(this.A, this.B, p3).area(); 157 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 158 159 ps[0] = this.A; 160 ps[1] = this.C; 161 ds[0] = d1; 162 ds[1] = d2; 163 164 } 165 if (p1.equals(p3)) { 166 167 double d1 = new triangle(this.A, p2, this.C).area(); 168 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 169 ps[0] = this.C; 170 ps[1] = this.B; 171 ds[0] = d1; 172 ds[1] = d2; 173 } 174 if (p2.equals(p3)) { 175 176 double d1 = new triangle(p1, this.C, this.A).area(); 177 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 178 ps[0] = this.A; 179 ps[1] = this.B; 180 ds[0] = d1; 181 ds[1] = d2; 182 } 183 return 2; 184 } 185 186 }
Triangle类的构造方法需要三个点,属性有三个点A,B,C和三条边AB,BC,AC,方法也同Line类,可以不断丰富完善,boolean isTriangle(Point a, Point b, Point c)三点能否组成一线,double per(),public double area(), public Point core() 返回三角形的周长,面积和重心坐标
接下来设计我们本次要用到的四边形类,其属性有四个点以及四条边,方法可以有很多很多,每个同学也可以玩出不同的花样,比如求面积、周长,与直线的切割方法等:

1 @SuppressWarnings("all") 2 class Quadrangle extends Shape { 3 4 Point A; 5 Point B; 6 Point C; 7 Point D; 8 Line AB; 9 Line BC; 10 Line CD; 11 Line DA; 12 13 public int cutting(Line line, double[] ds, Point[] ps) { 14 15 16 if (this.AB.isOne(line) || this.BC.isOne(line) || this.CD.isOne(line) || this.DA.isOne(line)) { 17 return -1; 18 } 19 double[] ds1 = new double[2]; 20 Point[] ps1 = new Point[2]; 21 double[] ds2 = new double[2]; 22 Point[] ps2 = new Point[2]; 23 triangle t1 = new triangle(this.A, this.B, this.D); 24 triangle t2 = new triangle(this.B, this.C, this.D); 25 int i1 = t1.cutting(line, ds1, ps1); 26 int i2 = t2.cutting(line, ds2, ps2); 27 Line l = new Line(this.B, this.D); 28 Line ll = new Line(this.A, this.C); 29 if (l.isOne(line)) { 30 31 ds[0] = t1.area(); 32 ds[1] = t2.area(); 33 ps[0] = B; 34 ps[1] = D; 35 return 2; 36 } 37 if (ll.isOne(line)) { 38 ds[0] = new triangle(this.A, this.C, this.B).area(); 39 ds[1] = new triangle(this.A, this.C, this.D).area(); 40 ps[0] = A; 41 ps[1] = C; 42 return 2; 43 44 } 45 if (i1 == 0 && i2 == 0) { 46 return 0; 47 } 48 if (i1 == 1 && i2 == 1) { 49 return 1; 50 } 51 if (i1 + i2 == 1) { 52 return 1; 53 } 54 if (i1 == 2) { 55 56 if (i2 == 0) { 57 58 double d1 = ds1[0]; 59 double d2 = ds1[1] + t2.area(); 60 ds[0] = d1; 61 ds[1] = d2; 62 ps[0] = null; 63 ps[1] = null; 64 65 66 } 67 if (i2 == 1) { 68 if (ps1[0].equals(this.A)) { 69 double d1 = ds1[0]; 70 double d2 = ds1[1] + t2.area(); 71 ds[0] = d1; 72 ds[1] = d2; 73 ps[0] = null; 74 ps[1] = null; 75 } else { 76 double d1 = ds1[1]; 77 double d2 = ds1[0] + t2.area(); 78 ds[0] = d1; 79 ds[1] = d2; 80 ps[0] = null; 81 ps[1] = null; 82 } 83 } 84 if (ps1[1] != null && ps2[1] == null) { 85 ps[0] = ps2[0]; 86 ps[1] = null; 87 if (ps1[0].equals(ps2[0])) { 88 double d1 = ds1[0] + ds2[0]; 89 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 90 ds[0] = d1; 91 ds[1] = d2; 92 } else { 93 double d1 = ds1[1] + ds2[0]; 94 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 95 ds[0] = d1; 96 ds[1] = d2; 97 } 98 } 99 //134 233 100 if (ps1[1] == null && ps2[1] != null){ 101 ps[0] = ps1[0]; 102 ps[1] = null; 103 if (ps2[0].equals(ps1[0])) { 104 double d1 = ds1[0] + ds2[0]; 105 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 106 ds[0] = d1; 107 ds[1] = d2; 108 } else { 109 double d1 = ds1[0] + ds2[1]; 110 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 111 ds[0] = d1; 112 ds[1] = d2; 113 } 114 115 } 116 117 //134 234 118 if(ps1[1] == null&&ps2[1] == null){ 119 120 if(ps1[0].equals(this.B)&&ps2[0].equals(this.B)){ 121 ps[0] = B; 122 ps[1] = null; 123 double d1 = ds1[0] + ds2[0]; 124 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 125 ds[0] = d1; 126 ds[1] = d2; 127 } 128 if(ps1[0].equals(this.D)&&ps2[0].equals(this.D)){ 129 ps[0] = D; 130 ps[1] = null; 131 double d1 = ds1[0] + ds2[0]; 132 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 133 ds[0] = d1; 134 ds[1] = d2; 135 } 136 if(ps1[0].equals(this.B)&&ps2[0].equals(this.D)){ 137 ps[0] = B; 138 ps[1] = C; 139 double d1 = ds1[0] + ds2[1]; 140 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 141 ds[0] = d1; 142 ds[1] = d2; 143 } 144 if(ps1[0].equals(this.D)&&ps2[0].equals(this.B)){ 145 ps[0] = A; 146 ps[1] = B; 147 double d1 = ds1[1] + ds2[0]; 148 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 149 ds[0] = d1; 150 ds[1] = d2; 151 } 152 153 } 154 return 2; 155 } 156 if (i2 == 2) { 157 158 if (i1 == 0) { 159 double d1 = ds2[0]; 160 double d2 = ds2[1] + t1.area(); 161 ds[0] = d1; 162 ds[1] = d2; 163 ps[0] = null; 164 ps[1] = null; 165 } 166 if (i1 == 1) { 167 if (ps2[0].equals(this.C)) { 168 double d1 = ds2[0]; 169 double d2 = ds2[1] + t1.area(); 170 ds[0] = d1; 171 ds[1] = d2; 172 ps[0] = null; 173 ps[1] = null; 174 } else { 175 double d1 = ds2[1]; 176 double d2 = ds2[0] + t1.area(); 177 ds[0] = d1; 178 ds[1] = d2; 179 ps[0] = null; 180 ps[1] = null; 181 } 182 } 183 /* 184 if (i1 == 2) { 185 if (ps2[1] == null) { 186 if (ps1[0].equals(ps2[0])) { 187 double d1 = ds1[0] + ds2[0]; 188 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 189 ds[0] = d1; 190 ds[1] = d2; 191 ps[0] = null; 192 ps[1] = null; 193 } else { 194 double d1 = ds1[1] + ds2[0]; 195 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 196 ds[0] = d1; 197 ds[1] = d2; 198 ps[0] = null; 199 ps[1] = null; 200 } 201 } else { 202 if (ps2[0].equals(ps1[0])) { 203 double d1 = ds1[0] + ds2[0]; 204 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 205 ds[0] = d1; 206 ds[1] = d2; 207 ps[0] = null; 208 ps[1] = null; 209 } else { 210 double d1 = ds1[0] + ds2[1]; 211 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 212 ds[0] = d1; 213 ds[1] = d2; 214 ps[0] = null; 215 ps[1] = null; 216 } 217 } 218 219 } 220 */ 221 222 return 2; 223 } 224 return 5; 225 } 226 227 public Quadrangle(Point a, Point