mlp房价预测
跟着李沐的动手学深度学习,跟着写了一遍房价预测的处理和预测,加了一些注释,同时稍微改动了一些地方,把线性回归改成了mlp
由于数据集比较小而且没有缺失值,这里也没有去做特征工程,如果特征量比较多的话,直接用pd.dummies()会出现很多无用特征,所以在特征比较多且数据量大的情况下还是要先做特征工程,删去一些特征
之后有空再去做kaggle上的比赛
import hashlib
import os
import tarfile
import zipfile
import requests
DATA_HUB = dict()
DATA_URL = 'http://d2l-data.s3-accelerate.amazonaws.com/'
def download(name, cache_dir = os.path.join('..', 'data')):
"""下载一个DATA_HUB中的文件,返回本地文件名。"""
assert name in DATA_HUB, f"{name} 不存在于 {DATA_HUB}."
url, sha1_hash = DATA_HUB[name]
os.makedirs(cache_dir, exist_ok=True)
fname = os.path.join(cache_dir, url.split('/')[-1])
if os.path.exists(fname):
sha1 = hashlib.sha1()
with open(fname, 'rb') as f:
while True:
data = f.read(1048576)
if not data:
break
sha1.update(data)
if sha1.hexdigest() == sha1_hash:
return fname
print(f'正在从{url}下载{fname}...')
r = requests.get(url, stream=True, verify=True)
with open(fname, 'wb') as f:
f.write(r.content)
return fname
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import torch
from torch import nn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# from d2l import torch as d2l
from torch.utils import data
DATA_HUB['kaggle_house_train'] = (
DATA_URL + 'kaggle_house_pred_train.csv',
'585e9cc93e70b39160e7921475f9bcd7d31219ce')
DATA_HUB['kaggle_house_test'] = (
DATA_URL + 'kaggle_house_pred_test.csv',
'fa19780a7b011d9b009e8bff8e99922a8ee2eb90')
train_data = pd.read_csv(download('kaggle_house_train'))
test_data = pd.read_csv(download('kaggle_house_test'))
print(train_data.shape)
print(test_data.shape)
print(train_data.iloc[:4,[0,1,2,-3,-2,-1]])
print(test_data.iloc[:4,[0,1,2,-3,-2,-1]])
# 把训练集+测试集的特征放到一起,训练集的第0列是ID要去除,最后一列是标签
all_features = pd.concat((train_data.iloc[:, 1:-1], test_data.iloc[:, 1:]), axis = 0)
print(all_features.shape)
# 找出所有数值列
numeric_features = all_features.dtypes[all_features.dtypes != 'object'].index
# 对数值列用非nan值的均值填充nan
all_features[numeric_features] = all_features[numeric_features].apply(
lambda x : x.fillna( value = x[[y is not np.nan for y in x]].mean() ) )
# 标准化所有数值列,变成均值为0,方差为1
all_features[numeric_features] = all_features[numeric_features].apply(
lambda x : (x - x.mean()) / x.std())
# 用OneHot编码替换离散值
all_features = pd.get_dummies(all_features, dummy_na = True)
print(all_features.shape)
# 转化成torch.tensor类型
n_train = train_data.shape[0]
train_features = torch.tensor(all_features[:n_train].values,
dtype = torch.float32)
test_features = torch.tensor(all_features[n_train:].values,
dtype = torch.float32)
train_labels = torch.tensor(train_data.SalePrice.values.reshape(-1,1),
dtype = torch.float32)
# 定义训练用的损失函数
loss = nn.MSELoss()
# 输入特征数
in_features = train_features.shape[1]
# 线性回归模型
# def get_net():
# net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(in_features, 1))
# return net
# mlp
def get_net():
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(in_features, 256), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(0.5), nn.Linear(256, 1))
# net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(in_features, 1))
return net
# y的值比较大,所以都先取一个log,缩小范围,再用均方根误差
def log_rmse(net, features, labels):
# torch.clamp(input, min, max, out=None) → Tensor
# 将输入input张量每个元素的夹紧到区间 [min,max],并返回结果到一个新张量。
clipped_preds = torch.clamp(net(features), 1, float('inf'))
rmse = torch.sqrt(loss(torch.log(clipped_preds), torch.log(labels)))
return rmse.item()
# 训练函数
def train(net, train_features, train_labels, test_features, test_labels,
num_epochs, learning_rate, weight_decay, batch_size):
