c++ 2.0 总结
目录
前言
一些转眼就忘但是对于 c++ 面向对象的理解没有什么太大影响的东西就暂时不再记录了, 比如 const 的 N 种用法, 只会在代码中简单使用而不记录教科书式的答案
吊炸天
class 内存分配与释放
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
class Person {
public:
Person() {
cout << "person constructor" << endl;
}
~Person()
{
cout << "person destructor" << endl;
}
void sayHello()
{
cout << "person say hello" << endl;
}
};
static void f1()
{
cout << "不用指针:" << endl;
auto p = Person();
}
static void f2() {
cout << "new/delete:" << endl;
auto p = new Person();
delete p;
}
static void f3() {
cout << "unique_ptr:" << endl;
auto p = make_unique<Person>();
}
static void f5(const shared_ptr<Person> & p) {
p->sayHello();
}
static void f4()
{
cout << "shared_ptr 传参:" << endl;
auto p = make_shared<Person>();
f5(p);
p->sayHello();
}
static void f6(const unique_ptr<Person>& p) {
p->sayHello();
}
static void f5() {
cout << "unique_ptr 传参:" << endl;
auto p = make_unique<Person>();
f6(p);
p->sayHello();
}
int main()
{
f1();
cout << "================================" << std::endl;
f2();
cout << "================================" << std::endl;
f3();
cout << "================================" << std::endl;
f4();
cout << "================================" << std::endl;
f5();
return 0;
}
输出
不用指针:
person constructor
person destructor
================================
new/delete:
person constructor
person destructor
================================
unique_ptr:
person constructor
person destructor
================================
shared_ptr 传参:
person constructor
person say hello
person say hello
person destructor
================================
unique_ptr 传参:
person constructor
person say hello
person say hello
person destructor
类的创建与使用
默认构造函数的陷阱
公开课】第02讲:RAII与智能指针
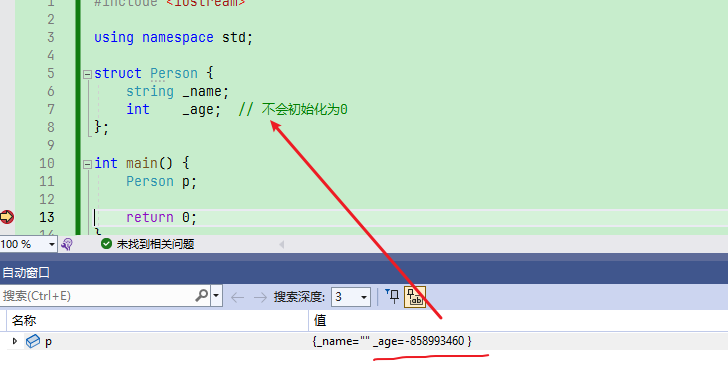
默认构造函数并不会把字段初始化为0
- int, float, double 等基础类型
void*,Object*等指针类型- 完全由这些类型组成的类
struct Person{
string _name;
int _age; // 不会初始化为0
};
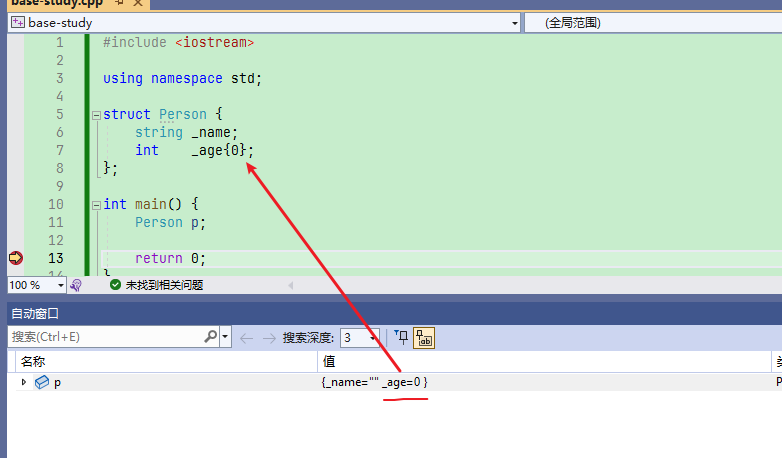
可以手动指定
struct Person{
string _name;
int _age{0};
};
拷贝构造与赋值函数
一个使用拷贝构造和赋值函数的例子
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct Vec3 {
Vec3(float x, float y, float z) : x(x), y(y), z(y) {}
float x;
float y;
float z;
};
int main() {
auto v1 = Vec3(1, 1, 1);
// 拷贝构造
auto v2 = Vec3(v1);
auto v3 = v1;
// 赋值函数
auto v4 = Vec3(1, 1, 1);
v4 = v1;
v1.x = 11;
v2.x = 12;
v3.x = 13;
v4.x = 14;
cout << v1.x << endl; // 11
cout << v2.x << endl; // 12
cout << v3.x << endl; // 13
cout << v4.x << endl; // 14
return 0;
}
自定义拷贝构造和赋值函数
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct Vec3 {
Vec3(float x, float y, float z) : x(x), y(y), z(y) {}
Vec3(const Vec3& v) {
cout << "拷贝构造" << endl;
x = v.x;
y = v.y;
z = v.z;
}
Vec3& operator=(const Vec3& v) {
if (this == &v) {
return *this;
}
cout << "赋值函数" << endl;
x = v.x;
y = v.y;
z = v.z;
return *this;
}
float x;
float y;
float z;
};
int main() {
auto v1 = Vec3(1, 1, 1);
auto v2 = Vec3(v1); // 调用 拷贝构造
auto v3 = v1; // 这个也是调用 拷贝构造
auto v4 = Vec3(1, 1, 1);
v4 = v1; // 这个是调用 赋值函数
return 0;
}
禁用拷贝构造和赋值函数