b, Point c, Point d) { 228 A = a; 229 B = b; 230 C = c; 231 D = d; 232 AB = new Line(A, B); 233 BC = new Line(B, C); 234 CD = new Line(C, D); 235 DA = new Line(D, A); 236 } 237 238 //0-非四边形,1-普通四边形,2-平行四边形 239 public static int shape1(Point p1, Point p2, Point p3, Point p4) { 240 241 if (p1.equals(p2) || p1.equals(p3) || p1.equals(p4) || p2.equals(p3) || p2.equals(p4) || p3.equals(p4)) { 242 return 0; 243 } 244 245 Line line1 = new Line(p1, p2); 246 if (line1.isOn(p3) || line1.isOn(p4)) { 247 return 0; 248 } 249 250 Line line2 = new Line(p2, p3); 251 if (line2.isOn(p1) || line2.isOn(p4)) { 252 253 return 0; 254 } 255 256 Line line3 = new Line(p3, p4); 257 if (line3.isOn(p1) || line3.isOn(p2)) { 258 return 0; 259 } 260 261 Line line4 = new Line(p1, p4); 262 if (line4.isOn(p2) || line4.isOn(p3)) { 263 return 0; 264 } 265 266 if (!line4.isParallel(line2)) { 267 Point p = line4.point(line2); 268 if (line4.isOnSeg(p) && line2.isOnSeg(p)) 269 return 0; 270 } 271 if (!line1.isParallel(line3)) { 272 Point p = line1.point(line3); 273 if (line1.isOnSeg(p) && line3.isOnSeg(p)) 274 return 0; 275 } 276 if (line1.isParallel(line3) && line1.seglen() == line3.seglen()) 277 return 2; 278 279 280 return 1; 281 } 282 283 //0-不是平行四边形,1-菱形,2-矩形,3-正方形,4-普通平行四边形 284 public static int shape2(Point p1, Point p2, Point p3, Point p4) { 285 286 if (shape1(p1, p2, p3, p4) != 2) { 287 return 0; 288 } 289 290 Line l1 = new Line(p1, p2); 291 Line l2 = new Line(p2, p3); 292 Line l3 = new Line(p3, p4); 293 Line l4 = new Line(p1, p4); 294 Line l5 = new Line(p1, p3); 295 if (l1.seglen() == l2.seglen()) { 296 if (Math.abs(Math.pow(l1.seglen(), 2) + Math.pow(l2.seglen(), 2) - Math.pow(l5.seglen(), 2)) < 0.00001) { 297 298 return 3; 299 } else { 300 301 return 1; 302 } 303 304 305 } 306 307 if (Math.abs(Math.pow(l1.seglen(), 2) + Math.pow(l2.seglen(), 2) - Math.pow(l5.seglen(), 2)) < 0.00001) 308 return 2; 309 else 310 return 4; 311 } 312 313 //判断是否可以组成三角形 314 public static triangle shape3(Point p1, Point p2, Point p3, Point p4) { 315 316 if (p1.equals(p2) && p1.equals(p3) && p1.equals(p4) && p2.equals(p3)) { 317 return null; 318 } 319 320 if (p1.equals(p2)) { 321 if (triangle.isTriangle(p1, p3, p4)) { 322 return new triangle(p1, p3, p4); 323 } 324 } 325 if (p1.equals(p3)) { 326 if (triangle.isTriangle(p1, p2, p4)) { 327 return new triangle(p1, p2, p4); 328 } 329 } 330 if (p1.equals(p4)) { 331 if (triangle.isTriangle(p1, p2, p3)) { 332 return new triangle(p1, p2, p3); 333 } 334 } 335 if (p2.equals(p3)) { 336 if (triangle.isTriangle(p1, p3, p4)) { 337 return new triangle(p1, p3, p4); 338 } 339 } 340 if (p2.equals(p4)) { 341 if (triangle.isTriangle(p1, p3, p4)) { 342 return new triangle(p1, p3, p4); 343 } 344 } 345 if (p3.equals(p4)) { 346 if (triangle.isTriangle(p1, p2, p3)) { 347 return new triangle(p1, p2, p3); 348 } 349 } 350 351 if (!p1.equals(p2)) { 352 if (Line.isColl(p1, p2, p3) && Line.isColl(p1, p2, p4)) 353 return null; 354 } 355 if (!p2.equals(p3)) { 356 if (Line.isColl(p1, p2, p3) && Line.isColl(p3, p2, p4)) 357 return null; 358 } 359 if (!p3.equals(p4)) { 360 if (Line.isColl(p1, p4, p3) && Line.isColl(p3, p2, p4)) 361 return null; 362 } 363 if (!p1.equals(p4)) { 364 if (Line.isColl(p1, p2, p4) && Line.isColl(p1, p3, p4)) 365 return null; 366 } 367 368 369 if (Line.isColl(p1, p2, p3)) { 370 371 Line l = new Line(p1, p3); 372 if (l.isOnSeg(p2)) { 373 return new triangle(p1, p3, p4); 374 } else 375 return null; 376 377 } 378 if (Line.isColl(p1, p2, p4)) { 379 380 Line l = new Line(p2, p4); 381 if (l.isOnSeg(p1)) { 382 return new triangle(p2, p3, p4); 383 } else 384 return null; 385 386 } 387 if (Line.isColl(p2, p3, p4)) { 388 389 Line l = new Line(p2, p4); 390 if (l.isOnSeg(p3)) { 391 return new triangle(p1, p2, p4); 392 } else 393 return null; 394 395 } 396 if (Line.isColl(p1, p3, p4)) { 397 398 Line l = new Line(p1, p3); 399 if (l.isOnSeg(p4)) { 400 return new triangle(p1, p2, p3); 401 } else 402 return null; 403 404 } 405 406 407 return null; 408 } 409 410 411 //是否为凹 412 public boolean isConcave() { 413 414 double d1 = new triangle(A, B, C).area(); 415 double d2 = new triangle(A, D, C).area(); 416 double d3 = new triangle(B, A, D).area(); 417 double d4 = new triangle(B, C, D).area(); 418 if (Math.abs(d1 + d2 - d3 - d4) < 0.00001) 419 return false; 420 else 421 return true; 422 423 } 424 425 public double perimeter() { 426 Line l1 = new Line(A, B); 427 Line l2 = new Line(B, C); 428 Line l3 = new Line(C, D); 429 Line l4 = new Line(D, A); 430 return l1.seglen() + l2.seglen() + l3.seglen() + l4.seglen(); 431 432 } 433 434 public double area() { 435 double d1 = new triangle(A, B, C).area(); 436 double d2 = new triangle(A, D, C).area(); 437 double d3 = new triangle(B, A, D).area(); 438 double d4 = new triangle(B, C, D).area(); 439 double s1 = d1 + d2; 440 double s2 = d3 + d4; 441 if (Math.abs(s1 - s2) < 0.00001) 442 return s1; 443 else { 444 if (s1 < s2) 445 return s1; 446 else 447 return s2; 448 } 449 450 } 451 452 public static double qualArea(Point p1, Point p2, Point p3, Point p4) { 453 454 triangle t = Quadrangle.shape3(p1, p2, p3, p4); 455 if (t == null) 456 return new Quadrangle(p1, p2, p3, p4).area(); 457 else 458 return t.area(); 459 460 } 461 462 463 }
选项一判断四个点能不能组成四边形,原理就是不能出现三、四点共线(重复点也不行)以及非邻边不能有交点:
