二维凸包算法学习笔记
开始补一些算几的东西。
定义引入
凸包到底是个什么东西呢?
在一个实数向量空间V中,对于给定集合X,所有包含X的凸集的交集S被称为X的凸包。X的凸包可以用X内所有点(X1,...Xn)的凸组合来构造.
——摘自百度百科
有没有整个人都mengbi了
对于二维凸包,有一个很形象的描述:
平面上有若干颗钉子,现在绷一圈橡皮筋把所有的钉子都围住,松手之后橡皮筋的形状就是凸包。
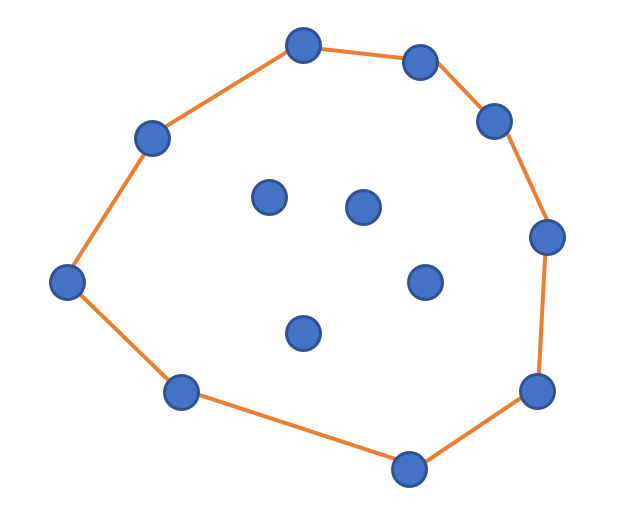
如图的橙色线段是这个点集的凸包。
先来看一道例题:
题意是要求凸包的长度。先把点用结构体存一下,注意读入的时候不要用读优!不要用读优!不要用读优!
重要的事情说三遍都不够。调了一个小时的血泪史
当然如果你写了小数读优当我没说
我们的主要思想是,类似斜率优化,先找下凸壳,再找上凸壳,最后拼起来就是凸包了。
我们先定义几个待会儿会用的函数:
-
斜率比较
inline bool slope_judge (node a, node b, node c) { return (a.y - b.y) * (b.x - c.x) < (a.x - b.x) * (b.y - c.y); }其中\(b\)点因为找凸包的时候要用两遍,就写一个了
这个函数用来比较直线\(AB\)与直线\(BC\)的斜率,如果\(k_{AB}<k_{BC}\)则返回真,否则返回假
乘在一起是为了防止被卡精
-
两点之间距离
inline double dis(node a, node b) { return sqrt((b.y - a.y) * (b.y - a.y) + (b.x - a.x) * (b.x - a.x)); }这个暂时没想到可以防掉精的办法……
准备工作做好了,第一步是排个序。
因为题目并不一定有序给出点,所以我们先把点按\(x\)坐标为第一关键字,\(y\)坐标为第二关键字排序:
inline bool cmp(node a, node b) {
return a.x != b.x ? a.x < b.x : a.y < b.y;
}
sort(Point + 1, Point + n + 1, cmp)
我们开个栈维护一下。这里我们先找下凸壳。
什么时候这个点可以被丢掉呢?我们先看一张图:
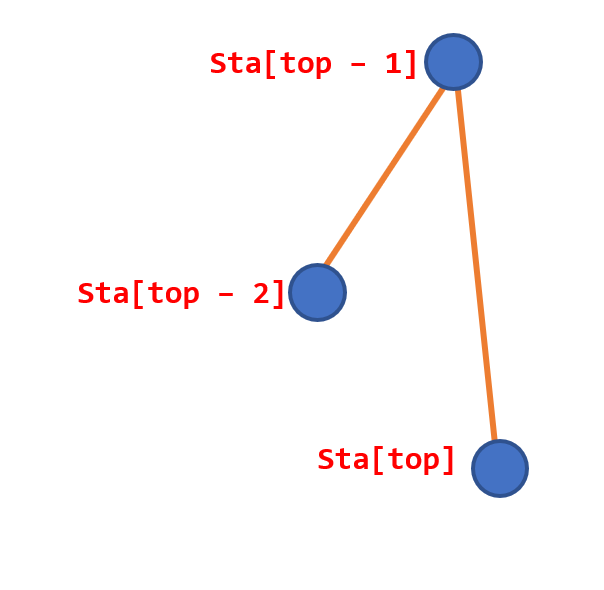
当我们找下凸壳的时候,很显然这个时候应该丢掉\(Sta[top - 1]\)这个点了(可以被\(Sta[top - 2]\)到\(Sta[top]\)的线段框住)
那么可以丢掉一个点的充要条件到底是什么呢?