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct Vec3 {
Vec3(float x, float y, float z) : x(x), y(y), z(y) {}
// 禁用拷贝构造
Vec3(const Vec3&) = delete;
// 禁用赋值函数
Vec3& operator=(const Vec3&) = delete;
float x;
float y;
float z;
};
int main() {
auto v1 = Vec3(1, 1, 1);
auto v4 = Vec3(1, 1, 1);
// 如下代码都报错
auto v2 = Vec3(v1);
auto v3 = v1;
v4 = v1;
return 0;
}
移动与 std::move
总结如下:
std::move是为性能而生- 左值可以赋值,右值不可以赋值
- 尽量给类添加移动构造和移动赋值函数,而减少拷贝构造和拷贝赋值的消耗。 移动构造,移动赋值要加上
noexcept,用于通知标准库不抛出异常
所以以后得 vector 就应该这样用了
string str = "Hello";//这里假设我们只需要将str的内容放到vector中,完成以后永远都不需要再用到str
vector<string> v;
//调用常规的拷贝构造函数,新建字符数组,拷贝数据
v.push_back(str);
cout << "After copy, str is :" << str << endl;
//先把str转为右值引用,然后调用移动构造函数转交所有权
v.push_back(move(str)); // 重点
拷贝与移动经验
- 如果一个类定义了解构函数,那么您必须同时定义或删除拷贝构造函数和拷贝赋值函数,否则出错。
- 如果一个类定义了拷贝构造函数,那么您必须同时定义或删除拷贝赋值函数,否则出错,删除可导致低效。
- 如果一个类定义了移动构造函数,那么您必须同时定义或删除移动赋值函数,否则出错,删除可导致低效。
- 如果一个类定义了拷贝构造函数或拷贝赋值函数,那么您必须最好同时定义移动构造函数或移动赋值函数,否则低效。
初始化列表以及构造函数委托
注意:避免死循环
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Person {
public:
// 默认无参构造函数
Person() {}
// 带参数的构造函数, 使用了初始化列表(类内初始化器)
Person(string name, int age) : _name(name), _age(age) {}
// 委托构造函数
Person(string name) : Person(name, 20) {}
~Person() {}
string _name = "";
int _age = 0;
};
int main() {
auto thresh = make_unique<Person>("Thresh", 18);
auto teemo = make_unique<Person>("Teemo");
cout << thresh->_name << "," << thresh->_age << endl; // thresh,18
cout << teemo->_name << "," << thresh->_age << endl; // teemo,20
return 0;
}
explicit
如果构造函数只有一个参数, 那么其行为类似于从参数类型到类自身类型的转换
暂时不理解此特性的具体意义在哪儿
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Person {
public:
// 默认无参构造函数
Person() {}
// 带参数的构造函数, 使用了初始化列表(类内初始化器)
Person(string name, int age) : _name(name), _age(age) {}
/**
* 如果构造函数只有一个参数, 那么应该使用 explicit 禁止隐式类型转换
*/
explicit Person(string name) : Person(name, 20) {}
~Person() {}
string _name = "";
int _age = 0;
};
int main() {
auto thresh = make_unique<Person>("Thresh", 18);
string name = "Teemo";
Person teemo = name; // 报错
return 0;
}
static 成员的初始化
通常
class的static的成员应该在类内声明, 在类外初始化
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Person {
public:
static const int class_num = 7;
static int grade_num;
private:
string _name = "";
int _age = 0;
};
int Person::grade_num = 3;
int main() {
auto p1 = Person();
auto p2 = Person();
// Person::class_num = 8; // 错误
Person::grade_num = 4;
cout << p1.class_num << endl; // 7
cout << p1.grade_num << endl; // 4
cout << p2.class_num << endl; // 7
cout << p2.grade_num << endl; // 4
return 0;
}
inline 与宏定义生成 get/set
一些简短而又很少修改的函数, 可以使用 inine 定义在 class 内部
inline是一种编译器优化技术,将函数调用处直接替换为函数体,以减少函数调用带来的开销
但是:
将函数标记为inline并不一定保证编译器会进行内联展开,这只是一个提示。编译器是否真正内联展开函数取决于多个因素,如函数复杂度、函数体大小、编译器对内联的支持等。
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
// clang-format off
// 简单的宏定义, 生成 get , set
// 要求字段名前带 _
#define Property(type, name) \
inline type name() { \
return _##name; \
} \
\
inline void name(type name##Value) { \
_##name = ##name##Value; \
} \
//clang-format on