1 //0-非四边形,1-普通四边形,2-平行四边形 2 public static int shape1(Point p1, Point p2, Point p3, Point p4) { 3 4 if (p1.equals(p2) || p1.equals(p3) || p1.equals(p4) || p2.equals(p3) || p2.equals(p4) || p3.equals(p4)) { 5 return 0; 6 } 7 8 Line line1 = new Line(p1, p2); 9 if (line1.isOn(p3) || line1.isOn(p4)) { 10 return 0; 11 } 12 13 Line line2 = new Line(p2, p3); 14 if (line2.isOn(p1) || line2.isOn(p4)) { 15 16 return 0; 17 } 18 19 Line line3 = new Line(p3, p4); 20 if (line3.isOn(p1) || line3.isOn(p2)) { 21 return 0; 22 } 23 24 Line line4 = new Line(p1, p4); 25 if (line4.isOn(p2) || line4.isOn(p3)) { 26 return 0; 27 } 28 29 if (!line4.isParallel(line2)) { 30 Point p = line4.point(line2); 31 if (line4.isOnSeg(p) && line2.isOnSeg(p)) 32 return 0; 33 } 34 if (!line1.isParallel(line3)) { 35 Point p = line1.point(line3); 36 if (line1.isOnSeg(p) && line3.isOnSeg(p)) 37 return 0; 38 } 39 if (line1.isParallel(line3) && line1.seglen() == line3.seglen()) 40 return 2; 41 42 43 return 1; 44 }
选项二判断是不是菱形、矩形、正方形,优先要通过选项一确定是四边形,然后根据四边的相等情况,以及勾股定理进行判断:
1 //0-不是平行四边形,1-菱形,2-矩形,3-正方形,4-普通平行四边形 2 public static int shape2(Point p1, Point p2, Point p3, Point p4) { 3 4 if (shape1(p1, p2, p3, p4) != 2) { 5 return 0; 6 } 7 8 Line l1 = new Line(p1, p2); 9 Line l2 = new Line(p2, p3); 10 Line l3 = new Line(p3, p4); 11 Line l4 = new Line(p1, p4); 12 Line l5 = new Line(p1, p3); 13 if (l1.seglen() == l2.seglen()) { 14 if (Math.abs(Math.pow(l1.seglen(), 2) + Math.pow(l2.seglen(), 2) - Math.pow(l5.seglen(), 2)) < 0.00001) { 15 16 return 3; 17 } else { 18 19 return 1; 20 } 21 22 23 } 24 25 if (Math.abs(Math.pow(l1.seglen(), 2) + Math.pow(l2.seglen(), 2) - Math.pow(l5.seglen(), 2)) < 0.00001) 26 return 2; 27 else 28 return 4; 29 }
选项三判断四边形凹凸性,原理连接两组对顶点,连线分别和另外两点组成两个三角形,如果两组三角形面积之和相等,则为凸四边形,反之为凹:
1 //是否为凹 2 public boolean isConcave() { 3 4 double d1 = new triangle(A, B, C).area(); 5 double d2 = new triangle(A, D, C).area(); 6 double d3 = new triangle(B, A, D).area(); 7 double d4 = new triangle(B, C, D).area(); 8 if (Math.abs(d1 + d2 - d3 - d4) < 0.00001) 9 return false; 10 else 11 return true; 12 13 }
选项四最为麻烦,直线切割问题,首先进行判断是三角形还是四边形,三角形则调用三角形类之间封装切割方法即可,四边形就切割成两个三角形分别调用、根据返回信息进行判断即可,非常考验同学之前三角形类设计的能力

1 //判断是否可以组成三角形 2 public static triangle shape3(Point p1, Point p2, Point p3, Point p4) { 3 4 if (p1.equals(p2) && p1.equals(p3) && p1.equals(p4) && p2.equals(p3)) { 5 return null; 6 } 7 8 if (p1.equals(p2)) { 9 if (triangle.isTriangle(p1, p3, p4)) { 10 return new triangle(p1, p3, p4); 11 } 12 } 13 if (p1.equals(p3)) { 14 if (triangle.isTriangle(p1, p2, p4)) { 15 return new triangle(p1, p2, p4); 16 } 17 } 18 if (p1.equals(p4)) { 19 if (triangle.isTriangle(p1, p2, p3)) { 20 return new triangle(p1, p2, p3); 21 } 22 } 23 if (p2.equals(p3)) { 24 if (triangle.isTriangle(p1, p3, p4)) { 25 return new triangle(p1, p3, p4); 26 } 27 } 28 if (p2.equals(p4)) { 29 if (triangle.isTriangle(p1, p3, p4)) { 30 return new triangle(p1, p3, p4); 31 } 32 } 33 if (p3.equals(p4)) { 34 if (triangle.isTriangle(p1, p2, p3)) { 35 return new triangle(p1, p2, p3); 36 } 37 } 38 39 if (!p1.equals(p2)) { 40 if (Line.isColl(p1, p2, p3) && Line.isColl(p1, p2, p4)) 41 return null; 42 } 43 if (!p2.equals(p3)) { 44 if (Line.isColl(p1, p2, p3) && Line.isColl(p3, p2, p4)) 45 return null; 46 } 47 if (!p3.equals(p4)) { 48 if (Line.isColl(p1, p4, p3) && Line.isColl(p3, p2, p4)) 49 return null; 50 } 51 if (!p1.equals(p4)) { 52 if (Line.isColl(p1, p2, p4) && Line.isColl(p1, p3, p4)) 53 return null; 54 } 55 56 57 if (Line.isColl(p1, p2, p3)) { 58 59 Line l = new Line(p1, p3); 60 if (l.isOnSeg(p2)) { 61 return new triangle(p1, p3, p4); 62 } else 63 return null; 64 65 } 66 if (Line.isColl(p1, p2, p4)) { 67 68 Line l = new Line(p2, p4); 69 if (l.isOnSeg(p1)) { 70 return new triangle(p2, p3, p4); 71 } else 72 return null; 73 74 } 75 if (Line.isColl(p2, p3, p4)) { 76 77 Line l = new Line(p2, p4); 78 if (l.isOnSeg(p3)) { 79 return new triangle(p1, p2, p4); 80 } else 81 return null; 82 83 } 84 if (Line.isColl(p1, p3, p4)) { 85 86 Line l = new Line(p1, p3); 87 if (l.isOnSeg(p4)) { 88 return new triangle(p1, p2, p3); 89 } else 90 return null; 91 92 } 93 94 95 return null; 96 }

1 public int cutting(Line line, double[] ds, Point[] ps) { 2 if (this.AB.isOne(line) || this.BC.isOne(line) || this.AC.isOne(line)) { 3 4 return -1; 5 } 6 Point p1 = null, p2 = null, p3 = null, tool = null; 7 8 if (this.AB.isParallel(line)) { 9 p1 = null; 10 } else { 11 tool = this.AB.point(line); 12 if (this.AB.isOnSeg(tool)) { 13 p1 = tool; 14 } else 15 p1 = null; 16 } 17 if (this.BC.isParallel(line)) { 18 p2 = null; 19 } else { 20 tool = this.BC.point(line); 21 if (this.BC.isOnSeg(tool)) { 22 p2 = tool; 23 } else 24 p2 = null; 25 } 26 if (this.AC.isParallel(line)) { 27 p3 = null; 28 } else { 29 tool = this.AC.point(line); 30 if (this.AC.isOnSeg(tool)) { 31 p3 = tool; 32 } else 33 p3 = null; 34 } 35 36 if (p1 == null && p2 == null && p3 == null) { 37 return 0; 38 } 39 if (p1 == null) { 40 if (p2.equals(p3)) { 41 return 1; 42 } else { 43 44 double d1 = new triangle(p2, p3, this.C).area(); 45 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 46 ps[0] = this.C; 47 ps[1] = null; 48 ds[0] = d1; 49 ds[1] = d2; 50 return 2; 51 } 52 } 53 if (p2 == null) { 54 if (p1.equals(p3)) { 55 return 1; 56 } else { 57 58 double d1 = new triangle(p1, p3, this.A).area(); 59 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 60 ps[0] = this.A; 61 ps[1] = null; 62 ds[0] = d1; 63 ds[1] = d2; 64 return 2; 65 } 66 } 67 if (p3 == null) { 68 if (p1.equals(p2)) { 69 return 1; 70 } else { 71 72 double d1 = new triangle(p1, p2, this.B).area(); 73 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 74 ps[0] = this.B; 75 ps[1] = null; 76 ds[0] = d1; 77 ds[1] = d2; 78 return 2; 79 } 80 } 81 82 83 if (p1.equals(p2)) { 84 85 double d1 = new triangle(this.A, this.B, p3).area(); 86 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 87 88 ps[0] = this.A; 89 ps[1] = this.C; 90 ds[0] = d1; 91 ds[1] = d2; 92 93 } 94 if (p1.equals(p3)) { 95 96 double d1 = new triangle(this.A, p2, this.C).area(); 97 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 98 ps[0] = this.C; 99 ps[1] = this.B; 100 ds[0] = d1; 101 ds[1] = d2; 102 } 103 if (p2.equals(p3)) { 104 105 double d1 = new triangle(p1, this.C, this.A).area(); 106 double d2 = this.area() - d1; 107 ps[0] = this.A; 108 ps[1] = this.B; 109 ds[0] = d1; 110 ds[1] = d2; 111 } 112 return 2; 113 }