# 数据迭代器,用于每次得到随机的一组batch
train_iter = data.DataLoader(dataset = data.TensorDataset(train_features, train_labels),
batch_size = batch_size,
shuffle = True,
num_workers = 4,
drop_last = True)
# 设置优化器, 这里用了Adam
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr = learning_rate,
weight_decay = weight_decay)
# 保存每一轮迭代之后的损失
train_ls, test_ls = [], []
# num_epochs轮训练
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# 变成train模式
net.train()
for X, y in train_iter:
optimizer.zero_grad()
l = loss(net(X), y)
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 变成eval模式
net.eval()
train_ls.append(log_rmse(net, train_features, train_labels))
if test_labels is not None:
test_ls.append(log_rmse(net, test_features, test_labels))
return train_ls, test_ls
# k折交叉验证,训练数据在第i折,X: 特征, y: 标签
def get_k_fold_data(k, i, X, y):
# 要保证k>1
assert k > 1
fold_size = X.shape[0] // k
X_train, y_train = None, None
for j in range(k):
# slice用于获取一个切片对象 https://m.runoob.com/python/python-func-slice.html
idx = slice(j * fold_size, (j + 1) * fold_size)
X_part, y_part = X[idx,:], y[idx]
if j == i:
X_valid, y_valid = X_part, y_part
elif X_train is None:
X_train, y_train = X_part, y_part
else:
X_train = torch.cat([X_train, X_part], 0)
y_train = torch.cat([y_train, y_part], 0)
return X_train, y_train, X_valid, y_valid
# k折交叉验证
def k_fold(k, X_train, y_train, num_epochs, learning_rate, weight_decay, batch_size):
# k折交叉验证的平均训练集损失和验证集损失
train_l_sum, valid_l_sum = 0, 0
for i in range(k):
data = get_k_fold_data(k, i, X_train, y_train)
net = get_net()
# *data用于把data解包成X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test
train_ls, valid_ls = train(net, *data, num_epochs, learning_rate, weight_decay, batch_size)
train_l_sum += train_ls[-1]
valid_l_sum += valid_ls[-1]
if i == 0:
plt.figure()
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.ylabel('rmse')
plt.xlim([1, num_epochs])
plt.plot(list(range(1,num_epochs + 1)), train_ls, label = 'train')
plt.yscale('log')
plt.plot(list(range(1,num_epochs + 1)), valid_ls, label = 'valid')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
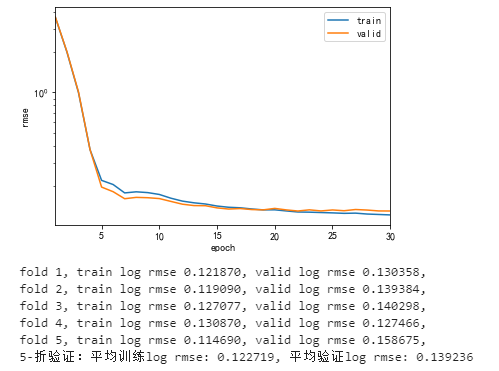
print(f'fold {i+1}, train log rmse {float(train_ls[-1]):f}, valid log rmse {float(valid_ls[-1]):f}, ')
# 取平均损失
return train_l_sum / k, valid_l_sum / k
k, num_epochs, lr, weight_decay, batch_size = 5, 30, 0.05, 0.3, 64
train_l, valid_l = k_fold(k, train_features, train_labels, num_epochs, lr, weight_decay, batch_size)
print(f'{k}-折验证:平均训练log rmse: {float(train_l):f}, 平均验证log rmse: {float(valid_l):f}')
def train_and_pred(train_features, test_features, train_labels, test_data,
num_epochs, lr, weight_decay, batch_size):
net = get_net()
train_ls, _ = train(net, train_features, train_labels, None, None,
num_epochs, lr, weight_decay, batch_size)
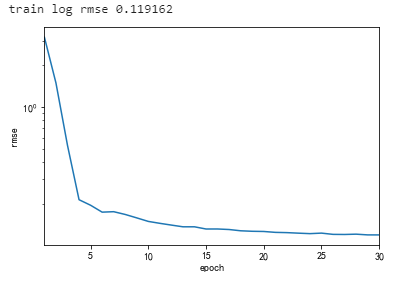
print(f'train log rmse {float(train_ls[-1]):f}')
plt.figure()
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.ylabel('rmse')
plt.xlim([1, num_epochs])
plt.plot(list(range(1,num_epochs + 1)), train_ls)
plt.yscale('log')
plt.show()
# 转换成eval模式
net.eval()
preds = net(test_features).detach().numpy()
test_data['SalePrice'] = pd.Series(preds.reshape(1,-1)[0])
submission = pd.concat([test_data['Id'], test_data['SalePrice']], axis = 1)
submission.to_csv('submission.csv', index = False)
train_and_pred(train_features, test_features, train_labels, test_data, num_epochs, lr, weight_decay, batch_size)
k折交叉验证时的误差:
最后训练得到的网络的误差:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号