class Person {
public:
// 默认无参构造函数
Person() {}
// 带参数的构造函数, 使用了初始化列表(类内初始化器)
Person(string name, int age) : _name(name), _age(age) {}
~Person() {}
// 一些简短而又很少修改的函数, 可以使用 inine 定义在 class 内部
inline int age() {
return _age;
}
inline void age(int ageValue) {
_age = ageValue;
}
Property(string, name);
private:
string _name = "";
int _age = 0;
};
int main() {
auto thresh = make_unique<Person>("Thresh", 18);
thresh->age(20);
cout << thresh->name() << endl; // Thresh
cout << thresh->age() << endl; // 20
return 0;
}
继承与多态
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// clang-format off
// 简单的宏定义, 生成 get , set
// 要求字段名前带 _
#define Property(type, name) \
inline const type & name() const { \
return _##name; \
} \
\
inline void name(const type name##Value) { \
_##name = ##name##Value; \
} \
// clang-format on
// 接口
class Human {
public:
virtual void sayHello() = 0;
};
// 抽象类
class Person : public Human {
public:
// 实现接口, 提供一个默认实现
// 使用 override 显示的标记重写的函数, 以供编译器检查
virtual void sayHello() override {
cout << "Hi ";
}
protected:
Person(string name, int age) : _name(name), _age(age) {}
protected:
// 基类的析构函数应当定义为 virtual , 保证基类的析构函数会被调用
virtual ~Person() {
cout << "Person 析构" << endl;
}
private:
// 基类不需要初始化
Person(){};
public:
Property(string, name);
Property(int, age);
protected:
string _name;
int _age;
};
class Student : public Person {
public:
// 构造函数委托父类构造函数
Student(string name, int age) : Person(name, age) {}
void sayHello() override {
Person::sayHello();
cout << "my name is " << name() << endl;
}
~Student() {
cout << "Student 析构" << endl;
}
};
static void say() {
auto stu = make_shared<Student>("laolang", 18);
stu->sayHello(); // Hi my name is laolang
// 子类指针转父类指针要用 dynamic_cast 而不是强转
Person* p = dynamic_cast<Person*>(stu.get());
// 指针指针的转换则用 dynamic_pointer_cast, 但是智能用于 shared_ptr
shared_ptr<Person> p_ptr = dynamic_pointer_cast<Person>(stu);
p_ptr->sayHello(); // Hi my name is laolang
}
int main() {
cout << "start" << endl;
say();
cout << "end" << endl;
return 0;
}
输出如下
start
Hi my name is laolang
Hi my name is laolang
Student 析构
Person 析构
end
模板与泛型
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#if defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__clang__)
#include <cxxabi.h>
#endif
template <class T> std::string cpp_type_name() {
const char *name = typeid(T).name();
#if defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__clang__)
int status;
char *p = abi::__cxa_demangle(name, 0, 0, &status);
std::string s = p;
std::free(p);
#else
std::string s = name;
#endif
if (std::is_const_v<std::remove_reference_t<T>>) s += " const";
if (std::is_volatile_v<std::remove_reference_t<T>>) s += " volatile";
if (std::is_lvalue_reference_v<T>) s += " &";
if (std::is_rvalue_reference_v<T>) s += " &&";
return s;
}
#define SHOW(T) std::cout << cpp_type_name<T>() << std::endl;
本文来自博客园,作者:laolang2016,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/khlbat/p/17491837.html




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号