如果是四边形,就切割进行分别调用:
1 Quadrangle quadrangle = new Quadrangle(points[2], points[3], points[4], points[5]); 2 double[] ds = new double[2]; 3 Point[] ps = new Point[2]; 4 int cutting = quadrangle.cutting(line, ds, ps); 5 if (cutting == 0) 6 System.out.println("0"); 7 else if(cutting == 1) 8 System.out.println("1"); 9 else if(cutting == -1) 10 System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines"); 11 else if(cutting == 2){ 12 System.out.print("2 "); 13 print2(ds[0],ds[1]); 14 }
作业五:点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算

用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与五边形有关的计算。 以下五边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。 选项包括: 1:输入五个点坐标,判断是否是五边形,判断结果输出true/false。 2:输入五个点坐标,判断是凹五边形(false)还是凸五边形(true),如果是凸五边形,则再输出五边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若五个点坐标无法构成五边形,输出"not a pentagon" 3:输入七个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后五个点构成一个凸五边形、凸四边形或凸三角形,输出直线与五边形、四边形或三角形相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与多边形形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后五个点不符合五边形输入,若前两点重合,输出"points coincide"。 以上3选项中,若输入的点无法构成多边形,则输出"not a polygon"。输入的五个点坐标可能存在冗余,假设多边形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s: 1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如:x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。 2) 不符合要求的输入:z不与xy都相邻,如:z x y s、x z s y、x s z y 用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与五边形有关的计算。 以下五边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。 选项包括: 4:输入十个点坐标,前、后五个点分别构成一个凸多边形(三角形、四边形、五边形),判断它们两个之间是否存在包含关系(一个多边形有一条或多条边与另一个多边形重合,其他部分都包含在另一个多边形内部,也算包含)。 两者存在六种关系:1、分离(完全无重合点) 2、连接(只有一个点或一条边重合) 3、完全重合 4、被包含(前一个多边形在后一个多边形的内部)5、交错 6、包含(后一个多边形在前一个多边形的内部)。 各种关系的输出格式如下: 1、no overlapping area between the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon and the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon 2、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is connected to the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon 3、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon coincides with the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon 4、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is inside the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon 5、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is interlaced with the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon 6、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon contains the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon 5:输入十个点坐标,前、后五个点分别构成一个凸多边形(三角形、四边形、五边形),输出两个多边形公共区域的面积。注:只考虑每个多边形被另一个多边形分割成最多两个部分的情况,不考虑一个多边形将另一个分割成超过两个区域的情况。 6:输入六个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后五个点所构成的多边形(限定为凸多边形,不考虑凹多边形),的内部(若是五边形输出in the pentagon/outof the pentagon,若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。输入入错存在冗余点要排除,冗余点的判定方法见选项5。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle/on the quadrilateral/on the pentagon"。 以上4、5、6选项输入的五个点坐标可能存在冗余,假设多边形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s: 1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如:x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。 2) 不符合要求的输入:z不与xy都相邻,如:z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
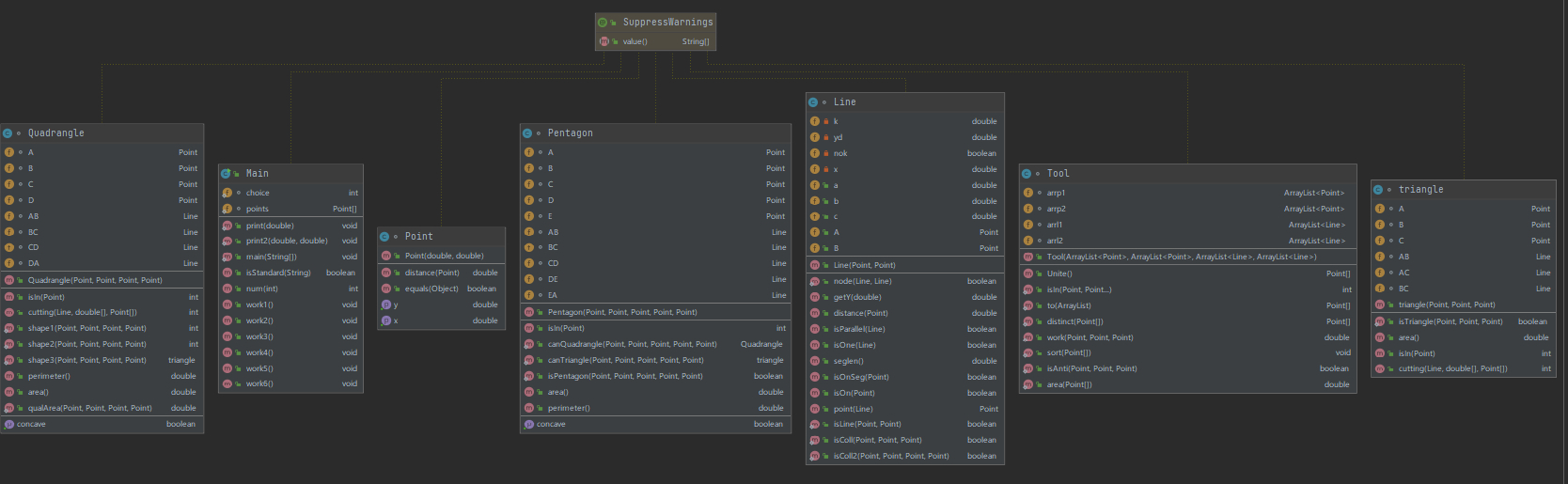
由于选项四五六存在很多重复操作,可以创建一个工具类,进行集合-数组转化、对点进行顺逆时针排序(可以采用极坐标或者向量叉乘的几何含义进行判断),我采用的是向量叉乘

1 @SuppressWarnings("all") 2 class Tool { 3 4 ArrayList<Point> arrp1; 5 ArrayList<Point> arrp2; 6 ArrayList<Line> arrl1; 7 ArrayList<Line> arrl2; 8 9 public Tool(ArrayList<Point> arrp1, ArrayList<Point> arrp2, ArrayList<Line> arrl1, ArrayList<Line> arrl2) { 10 this.arrp1 = arrp1; 11 this.arrp2 = arrp2; 12 this.arrl1 = arrl1; 13 this.arrl2 = arrl2; 14 } 15 16 public Point[] Unite() { 17 ArrayList<Point> arr = new ArrayList<>(); 18 for (int i = 0; i < arrl1.size(); i++) { 19 for (int j = 0; j < arrl2.size(); j++) { 20 if (!arrl1.get(i).isParallel(arrl2.get(j))) { 21 Point t = arrl1.get(i).point(arrl2.get(j)); 22 if (arrl1.get(i).isOnSeg(t) && arrl2.get(j).isOnSeg(t) && Tool.isIn(t, Tool.to(arrp1)) != 0 && Tool.isIn(t, Tool.to(arrp2)) != 0) 23 arr.add(t); 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 for (int i = 0; i < arrp1.size(); i++) { 28 if (Tool.isIn(arrp1.get(i), Tool.to(arrp1)) != 0 && Tool.isIn(arrp1.get(i), Tool.to(arrp2)) != 0) 29 arr.add(arrp1.get(i)); 30 } 31 for (int i = 0; i < arrp2.size(); i++) { 32 if (Tool.isIn(arrp2.get(i), Tool.to(arrp1)) != 0 && Tool.isIn(arrp2.get(i), Tool.to(arrp2)) != 0) 33 arr.add(arrp2.get(i)); 34 } 35 36 return Tool.to(arr); 37 } 38 39 public static int isIn(Point p, Point... x) { 40 int i = 0; 41 if (x.length == 3) 42 i = new triangle(x[0], x[1], x[2]).isIn(p); 43 if (x.length == 4) 44 i = new Quadrangle(x[0], x[1], x[2], x[3]).isIn(p); 45 if (x.length == 5) 46 i = new Pentagon(x[0], x[1], x[2], x[3], x[4]).isIn(p); 47 return i; 48 } 49 50 public static Point[] to(ArrayList arrayList) { 51 Point[] ps = new Point[arrayList.size()]; 52 Object[] objects = arrayList.toArray(); 53 for (int i = 0; i < ps.length; i++) { 54 ps[i] = (Point) objects[i]; 55 } 56 return ps; 57 } 58 59 60 public static Point[] distinct(Point[] ps) { 61 Point[] result = null, t = null; 62 if (ps == null || ps.length == 0) 63 return null; 64 int i = 0; 65 boolean flag = true; 66 result = new Point[i + 1]; 67 result[i] = ps[i]; 68 i++; 69 for (int j = 1; j < ps.length; j++) { 70 flag = true; 71 for (int k = 0; k < j; k++) { 72 if (ps[k].equals(ps[j])) { 73 flag = false; 74 } 75 } 76 if (flag) { 