一,单例模式
1-1 饿汉式(静态常量)
-
代码实现
public class Singleton01 { // 1,私有化构造方法 private Singleton01() { } // 2,创建实例对象 private final static Singleton01 instance = new Singleton01(); // 3,对外提供获取实例的方法 public static Singleton01 getInstance() { return instance; } } -
优缺点
- 优点:实现方式简单,实例对象在类加载的时候完成实例化操作,避免了多线程的问题。
- 缺点:没有达到Lazy loading,如果该实例对象一直没有被使用,则会造成内存浪费。
1-2 饿汉式(静态代码块)
-
代码实现
public class SingletonType02 { // 1,私有化构造方法 private SingletonType02() { } // 2,创建实例对象 private static SingletonType02 instance; static { instance = new SingletonType02(); } // 3,对外提供获取实例的方法 public static SingletonType02 getInstance() { return instance; } } -
优缺点
和静态常量的方式唯一的区别就是:将实例化操作放在了静态代码块中,所以和静态常量方式的优缺点相同。
1-3 懒汉式(线程不安全)
-
代码实现
public class SingletonType03 { // 1,私有化构造方法 private SingletonType03() { } // 2,定义实例对象 private static SingletonType03 instance; // 3,对外提供获取实例的方法 public static SingletonType03 getInstance() { // 获取实例对象时,判断实例对象是否为空,为空时才对其进行实例化 if(instance == null) { instance = new SingletonType03(); } return instance; } } -
优缺点
-
优点:实现了Lazy loading
-
缺点:线程不安全。在多线程的情况下,可能会生成多个实例化对象。所以,在开发中,不要使用该方式
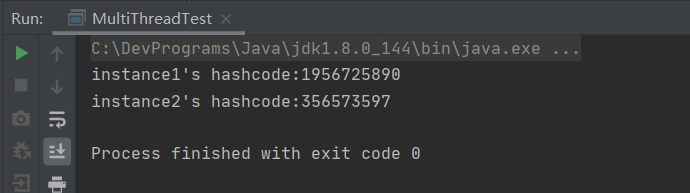
例如,当一个线程在执行if(instance == null) 时,另外一个线程也执行该代码,最终会生成两个实例化对象。
public class MultiThreadTest implements Callable<SingletonType03> { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { MultiThreadTest mt = new MultiThreadTest(); FutureTask<SingletonType03> ft = new FutureTask<>(mt); new Thread(ft, "子线程").start(); SingletonType03 instance1 = SingletonType03.getInstance(); SingletonType03 instance2 = ft.get(); System.out.println("instance1's hashcode:" + instance1.hashCode()); System.out.println("instance2's hashcode:" + instance2.hashCode()); } @Override public SingletonType03 call() throws Exception { return SingletonType03.getInstance(); } }![]()
-
1-4 懒汉式(线程安全,同步方法)
-
代码实现
public class SingletonType04 { // 1,私有化构造方法 private SingletonType04() { } // 2,定义实例对象 private static SingletonType04 instance; // 3,对外提供获取实例的方法 public static synchronized SingletonType04 getInstance() { // 获取实例对象时,判断实例对象是否为空,为空时才对其进行实例化 if(instance == null) { instance = new SingletonType04(); } return instance; } } -
优缺点
- 优点:线程安全
- 缺点:效率低,每次获取instance时,都要进行线程同步。
1.5 双重检查
-
代码实现
public class SingletonType05 { // 1,私有化构造方法 private SingletonType05() { } // 2,定义实例对象 private static volatile SingletonType05 instance; // 3,对外提供获取实例的方法 public static SingletonType05 getInstance() { // 获取实例对象时,判断实例对象是否为空,为空时才对其进行实例化 if(instance == null) { synchronized (SingletonType05.class) { // 再次检查实例对象是否为空 if(instance == null) { instance = new SingletonType05(); } } } return instance; } } -
优缺点
- 优点:实现了Lazy loading,线程安全,保证了效率。
1-6 静态内部类
-
代码实现
public class SingletonType06 { // 1,私有化构造方法 private SingletonType06() { } // 2,定义实例对象 private static volatile SingletonType06 instance; // 3,定义静态内部类 // 3-1,静态内部类SingleInstance不会被立即加载,只有在调用getInstance方法时,才会被加载 // 3-2,在加载静态内部类时,其静态属性INSTANCE会被初始化,且JVM保证了线程安全 private static class SingleInstance { private static final SingletonType06 INSTANCE = new SingletonType06(); } // 3,对外提供获取实例的方法 public static SingletonType06 getInstance() throws InterruptedException { return SingleInstance.INSTANCE; } } -
优缺点
- 优点:实现了Lazy loading,线程安全,效率高
1.7 枚举方式
-
代码实现
public class SingletonType07 { public static void main(String[] args) { Singleton instance1 = Singleton.INSTANCE; Singleton instance2 = Singleton.INSTANCE; System.out.println("instance1's hashcode:" + instance1.hashCode()); System.out.println("instance2's hashcode:" + instance2.hashCode()); } } enum Singleton { INSTANCE; public void xxMethod () { System.out.println("xxMethod"); } } -
优缺点
- 优点:避免了线程同步问题,还能防止反序列化重新创建新的对象。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号