我们先从成品图来考虑(往上翻翻第一幅图)可以发现整个下凸壳的线段斜率是单调递增的。这是因为如果有上图那样的情况出现,则凹进去那个点一定能被另外两个点的连线框在里面。所以我们维护一个斜率单调的栈,每次遇到不单调的情况就弹出栈内元素,用新的点来替换,直到达到单调或还剩下两个点。
看一下代码:
for (register int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sta[++cnt].x = Point[i].x, sta[cnt].y = Point[i].y;
while (cnt >= 3 && slope_judge(sta[cnt - 2], sta[cnt - 1], sta[cnt])) {
sta[cnt - 1] = sta[cnt], --cnt;
}
}
这样做一遍之后得到的是一个成品的下凸壳。
统计一下答案
for (register int i = 1; i <= cnt - 1; i++) ans += dis(sta[i], sta[i + 1]);
然后我们反过来做一遍就是一个上凸壳了~上凸壳相反,维护的是一个斜率单调递减的单调栈。
注意找上凸壳之前\(sta\)数组要清空,栈顶指针\(cnt\)要置零。
看一下完整代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define N (10000 + 5)
#define INF (1000000000 + 9)
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int cnt = 0, f = 1; char c = getchar();
while (!isdigit(c)) {if (c == '-') f = -f; c = getchar();}
while (isdigit(c)) {cnt = (cnt << 3) + (cnt << 1) + c - '0'; c = getchar();}
return cnt * f;
}
int n, cnt;
struct node{
double x, y;
}Point[N], sta[N];
double ans;
inline bool cmp(node a, node b) {
return a.x != b.x ? a.x < b.x : a.y < b.y;
}
inline bool slope_judge (node a, node b, node c) {
return (a.y - b.y) * (b.x - c.x) < (a.x - b.x) * (b.y - c.y);
}
inline double dis(node a, node b) {
return sqrt((b.y - a.y) * (b.y - a.y) + (b.x - a.x) * (b.x - a.x));
}
int main() {
n = read();
for (register int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%lf%lf", &Point[i].x, &Point[i].y);
sort(Point + 1, Point + n + 1, cmp);
for (register int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sta[++cnt].x = Point[i].x, sta[cnt].y = Point[i].y;
while (cnt >= 3 && slope_judge(sta[cnt - 2], sta[cnt - 1], sta[cnt])) {
sta[cnt - 1] = sta[cnt], --cnt;
}
}
for (register int i = 1; i <= cnt - 1; i++) ans += dis(sta[i], sta[i + 1]);
cnt = 0;
memset(sta, 0, sizeof(sta));
for (register int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sta[++cnt].x = Point[i].x, sta[cnt].y = Point[i].y;
while (cnt >= 3 && !slope_judge(sta[cnt - 2], sta[cnt - 1], sta[cnt])) {
sta[cnt - 1] = sta[cnt], --cnt;
}
}
for (register int i = 1; i <= cnt - 1; i++) ans += dis(sta[i], sta[i + 1]);
printf("%.2f", ans);
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号