77 t = result; 78 result = new Point[i + 1]; 79 result[i] = ps[j]; 80 i++; 81 for (int k = 0; k < i - 1; k++) { 82 result[k] = t[k]; 83 } 84 } 85 } 86 87 return result; 88 } 89 90 //求叉乘值正负性 91 public static double work(Point p, Point A, Point B) { 92 double d = (A.getX() - p.getX()) * (B.getY() - p.getY()) - (B.getX() - p.getX()) * (A.getY() - p.getY()); 93 return d; 94 } 95 96 public static void sort(Point[] ps) { 97 98 double x = 0, y = 0; 99 for (int i = 0; i < ps.length; i++) { 100 x += ps[i].getX(); 101 y += ps[i].getY(); 102 } 103 x = x / ps.length; 104 y = y / ps.length; 105 Point p = new Point(x, y); 106 Point t = null; 107 for (int i = 0; i < ps.length - 1; i++) { 108 for (int j = 0; j < ps.length - 1 - i; j++) { 109 if (isAnti(p, ps[j], ps[j + 1])) { 110 111 t = ps[j]; 112 ps[j] = ps[j + 1]; 113 ps[j + 1] = t; 114 115 } 116 117 } 118 } 119 120 } 121 122 public static boolean isAnti(Point p, Point A, Point B) { 123 /* 124 if (A.getX() >= 0 && B.getX() < 0) 125 return true; 126 if (A.getX() == 0 && B.getX() == 0) 127 return A.getY() > B.getY(); 128 129 130 */ 131 132 double d = (A.getX() - p.getX()) * (B.getY() - p.getY()) - (B.getX() - p.getX()) * (A.getY() - p.getY()); 133 if (d < 0) 134 return true; 135 if (d > 0) 136 return false; 137 double d1 = A.distance(p); 138 double d2 = B.distance(p); 139 return d1 > d2; 140 141 } 142 143 144 public static double area(Point[] ps) { 145 146 if (ps.length < 3) 147 return 0; 148 int index = 0; 149 Point p1 = ps[index], p2 = ps[index + 1]; 150 double result = 0; 151 while (p2 != ps[ps.length - 1]) { 152 153 result += (p1.getX() * p2.getY()) - (p1.getY() * p2.getX()); 154 155 index++; 156 p1 = ps[index]; 157 p2 = ps[index + 1]; 158 } 159 result += (p1.getX() * p2.getY()) - (p1.getY() * p2.getX()); 160 161 index++; 162 p1 = ps[index]; 163 p2 = ps[0]; 164 result += (p1.getX() * p2.getY()) - (p1.getY() * p2.getX()); 165 return result / 2; 166 167 } 168 169 }
选项一判断是否组成五边形,原理还是不能有若干点共线情况以及非邻边不能有交点进行判断即可。
选项二判断凹凸性,可以使用每次连续读取三点,直至全部读完,三点构建两个向量,又向量叉乘进行判断:
1 //是否为凹 2 public boolean isConcave() { 3 4 double d1 = Tool.work(B, A, C); 5 double d2 = Tool.work(C, B, D); 6 double d3 = Tool.work(D, C, E); 7 double d4 = Tool.work(E, D, A); 8 double d5 = Tool.work(A, E, B); 9 if ((d1 > 0 && d2 > 0 && d3 > 0 && d4 > 0 && d5 > 0) || (d1 < 0 && d2 < 0 && d3 < 0 && d4 < 0 && d5 < 0)) 10 11 return false; 12 else 13 return true; 14 }
选项三直线切割问题,同样先进行判断五个点围成的图形,三角形就调用三角形切割方法,四边形就调用四边形切割方法,五边形就切割成三角形和四边形两部分分别调用即可
1 //五边形情况 2 if (pentagon) { 3 Pentagon pentagon1 = new Pentagon(points[2], points[3], points[4], points[5], points[6]); 4 if (line.isOne(pentagon1.AB) || line.isOne(pentagon1.BC) || line.isOne(pentagon1.CD) || line.isOne(pentagon1.DE) || line.isOne(pentagon1.EA)) { 5 System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines"); 6 System.exit(0); 7 } 8 if (line.isOne(new Line(pentagon1.A, pentagon1.C))) { 9 System.out.print("2 "); 10 print2(new triangle(pentagon1.A, pentagon1.B, pentagon1.C).area(), new Quadrangle(pentagon1.A, pentagon1.C, pentagon1.D, pentagon1.E).area()); 11 System.exit(0); 12 } 13 if (line.isOne(new Line(pentagon1.A, pentagon1.D))) { 14 System.out.print("2 "); 15 print2(new triangle(pentagon1.A, pentagon1.D, pentagon1.E).area(), new Quadrangle(pentagon1.A, pentagon1.B, pentagon1.C, pentagon1.D).area()); 16 System.exit(0); 17 } 18 if (line.isOne(new Line(pentagon1.C, pentagon1.E))) { 19 System.out.print("2 "); 20 print2(new triangle(pentagon1.C, pentagon1.D, pentagon1.E).area(), new Quadrangle(pentagon1.A, pentagon1.B, pentagon1.C, pentagon1.E).area()); 21 System.exit(0); 22 } 23 triangle triangle1 = new triangle(pentagon1.A, pentagon1.B, pentagon1.C); 24 Quadrangle quadrangle1 = new Quadrangle(pentagon1.A, pentagon1.C, pentagon1.D, pentagon1.E); 25 double[] ds1 = new double[2]; 26 double[] ds2 = new double[2]; 27 Point[] ps1 = new Point[2]; 28 Point[] ps2 = new Point[2]; 29 int cutting1 = triangle1.cutting(line, ds1, ps1); 30 int cutting2 = quadrangle1.cutting(line, ds2, ps2); 31 if (cutting1 == 0 && cutting2 == 0) { 32 System.out.println("0"); 33 System.exit(0); 34 } 35 if (cutting1 == 1 && cutting2 == 0) { 36 System.out.println("1"); 37 System.exit(0); 38 } 39 if (cutting2 == 1 && cutting1 == 0) { 40 System.out.println("1"); 41 System.exit(0); 42 } 43 if (cutting1 == 1 && cutting2 == 1) { 44 System.out.println("1"); 45 System.exit(0); 46 } 47 if (cutting1 == 2) { 48 System.out.print("2 "); 49 if (cutting2 == 0) { 50 double d1 = ds1[0]; 51 double d2 = ds1[1] + quadrangle1.area(); 52 print2(d1, d2); 53 System.exit(0); 54 } 55 if (cutting2 == 1) { 56 if (ps1[0].equals(pentagon1.B)) { 57 double d1 = ds1[0]; 58 double d2 = ds1[1] + quadrangle1.area(); 59 print2(d1, d2); 60 System.exit(0); 61 } else { 62 double d1 = ds1[1]; 63 double d2 = ds1[0] + quadrangle1.area(); 64 print2(d1, d2); 65 System.exit(0); 66 } 67 } 68 if (cutting2 == 2) { 69 //133 234 70 if (ps1[1] != null && ps2[1] == null) { 71 if (ps1[0].equals(ps2[0])) { 72 double d1 = ds1[0] + ds2[0]; 73 double d2 = pentagon1.area() - d1; 74 print2(d1, d2); 75 System.exit(0); 76 } else { 77 double d1 = ds1[1] + ds2[0]; 78 double d2 = pentagon1.area() - d1; 79 print2(d1, d2); 80 System.exit(0); 81 } 82 }//133 244 83 else if (ps1[1] != null && ps2[1] != null) { 84 if (ps2[0].equals(ps1[0]) || ps2[1].equals(ps1[0])) { 85 double d1 = ds1[0] + ds2[0]; 86 double d2 = pentagon1.area() - d1; 87 print2(d1, d2); 88 System.exit(0); 89 90 } else { 91 double d1 = ds1[1] + ds2[0]; 92 double d2 = pentagon1.area() - d1; 93 print2(d1, d2); 94 System.exit(0); 95 } 96 97 }//134 234 98 else if (ps1[1] == null && ps2[1] == null) { 99 100 if (ps1[0].equals(ps2[0])) { 101 double d1 = ds1[0] + ds2[0]; 102 double d2 = pentagon1.area() - d1; 103 print2(d1, d2); 104 System.exit(0); 105 } else { 106 double d1 = ds1[1] + ds2[0]; 107 double d2 = pentagon1.area() - d1; 108 print2(d1, d2); 109 System.exit(0); 110 } 111 112 } else { 113 if (ps2[0].equals(ps1[0]) || ps2[1].equals(ps1[0])) { 114 double d1 = ds1[0] + ds2[0]; 115 double d2 = pentagon1.area() - d1; 116 print2(d1, d2); 117 System.exit(0); 118 119 } else { 120 double d1 = ds1[1] + ds2[0]; 121 double d2 = pentagon1.area() - d1; 122 print2(d1, d2); 123 System.exit(0); 124 } 125 126 } 127 128 129 } 130 131 132 } 133 if (cutting2 == 2) { 134 System.out.print("2 "); 135 if (cutting1 == 0) { 136 if (ps2[1] == null) { 137 double d1 = ds2[0]; 138 double d2 = ds2[1] + triangle1.area(); 139 print2(d1, d2); 140 System.exit(0); 141 } else { 142 if (ps2[0].equals(pentagon1.E) || ps2[1].equals(pentagon1.E)) { 143 double d1 = ds2[0]; 144 double d2 = ds2[1] + triangle1.area(); 145 print2(d1, d2); 146 System.exit(0); 147 } else { 148 double d1 = ds2[1]; 149 double d2 = ds2[0] + triangle1.area(); 150 print2(d1, d2); 151 System.exit(0); 152 } 153 } 154 } 155 if (cutting1 == 1) { 156 if (ps2[0].equals(pentagon1.E) || ps2[0].equals(pentagon1.D)) { 157 double d1 = ds2[0]; 158 double d2 = ds2[1] + triangle1.area(); 159 print2(d1, d2); 160 System.exit(0); 161 } else { 162 double d1 = ds2[1]; 163 double d2 = ds2[0] + triangle1.area(); 164 print2(d1, d2); 165 System.exit(0); 166 } 167 } 168 169 170 } 171 172 173 }
选项四五六推荐倒着做,因为六五四是又简到繁,且会用到之前的:
选项六较为简单,可以统一根据面积法进行判断,所求点和多边形每条边组成若干个三角形,每个面积和相加与多边形面积是否相同来进行判断
1 public int isIn(Point p) { 2 3 if (AB.isOnSeg(p) || BC.isOnSeg(p) || CD.isOnSeg(p) || DA.isOnSeg(p)) { 4 return -1; 5 } 6 if (new Line(B, D).isOnSeg(p)) 7 return 1; 8 if (new triangle(A, B, D).isIn(p) == 1 || new triangle(B, C, D).isIn(p) == 1) 9 return 1; 10 return 0; 11 }
选项五将前五个点组成的多边形的每个点放到一个集合里面,每条边放到另一个集合里面,后五个点执行同样的操作,然后求两个边集合所有边的相交情况,如果有交点且在两条线段之内,就保存到unite集合里面,然后遍历两个点集合,如果该点同时存在两个多边形之内,也保存到unite集合里面,然后对unite集合进行去重、顺逆时针排序,利用鞋带定理求得面积即可:

1 public void work5() { 2 3 ArrayList<Point> p1 = new ArrayList<>(); 4 ArrayList<Point> p2 = new ArrayList<>(); 5 ArrayList<Line> l1 = new ArrayList<>(); 6 ArrayList<Line> l2 = new ArrayList<>(); 7 boolean b1 = Pentagon.isPentagon(points[0], points[1], points[2], points[3], points[4]); 8 boolean b2 = Pentagon.isPentagon(points[5], points[6], points[7], points[8], points[9]); 9 triangle t1 = Pentagon.canTriangle(points[0], points[1], points[2], points[3], points[4]); 10 triangle t2 = Pentagon.canTriangle(points[5], points[6], points[7], points[8], points[9]); 11 Quadrangle q1 = Pentagon.canQuadrangle(points[0], points[1], points[2], points[3], points[4]); 12 Quadrangle q2 = Pentagon.canQuadrangle(points[5], points[6], points[7], points[8], points[9]); 13 if (b1) { 14 Pentagon pentagon1 = new Pentagon(points[0], points[1], points[2], points[3], points[4]); 15 p1.add(pentagon1.A); 16 p1.add(pentagon1.B); 17 p1.add(pentagon1.C); 18 p1.add(pentagon1.D); 19 p1.add(pentagon1.E); 20 l1.add(pentagon1.AB); 21 l1.add(pentagon1.BC); 22 l1.add(pentagon1.CD); 23 l1.add(pentagon1.DE); 24 l1.add(pentagon1.EA); 25 } else if (t1 != null) { 26 p1.add(t1.A); 27 p1.add(t1.B); 28 p1.add(t1.C); 29 l1.add(t1.AB); 30 l1.add(t1.BC); 31 l1.add(t1.AC); 32 } else if (q1 != null) { 33 p1.add(q1.A); 34 p1.add(q1.B); 35 p1.add(q1.C); 36 p1.add(q1.D); 37 l1.add(q1.AB); 38 l1.add(q1.BC); 39 l1.add(q1.CD); 40 l1.add(q1.DA); 41 42 } 43 if (b2) { 44 Pentagon pentagon2 = new Pentagon(points[5], points[6], points[7], points[8], points[9]); 45 p2.add(pentagon2.A); 46 p2.add(pentagon2.B); 47 p2.add(pentagon2.C); 48 p2.add(pentagon2.D); 49 p2.add(pentagon2.E); 50 l2.add(pentagon2.AB); 51 l2.add(pentagon2.BC); 52 l2.add(pentagon2.CD); 53 l2.add(pentagon2.DE); 54 l2.add(pentagon2.EA); 55 } else if (t2 != null) { 56 p2.add(t2.A); 57 p2.add(t2.B); 58 p2.add(t2.C); 59 l2.add(t2.AB); 60 l2.add(t2.BC); 61 l2.add(t2.AC); 62 } else if (q2 != null) { 63 p2.add(q2.A); 64 p2.add(q2.B); 65 p2.add(q2.C); 66 p2.add(q2.D); 67 l2.add(q2.AB); 68 l2.add(q2.BC); 69 l2.add(q2.CD); 70 l2.add(q2.DA); 71 } 72 Tool tool = new Tool(p1, p2, l1, l2); 73 Point[] unite = tool.Unite(); 74 unite = Tool.distinct(unite); 75 Tool.sort(unite); 76 double area = Tool.area(unite); 77 print(area); 78 79 }
选项四可以直接用选项五里面经过去重排序之后的unite集合来判断:
如果集合大小为0,就是“分离”;
集合大小为1或者2,就是“连接”;
集合所有点和多边形1和多边形2的点重复,就是“完全重合”;
跟一个多边形的点重复而另一个不等,就是“包含”/“被包含”;
全部都不是就是“交错”;
同时还要记录多边形1和多边形2的形状,输出时要用到:

1 public void work4() { 2 ArrayList<Point> p1 = new ArrayList<>(); 3 ArrayList<Point> p2 = new ArrayList<>(); 4 ArrayList<Line> l1 = new ArrayList<>(); 5 ArrayList<Line> l2 = new ArrayList<>(); 6 boolean b1 = Pentagon.isPentagon(points[0], points[1], points[2], points[3], points[4]); 7 boolean b2 = Pentagon.isPentagon(points[5], points[6], points[7], points[8], points[9]); 8 triangle t1 = Pentagon.canTriangle(points[0], points[1], points[2], points[3], points[4]); 9 triangle t2 = Pentagon.canTriangle(points[5], points[6], points[7], points[8], points[9]); 10 Quadrangle q1 = Pentagon.canQuadrangle(points[0], points[1], points[2], points[3], points[4]); 11 Quadrangle q2 = Pentagon.canQuadrangle(points[5], points[6], points[7], points[8], points[9]); 12 String[] str = {"triangle", "quadrilateral", "pentagon"}; 13 int i1 = 0, i2 = 0; 14 if (b1) { 15 Pentagon pentagon1 = new Pentagon(points[0], points[1], points[2], points[3], points[4]); 16 p1.add(pentagon1.A); 17 p1.add(pentagon1.B); 18 p1.add(pentagon1.C); 19 p1.add(pentagon1.D); 20 p1.add(pentagon1.E); 21 l1.add(pentagon1.AB); 22 l1.add(pentagon1.BC); 23 l1.add(pentagon1.CD); 24 l1.add(pentagon1.DE); 25 l1.add(pentagon1.EA); 26 i1 = 2; 27 } else if (t1 != null) { 28 p1.add(t1.A); 29 p1.add(t1.B); 30 p1.add(t1.C); 31 l1.add(t1.AB); 32 l1.add(t1.BC); 33 l1.add(t1.AC); 34 i1 = 0; 35 } else if (q1 != null) { 36 p1.add(q1.A); 37 p1.add(q1.B); 38 p1.add(q1.C); 39 p1.add(q1.D); 40 l1.add(q1.AB); 41 l1.add(q1.BC); 42 l1.add(q1.CD); 43 l1.add(q1.DA); 44 i1 = 1; 45 } 46 if (b2) { 47 Pentagon pentagon2 = new Pentagon(points[5], points[6], points[7], points[8], points[9]); 48 p2.add(pentagon2.A); 49 p2.add(pentagon2.B); 50 p2.add(pentagon2.C); 51 p2.add(pentagon2.D); 52 p2.add(pentagon2.E); 53 l2.add(pentagon2.AB); 54 l2.add(pentagon2.BC); 55 l2.add(pentagon2.CD); 56 l2.add(pentagon2.DE); 57 l2.add(pentagon2.EA); 58 i2 = 2; 59 } else if (t2 != null) { 60 p2.add(t2.A); 61 p2.add(t2.B); 62 p2.add(t2.C); 63 l2.add(t2.AB); 64 l2.add(t2.BC); 65 l2.add(t2.AC); 66 i2 = 0; 67 } else if (q2 != null) { 68 p2.add(q2.A); 69 p2.add(q2.B); 70 p2.add(q2.C); 71 p2.add(q2.D); 72 l2.add(q2.AB); 73 l2.add(q2.BC); 74 l2.add(q2.CD); 75 l2.add(q2.DA); 76 i2 = 1; 77 } 78 Tool tool = new Tool(p1, p2, l1, l2); 79 Point[] unite = tool.Unite(); 80 unite = Tool.distinct(unite); 81 if (unite == null) { 82 83 System.out.println("no overlapping area between the previous "+str[i1]+" and the following "+str[i2]); 84 System.exit(0); 85 } 86 if(unite.length == 1||unite.length == 2){ 87 88 System.out.println("the previous "+str[i1]+" is connected to the following "+str[i2]); 89 System.exit(0); 90 } 91 boolean f1 = true,f2 = true; 92 ArrayList<Point> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); 93 for (int i = 0; i < unite.length; i++) { 94 arrayList.add(unite[i]); 95 } 96 for (int i = 0; i < p1.size(); i++) { 97 if(Tool.isIn(p1.get(i),Tool.to(arrayList))==0) 98 f1 = false; 99 } 100 for (int i = 0; i < p2.size(); i++) { 101 if(Tool.isIn(p2.get(i),Tool.to(arrayList))==0) 102 f2 = false; 103 } 104 105 // System.out.println("the previous "+str[1]+" coincides with the following "+str[1]); 106 107 if(f1&&f2){ 108 109 System.out.println("the previous "+str[i1]+" coincides with the following "+str[i2]); 110 System.exit(0); 111 } 112 if(f1&&(!f2)){ 113 114 System.out.println("the previous "+str[i1]+" is inside the following "+str[i2]); 115 System.exit(0); 116 } 117 118 if(f2&&(!f1)){ 119 120 System.out.println("the previous "+str[i1]+" contains the following "+str[i2]); 121 System.exit(0); 122 } 123 124 125 126 System.out.println("the previous "+str[i1]+" is interlaced with the following "+str[i2]); 127 System.exit(0); 128 129 130 131 132 }
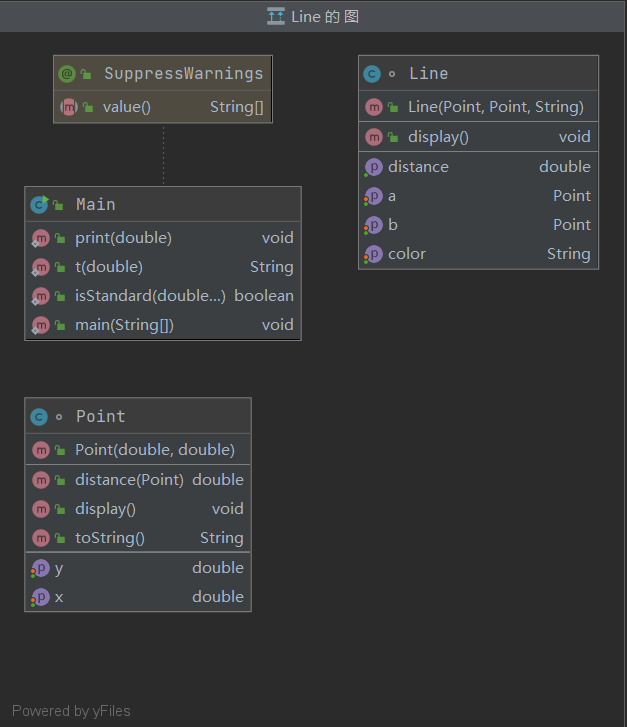
期中考试7-1点与线(类设计):

设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的点Point,私有属性分别为横坐标x与纵坐标y,数据类型均为实型数,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出该坐标点的坐标信息,格式如下:(x,y),数值保留两位小数。为简化题目,其中,坐标点的取值范围设定为(0,200]。若输入有误,系统则直接输出Wrong Format 设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的线Line,私有属性除了标识线段两端的点point1、point2外,还有一个字符串类型的color,用于表示该线段的颜色,同样,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于计算该线段长度的方法getDistance(),还有一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出线段的相关信息,输出格式如下: ``` The line's color is:颜色值 The line's begin point's Coordinate is: (x1,y1) The line's end point's Coordinate is: (x2,y2) The line's length is:长度值 ``` 其中,所有数值均保留两位小数,建议可用String.format("%.2f", data)方法。 输入格式: 分别输入线段的起点横坐标、纵坐标、终点的横坐标、纵坐标以及颜色,中间可用一个或多个空格、tab或者回车分隔。 输出格式: The line's color is:颜色值 The line's begin point's Coordinate is: (x1,y1) The line's end point's Coordinate is: (x2,y2) The line's length is:长度值
本题只需要按照题目的意思一步步走即可,依题意设计Point类和Line类:

1 class Point { 2 3 private double x; 4 private double y; 5 6 public Point(double x, double y) { 7 this.x = x; 8 this.y = y; 9 } 10 11 public double distance(Point point) { 12 13 return Math.sqrt((x - point.x) * (x - point.x) + (y - point.y) * (y - point.y)); 14 } 15 16 public double getX() { 17 return x; 18 } 19 20 public void setX(double x) { 21 this.x = x; 22 } 23 24 public double getY() { 25 return y; 26 } 27 28 public void setY(double y) { 29 this.y = y; 30 } 31 32 public void display() { 33 System.out.println(this); 34 } 35 36 @Override 37 public String toString() { 38 return "(" + Main.t(this.x) + "," + Main.t(this.y) + ")"; 39 } 40 } 41 42 43 class Line { 44 45 private Point A; 46 private Point B; 47 private String color; 48 49 public Line(Point a, Point b, String color) { 50 A = a; 51 B = b; 52 this.color = color; 53 } 54 55 public double getDistance() { 56 return A.distance(B); 57 } 58 59 public void display() { 60 61 System.out.println("The line's color is:" + this.color); 62 System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); 63 System.out.println(this.A); 64 System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); 65 System.out.println(this.B); 66 System.out.print("The line's length is:"); 67 Main.print(this.getDistance()); 68 } 69 70 public Point getA() { 71 return A; 72 } 73 74 public void setA(Point a) { 75 A = a; 76 } 77 78 public Point getB() { 79 return B; 80 } 81 82 public void setB(Point b) { 83 B = b; 84 } 85 86 public String getColor() { 87 return color; 88 } 89 90 public void setColor(String color) { 91 this.color = color; 92 } 93 }
主程序里只需要进行读取数据,并判断数据是否,然后构建Line对象调用display方法即可。我使用isStandard方法(可变参数)来判断传进去的各个数据是否有不合理的数据:
1 public static boolean isStandard(double... doubles) { 2 3 for (int i = 0; i < doubles.length; i++) { 4 if (doubles[i] <= 0 || doubles[i] > 200) 5 return false; 6 } 7 return true; 8 }
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 double x1 = 0, y1 = 0, x2 = 0, y2 = 0; 4 String str = ""; 5 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); 6 x1 = scanner.nextDouble(); 7 y1 = scanner.nextDouble(); 8 x2 = scanner.nextDouble(); 9 y2 = scanner.nextDouble(); 10 str = scanner.next(); 11 if (!isStandard(x1, y1, x2, y2)) { 12 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 13 System.exit(0); 14 } 15 Line line = new Line(new Point(x1, y1), new Point(x2, y2), str); 16 line.display(); 17 18 19 }
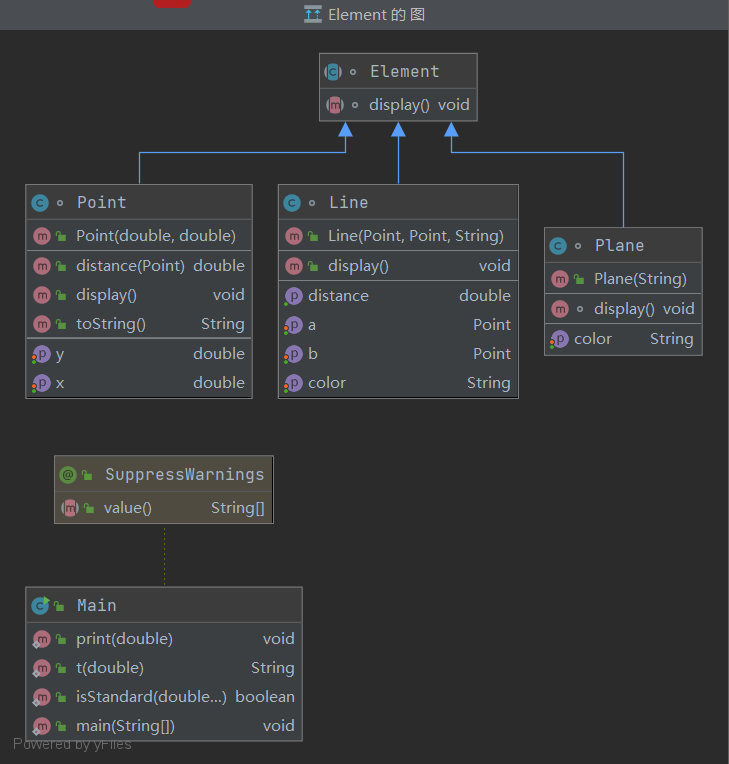
期中考试7-2 点线面问题重构(继承与多态)

在“点与线(类设计)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,以实现继承与多态的技术性需求。 对题目中的点Point类和线Line类进行进一步抽象,定义一个两个类的共同父类Element(抽象类),将display()方法在该方法中进行声明(抽象方法),将Point类和Line类作为该类的子类。 再定义一个Element类的子类面Plane,该类只有一个私有属性颜色color,除了构造方法和属性的getter、setter方法外,display()方法用于输出面的颜色,输出格式如下:The Plane's color is:颜色 在主方法内,定义两个Point(线段的起点和终点)对象、一个Line对象和一个Plane对象,依次从键盘输入两个Point对象的起点、终点坐标和颜色值(Line对象和Plane对象颜色相同),然后定义一个Element类的引用,分别使用该引用调用以上四个对象的display()方法,从而实现多态特性。示例代码如下: element = p1;//起点Point element.display(); element = p2;//终点Point element.display(); element = line;//线段 element.display(); element = plane;//面 element.display(); 输入格式: 分别输入线段的起点横坐标、纵坐标、终点的横坐标、纵坐标以及颜色,中间可用一个或多个空格、tab或者回车分隔。 输出格式: (x1,y1) (x2,y2) The line's color is:颜色值 The line's begin point's Coordinate is: (x1,y1) The line's end point's Coordinate is: (x2,y2) The line's length is:长度值 The Plane's color is:颜色值
同样,依题意设计Element抽象类,并设计Plane类,和之前的点线类都继承Element类:
1 abstract class Element { 2 abstract void display(); 3 }
主程序进行读取数据、构建对象、调用display方法即可:
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 double x1 = 0, y1 = 0, x2 = 0, y2 = 0; 4 String str = ""; 5 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); 6 x1 = scanner.nextDouble(); 7 y1 = scanner.nextDouble(); 8 x2 = scanner.nextDouble(); 9 y2 = scanner.nextDouble(); 10 str = scanner.next(); 11 if (!isStandard(x1, y1, x2, y2)) { 12 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 13 System.exit(0); 14 } 15 Point p1 = new Point(x1, y1); 16 Point p2 = new Point(x2, y2); 17 Plane plane = new Plane(str); 18 Line line = new Line(p1, p2, str); 19 Element element = null; 20 element = p1;//起点Point 21 element.display(); 22 23 element = p2;//终点Point 24 element.display(); 25 26 element = line;//线段 27 element.display(); 28 29 element = plane;//面 30 element.display(); 31 32 33 34 }
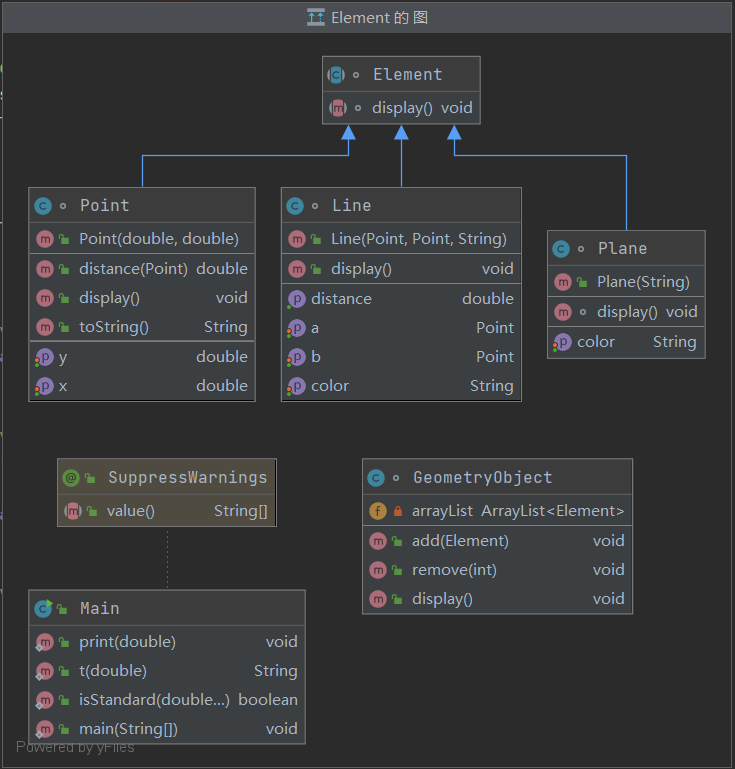
7-3 点线面问题再重构(容器类)

在“点与线(继承与多态)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,增加容器类保存点、线、面对象,并对该容器进行相应增、删、遍历操作。 在原有类设计的基础上,增加一个GeometryObject容器类,其属性为ArrayList<Element>类型的对象(若不了解泛型,可以不使用<Element>) 增加该类的add()方法及remove(int index)方法,其功能分别为向容器中增加对象及删除第index - 1(ArrayList中index>=0)个对象 在主方法中,用户循环输入要进行的操作(choice∈[0,4]),其含义如下: 1:向容器中增加Point对象 2:向容器中增加Line对象 3:向容器中增加Plane对象 4:删除容器中第index - 1个数据,若index数据非法,则无视此操作 0:输入结束 输入格式: switch(choice) { case 1://insert Point object into list 输入“点”对象的x,y值 break; case 2://insert Line object into list 输入“线”对象两个端点的x,y值 break; case 3://insert Plane object into list 输入“面”对象的颜色值 break; case 4://delete index - 1 object from list 输入要删除的对象位置(从1开始) ... } 输出格式: Point、Line、Plane的输出参考题目2 删除对象时,若输入的index超出合法范围,程序自动忽略该操作
在第二题的基础上再设计GeometryObject类,同样参照题目的提示即可,主程序进行读取数据、构建对象、调用display方法即可:
1 class GeometryObject { 2 3 private ArrayList<Element> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); 4 5 public void add(Element element) { 6 arrayList.add(element); 7 } 8 9 public void remove(int index) { 10 if (index<=0||index>arrayList.size()) 11 return; 12 arrayList.remove(index - 1); 13 } 14 15 public void display(){ 16 for (Element element : arrayList) { 17 element.display(); 18 } 19 20 } 21 22 }

1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 4 double x1 = 0, y1 = 0, x2 = 0, y2 = 0; 5 String str = ""; 6 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); 7 GeometryObject geometryObject = new GeometryObject(); 8 9 10 Point p1 = null, p2 = null; 11 Plane plane = null; 12 Line line = null; 13 14 int choice = scanner.nextInt(); 15 while (choice != 0) { 16 switch (choice) { 17 case 1://insert Point object into list 18 x1 = scanner.nextDouble(); 19 y1 = scanner.nextDouble(); 20 if (!isStandard(x1, y1)) { 21 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 22 System.exit(0); 23 } 24 p1 = new Point(x1, y1); 25 geometryObject.add(p1); 26 break; 27 case 2://insert Line object into list 28 x1 = scanner.nextDouble(); 29 y1 = scanner.nextDouble(); 30 x2 = scanner.nextDouble(); 31 y2 = scanner.nextDouble(); 32 if (!isStandard(x1, y1, x2, y2)) { 33 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 34 System.exit(0); 35 } 36 str = scanner.next(); 37 p1 = new Point(x1, y1); 38 p2 = new Point(x2, y2); 39 line = new Line(p1, p2, str); 40 geometryObject.add(line); 41 break; 42 case 3://insert Plane object into list 43 str = scanner.next(); 44 plane = new Plane(str); 45 geometryObject.add(plane); 46 break; 47 case 4://delete index - 1 object from list 48 int index = scanner.nextInt(); 49 geometryObject.remove(index); 50 51 } 52 choice = scanner.nextInt(); 53 } 54 55 geometryObject.display(); 56 57 58 }
三、踩坑心得
-
- 1.作业四:7-2前三个选项的输出有优先级,当不能组成四边形时输出“not a quadrilateral”,有重复点输出“points coincide”,可有重复点不然无法组成四边形,经测试应该输出“not a quadrilateral”而不是另一个,这一点很坑。还有选项四考虑四个点可以组成四边形的情况时,题目的描述很难理解,而且应该先进行去重,我自己在做的时候就没太读懂,没有先进行去重导致错误。
- 2.作业五:“多边形系列”题阴间的地方在于测试点很多很多,本题五边形可以说达到了顶点,而且还要调用之前的点、线、三角形、四边形类,非常考验对之前类的设计,可以说容易出错的地方极多极多,比如少考虑了什么特殊情况,又或者是之前的四个类有什么没有发现的bug(这种情况是最难发现的,因为你一遍都会在本次的设计中去找寻错误,而很少去想之前的是不是出了问题),可以说及其考验设计能力、耐心、细心度、找寻错误的能力,可能踩的小坑数不胜数,每个人遇到的情况也不完全一样……总之,在遇到这类“大型”题目的时候,一定要静下心来,找寻各个需求的共同点,多去包装类,每个类都要进行多次验证确保无误,一个一个选项攻破,切不可心急!!!
- 3.期中考试:考试内容较为简单,基本没什么坑,很直白都,只要理解了多态的使用,就可以很顺利的做出来
四、改进建议
作业四和作业五作为“多边形”系列最复杂的两道题,会调用到很多之前包装过的类的方法,而之前在设计类的时候,可能没想过后续还会用到,从而设计的不符合逻辑,很难后续调 用,可以对之前的Point、Line、triangle类进行重构,把无用的方法舍去,把有效的方法进一步重构的更合理,更统一,才能在调用方法的时候不至于在这些基本方面而犯迷糊,而把工作 重心放在如何解决问题本身上。
五、心得体会
1.如果有需要设计多个类来解决问题的时候,一定要对每一个类多次测试验证,把错误率降到最低,循序渐进,这样也能尽量避免盲目找寻bug的情况。
2.要做到深刻理解面向对象的思想,永远都要先想着工作由谁来做,而不是怎么去做,这样设计出的程序结构会更加明朗。
3.通过这几次的PTA大作业,最大的感受就是个人的能力是有限的,有时候自己实在找不到自己漏掉了什么情况,一定要找同学帮忙,同时学习别人的算法思路,看看是否比自己的简便。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号